Lesser occipital nerve
| Lesser occipital nerve | |
|---|---|
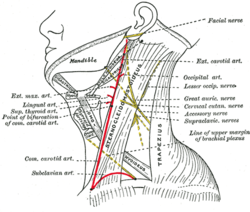 Side of neck, showing chief surface markings. (Lesser occip. nerve labeled at center right.) | |
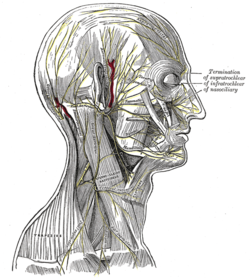 The nerves of the scalp, face, and side of neck. (Smaller occipital visible below and to the left of the ear.) | |
| Details | |
| From | cervical plexus (C2) |
| Innervates | Cutaneous innervation of the posterior aspect of the auricle and mastoid region |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | nervus occipitalis minor |
| TA98 | A14.2.02.017 |
| TA2 | 6384 |
| FMA | 6871 |
| Anatomical terms of neuroanatomy | |
The lesser occipital nerve or small occipital nerve is a cutaneous spinal nerve. It arises from cervical spinal nerve 2, along with the greater occipital nerve. It innervates the scalp in the lateral area of the head posterior to the ear.
Structure[]
The lesser occipital nerve is one of the four cutaneous branches of the cervical plexus.[1] It arises from the cervical spinal nerve 2.[2] This is from the lateral branch of the ventral ramus. This is between the atlas bone and the axis bone. Rarely, it may receive fibres from the cervical spinal nerve 3.[2] It curves around the accessory nerve (CN XI).[2] It curves around and ascends along the posterior border of the sternocleidomastoid muscle.[2] Rarely, it may pierce the muscle.[2]
Near the cranium, it perforates the deep fascia.[2] It is continued upwards along the side of the head behind the auricle. It gives branches to the skin.[2]
It gives off an auricular branch, which supplies the skin of the upper and back part of the auricula, communicating with the of the great auricular. This branch is occasionally derived from the greater occipital nerve.
Variation[]
Rarely, the lesser occipital nerve may be duplicated or triplicated.[2] It varies in size.
Function[]
The lesser occipital nerve supplies part of the scalp near the auricle.[1][2] It connects with the great auricular nerve, the greater occipital nerve, and the auricular branch of the facial nerve.[2]
Clinical significance[]
Problems with the lesser occipital nerve cause occipital neuralgia. Nerve block is difficult due to variation in the course of the nerve.[2]
History[]
The lesser occipital nerve may also be known as the occipitalis minor nerve,[2] or the small occipital nerve.[citation needed]
Additional images[]
Dermatome distribution of the trigeminal nerve
References[]
![]() This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 926 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 926 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
- ^ a b Rea, Paul (2016). "3 - Neck". Essential Clinically Applied Anatomy of the Peripheral Nervous System in the Head and Neck. Academic Press. pp. 131–183. doi:10.1016/B978-0-12-803633-4.00003-X. ISBN 978-0-12-803633-4.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l Cesmebasi, Alper (2015). "31 - Anatomy of the Cervical Plexus and Its Branches". Nerves and Nerve Injuries. Vol. 1: History, Embryology, Anatomy, Imaging, and Diagnostics. Academic Press. pp. 441–449. doi:10.1016/B978-0-12-410390-0.00032-9. ISBN 978-0-12-410390-0.
External links[]
- Anatomy figure: 25:03-01 at Human Anatomy Online, SUNY Downstate Medical Center
- http://www.dartmouth.edu/~humananatomy/figures/chapter_47/47-2.HTM
- http://www.dartmouth.edu/~humananatomy/figures/chapter_47/47-6.HTM
- Wikipedia articles incorporating text from the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
- Optic nerve
