K2-18
 Artist's impression of the K2-18 system, with K2-18 on left, K2-18b on right, and K2-18c between. Credit: ESA/Hubble | |
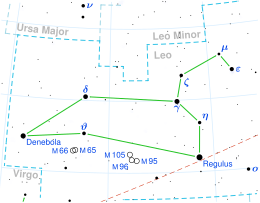
Approximate two-dimensional location of the star (in red circle); Sigma Leonis is the nearest bright star, which is in a southerly direction, and the boundary of Virgo is similarly far. | |
| Observation data Epoch J2000.0 Equinox J2000.0 | |
|---|---|
| Constellation | Leo |
| Right ascension | 11h 30m 14.518s[1] |
| Declination | +07° 35′ 18.26″[1] |
| Apparent magnitude (V) | 13.50[2] |
| Characteristics | |
| Evolutionary stage | Red dwarf |
| Spectral type | M2.8[3] |
| Astrometry | |
| Proper motion (μ) | RA: −80.377[1] mas/yr Dec.: −133.142[1] mas/yr |
| Parallax (π) | 26.2686 ± 0.0546[1] mas |
| Distance | 124.2 ± 0.3 ly (38.07 ± 0.08 pc) |
| Details | |
| Mass | 0.495[4] M☉ |
| Radius | 0.469[4] R☉ |
| Luminosity | 0.0234[5] L☉ |
| Temperature | 3,503[4] K |
| Metallicity [Fe/H] | 0.123±0.157[6] dex |
| Other designations | |
| Database references | |
| SIMBAD | data |
K2-18, also known as EPIC 201912552, is a red dwarf star located 124 light-years (38 pc)[4] from Earth, in the constellation of Leo.
Planetary system[]
The star has an exoplanet, called K2-18b, a super-Earth located within the habitable zone of K2-18.[7][8] It is the first exoplanet in the habitable zone, albeit a hydrogen-rich sub-neptune,[9] to have water discovered in its atmosphere. The star also has a second planet K2-18c,[10] which is proven by system tidal simulation to be a small gas giant.[11]
| Companion (in order from star) |
Mass | Semimajor axis (AU) |
Orbital period (days) |
Eccentricity | Inclination | Radius |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| c | 5.62±0.84 M |