Macular hypoplasia
| Macular hypoplasia | |
|---|---|
| Other names | Foveal hypoplasia |
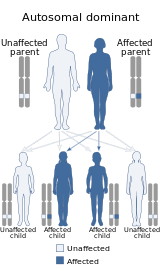 | |
| This condition is inherited via autosomal dominant manner | |
Macular hypoplasia (or foveal hypoplasia), is a rare medical condition involving the underdevelopment of the macula,[1] a small area on the retina (the eye's internal surface) responsible for seeing in detail. Macular hypoplasia is often associated with albinism.
Other diseases with foveal hypoplasia besides albinism include aniridia, retinopathy of prematurity, and Alport syndrome.[2][3]
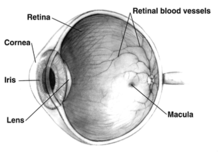
Human retina(top)
References[]
- ^ "OMIM Entry - # 136520 - FOVEAL HYPOPLASIA 1; FVH1". omim.org. Retrieved 2017-07-28.
- ^ Thomas MG, Papageorgiou E, Kuht HJ, Gottlob I (November 2020). "Normal and abnormal foveal development". Br J Ophthalmol. doi:10.1136/bjophthalmol-2020-316348. PMID 33148537.
- ^ Hess K, Pfau M, Wintergerst MW, Loeffler KU, Holz FG, Herrmann P (February 2020). "Phenotypic Spectrum of the Foveal Configuration and Foveal Avascular Zone in Patients With Alport Syndrome". Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 61 (2): 5. doi:10.1167/iovs.61.2.5. PMC 7324255. PMID 32031577.
External links[]
| Classification | |
|---|---|
| External resources |
Categories:
- Diseases of the eye and adnexa
- Rare diseases
- Disease stubs
- Eye stubs