Linear polarization
This article includes a list of general references, but it remains largely unverified because it lacks sufficient corresponding inline citations. (May 2020) |
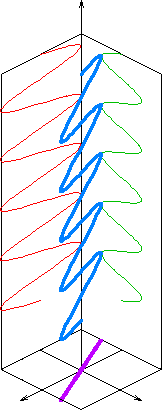
In electrodynamics, linear polarization or plane polarization of electromagnetic radiation is a confinement of the electric field vector or magnetic field vector to a given plane along the direction of propagation. The term linear polarization (French: polarisation rectiligne) was coined by Augustin-Jean Fresnel in 1822.[1] See polarization and plane of polarization for more information.
The orientation of a linearly polarized electromagnetic wave is defined by the direction of the electric field vector.[2] For example, if the electric field vector is vertical (alternately up and down as the wave travels) the radiation is said to be vertically polarized.
Mathematical description[]
The classical sinusoidal plane wave solution of the electromagnetic wave equation for the electric and magnetic fields is (cgs units)
for the magnetic field, where k is the wavenumber,
is the angular frequency of the wave, and is the speed of light.
Here is the amplitude of the field and
is the Jones vector in the x-y plane.
The wave is linearly polarized when the phase angles are equal,
- .
This represents a wave polarized at an angle with respect to the x axis. In that case, the Jones vector can be written
- .
The state vectors for linear polarization in x or y are special cases of this state vector.
If unit vectors are defined such that
and
then the polarization state can be written in the "x-y basis" as
- .
See also[]
- Sinusoidal plane-wave solutions of the electromagnetic wave equation
- Polarization
- Photon polarization
References[]
- Jackson, John D. (1998). Classical Electrodynamics (3rd ed.). Wiley. ISBN 0-471-30932-X.
- ^ A. Fresnel, "Mémoire sur la double réfraction que les rayons lumineux éprouvent en traversant les aiguilles de cristal de roche suivant les directions parallèles à l'axe", read 9 December 1822; printed in H. de Senarmont, E. Verdet, and L. Fresnel (eds.), Oeuvres complètes d'Augustin Fresnel, vol. 1 (1866), pp. 731–51; translated as "Memoir on the double refraction that light rays undergo in traversing the needles of quartz in the directions parallel to the axis", Zenodo: 4745976, 2021 (open access); §9.
- ^ Shapira, Joseph; Shmuel Y. Miller (2007). CDMA radio with repeaters. Springer. p. 73. ISBN 978-0-387-26329-8.
External links[]
- Animation of Linear Polarization (on YouTube)
- Comparison of Linear Polarization with Circular and Elliptical Polarizations (YouTube Animation)
![]() This article incorporates public domain material from the General Services Administration document: "Federal Standard 1037C".
This article incorporates public domain material from the General Services Administration document: "Federal Standard 1037C".
- Polarization (waves)
![{\mathbf {E}}({\mathbf {r}},t)=\mid {\mathbf {E}}\mid {\mathrm {Re}}\left\{|\psi \rangle \exp \left[i\left(kz-\omega t\right)\right]\right\}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/1f76514bed697200b46c30726b957614f01994ae)











