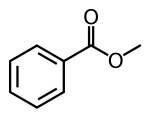
Methyl benzoate

| |||
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
Methyl benzoate | |||
| Systematic IUPAC name
Methyl benzenecarboxylate | |||
| Identifiers | |||
3D model (JSmol)
|
|||
| ChEMBL | |||
| ChemSpider | |||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.002.055 | ||
PubChem CID
|
|||
| UNII | |||
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| C8H8O2 | |||
| Molar mass | 136.150 g·mol−1 | ||
| Density | 1.0837 g/cm3 | ||
| Melting point | −12.5 °C (9.5 °F; 260.6 K) | ||
| Boiling point | 199.6 °C (391.3 °F; 472.8 K) | ||
| −81.95×10−6 cm3/mol | |||
Refractive index (nD)
|
1.5164 | ||
| Hazards | |||
| Safety data sheet (SDS) | ScienceLab MSDS | ||
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | 
0
2
0 | ||
| Flash point | 82 °C (180 °F; 355 K) | ||
| Related compounds | |||
Related compounds
|
|||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |||
| Infobox references | |||
Methyl benzoate is an organic compound. It is an ester with the chemical formula C6H5CO2CH3. It is a colorless liquid that is poorly soluble in water, but miscible with organic solvents. Methyl benzoate has a pleasant smell, strongly reminiscent of the fruit of the feijoa tree, and it is used in perfumery. It also finds use as a solvent and as a pesticide used to attract insects such as orchid bees.
Synthesis and reactions[]
Methyl benzoate is formed by the condensation of methanol and benzoic acid, in presence of a strong acid.[1] [2]
Methyl benzoate reacts at both the ring and the ester, depending on the substrate. Electrophiles attack the ring, illustrated by acid-catalysed nitration with nitric acid to give . Nucleophiles attack the carbonyl center, illustrated by hydrolysis with addition of aqueous NaOH to give methanol and sodium benzoate.
Occurrence[]
Methyl benzoate can be isolated from the freshwater fern Salvinia molesta.[3] It is one of many compounds that is attractive to males of various species of orchid bees, which apparently gather the chemical to synthesize pheromones; it is commonly used as bait to attract and collect these bees for study.[4]
Cocaine hydrochloride hydrolyzes in moist air to give methyl benzoate;[5] drug-sniffing dogs are thus trained to detect the smell of methyl benzoate.[6]
Uses[]
Non electric Heat cost allocators. See: DIN EN 835.
References[]
- ^ Maki, Takao; Takeda, Kazuo. "Benzoic Acid and Derivatives". Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry. Weinheim: Wiley-VCH. doi:10.1002/14356007.a03_555..
- ^ John McMurry (2008). Organic Chemistry, 7th Edition. Thompson - Brooks/Cole. ISBN 978-1-4390-4972-3.. Page 623
- ^ Choudhary, MI; Naheed, N; Abbaskhan, A; Musharraf, SG; Siddiqui, H; Atta-Ur-Rahman (2008). "Phenolic and other constituents of fresh water fern Salvinia molesta". Phytochemistry. 69 (4): 1018–23. doi:10.1016/j.phytochem.2007.10.028. PMID 18177906.
- ^ Schiestl, F.P.; Roubik, D.W. (2003). "Odor Compound Detection in Male Euglossine Bees". Journal of Chemical Ecology. 29 (1): 253–257. doi:10.1023/A:1021932131526. hdl:20.500.11850/57276. PMID 12647866.
- ^ Dejarme, Lindy E.; Gooding, Rachel E.; Lawhon, Sara J.; Ray, Prasenjit; Kuhlman, Michael R. (1997). "Formation of methyl benzoate from cocaine hydrochloride under different temperatures and humidities". In Works, George; Rudin, Leonid I; Hicks, John; et al. (eds.). Proceedings of SPIE. SPIE Proceedings. 2937. p. 19. doi:10.1117/12.266783.
- ^ Waggoner, L. Paul; Johnston, James M.; Williams, Marc; Jackson, Jan; Jones, Meredith H.; Boussom, Teresa; Petrousky, James A. (1997). "Canine olfactory sensitivity to cocaine hydrochloride and methyl benzoate". In Works, George; Rudin, Leonid I; Hicks, John; et al. (eds.). Proceedings of SPIE. SPIE Proceedings. 2937. p. 216. doi:10.1117/12.266775.
- Flavors
- Methyl esters
- Benzoate esters
- Perfume ingredients