Lake Chippewa
| Lake Chippewa | |
|---|---|
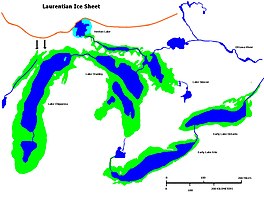 Glacial Lakes Chippewa, Stanley, Early Erie and Early Ontario. Low level lake stages during the end of the Wisconsin Glacial era in North America. Based on Larsen map, 1987. | |
 Lake Chippewa | |
| Location | North America |
| Group | Great Lakes |
| Coordinates | Coordinates: 44°N 87°W / 44°N 87°W |
| Lake type | former lake |
| Etymology | Chippewa People |
| Primary inflows | Laurentide Ice Sheet |
| Primary outflows | Grand River valley in Michigan |
| Basin countries | Canada United States |
| First flooded | 9,500 years before present |
| Max. length | 220 mi (350 km) |
| Max. width | 30 mi (48 km) |
| Residence time | 7300 years in existence |
| Surface elevation | 230 ft (70 m)[1] |
| References | United States Geological Survey, George Otis Smith, Director; The Pleistocene of Indiana and Michigan and the History of the Great Lakes; Frank Leverett and Frank B. Taylor; Department of the Interior, Monographs of the United States Geological Survey; Volume LIII; Washington; Government Printing Office; 1915 |
Lake Chippewa was a prehistoric proglacial lake. The basin is now Lake Michigan. It formed about 10,600 years before present (YBP). The lake occupied the depression left by the of the Laurentide Ice Sheet.[2]
Origin[]
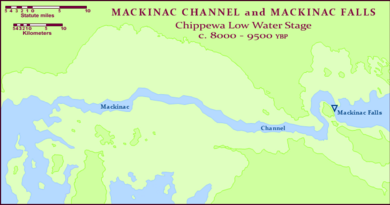
The lake formed from glacial Lake Algonquin as water levels dropped, occupying only the deepest parts of the Lake Michigan basin. The waters drained through the Straits of Mackinac, then across Lake Stanley into either and then to the St. Lawrence River by way of the Ottawa River valley, or through the St. Clair and Detroit rivers to an Early Lake Erie and out the Niagara River towards the St. Lawrence. Around 10,300 YBP, Lake Chippewa’s levels continued to drop, and the basin was a self-contained body of water without an outlet. Levels returned and Lake Chippewa again flowed through the canyon at Mackinac until around 7,500 YBP. At that time, the Nipissing Great Lakes merged with the waters in the Michigan Basin and created a single lake encompassing all three of the upper Great Lakes.
Size[]
Somewhat smaller than Lake Michigan, Lake Chippewa extended through the most of the Michigan Basin, north to the Straits of Mackinac, where there was a narrow channel which conveyed the lake's outflow over the now submerged Mackinac Falls to Lake Stanley. Its shoreline ranged from 10–30 miles (16–48 km) out from the present day Lake Michigan shore.
See also[]
References[]
- ^ Glacial Lakes Chippewa and Stanley (Map). Randall Schaetzl, Michigan State University. Retrieved January 27, 2020.
- ^ University of Wisconsin, Green Bay, Dept of Geology[full citation needed]
External links[]
- Glacial Lakes Chippewa and Stanley (Map). Randall Schaetzl, Michigan State University. Retrieved January 27, 2020.
- Moraines of the United States
- Geological history of the Great Lakes
- Geology of Illinois
- Geology of Michigan
- Geology of Wisconsin
