Mitchella repens
| Partridge berry | |
|---|---|

| |
| Leaves and berry | |

| |
| Flowers and berry | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Clade: | Tracheophytes |
| Clade: | Angiosperms |
| Clade: | Eudicots |
| Clade: | Asterids |
| Order: | Gentianales |
| Family: | Rubiaceae |
| Genus: | Mitchella |
| Species: | M. repens
|
| Binomial name | |
| Mitchella repens | |
Mitchella repens (partridge berry,[1][2][3][4] or squaw vine (no longer used)) is the best known plant in the genus Mitchella. It is a creeping prostrate herbaceous woody shrub occurring in North America belonging to the madder family (Rubiaceae).
Naming[]
Mitchella repens is one of the many species first described by Carl Linnaeus. Its species name is the Latin adjective repens, which means "creeping". Common names for Mitchella repens include partridge berry (or partridgeberry), squaw berry (no longer used), two-eyed berry, running fox, and Noon kie oo nah yeah (in the Mohawk language).
Description[]
Partridge berry is an evergreen plant growing as a non-climbing vine, no taller than 6 cm tall with creeping stems 15 to 30 cm long. The evergreen, dark green, shiny leaves are ovate to cordate in shape. The leaves have a pale yellow midrib. The petioles are short, and the leaves are paired oppositely on the stems. Adventitious roots may grow at the nodes;[5] and rooting stems may branch and root repeatedly, producing loose spreading mats.
The small, trumpet-shaped, axillary flowers are produced in pairs, and each flower pair arises from one common calyx which is covered with fine hairs. Each flower has four white petals, one pistil, and four stamens. Partridge Berry is a distylous taxon. The plants have either flowers with long pistils and short stamens (long-styled flowers, called the pin), or have short pistils and long stamens (short-styled flowers, called the thrum).[6] The two style morphs are genetically determined, so the pollen from one morph does not fertilize the other morph, resulting in a form of heteromorphic self-incompatibility.[7]
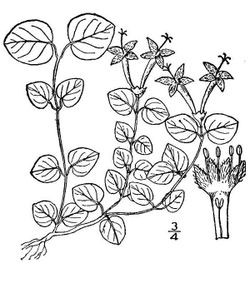


The ovaries of the twin flowers fuse together, so that there are two flowers for each berry. The two bright red spots on each berry are vestiges of this process. The fruit ripens between July and October, and may persist through the winter. The fruit is a drupe containing up to eight seeds. The fruits are never abundant. They may be part of the diets of several birds, such as ruffed grouse, sharp-tailed grouse, northern bobwhite, and wild turkey. They are also consumed by foxes, white-footed mice, and skunks.[8][9] The foliage is occasionally consumed by White-tailed deer.[10]
The common reproduction is vegetative, with plants forming spreading colonies.[11]
Distribution and habitat[]
The species is dispersed throughout eastern North America, from south Eastern Canada south to Florida and Texas, and to Guatemala. It is found growing in dry or moist woods, along stream banks and on sandy slopes.
Cultivation and uses[]
Mitchella repens is cultivated for its ornamental red berries and shiny, bright green foliage.[11] It is grown as a creeping ground cover in shady locations. It is rarely propagated for garden use by way of seeds but cuttings are easy.[12] The plants have been widely collected for Christmas decorations, and over collecting has impacted some local populations negatively.[11] American Indian women made a tea from the leaves and berries that was consumed during childbirth.[11] The plants are sometimes grown in terrariums.[13] The scarlet berries are edible[14] but rather tasteless, with a faint flavour of wintergreen, resembling cranberries (to which they are not closely related). Vaccinium vitis-idaea may be referred to by the same common name, "Newfoundland Partridgeberry" or "lingonberry" but is a different species.
References[]
- ^ Peterson, Roger Tory, and McKenny, Margaret (1996). A Field Guide to Wildflowers of Northeastern and North-central North America. ISBN 978-0-395-91172-3.CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link)
- ^ MacKenzie, David, S (2002). Perennial Ground Covers. ISBN 978-0-88192-557-9.CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link)
- ^ Hutchens, Alma R (1969). Indian Herbalogy of North America. ISBN 978-0-87773-639-4.
- ^ Hall, Joan Houston (2002). Dictionary of American Regional English. Harvard University Press. p. 47. ISBN 978-0-674-00884-7. Retrieved 2007-11-16.
- ^ Nathaniel Lord Britton; Addison Brown (1913). An illustrated flora of the northern United States, Canada and the British possessions: from Newfoundland to the parallel of the southern boundary of Virginia, and from the Atlantic Ocean westward to the 102d meridian. C. Scribner's sons. pp. 255–. Retrieved 4 September 2010.
- ^ Reproductive Biology of Distylous Partridgeberry, Mitchella repens. David J. Hicks, Robert Wyatt and Thomas R. Meagher Vol. 72, No. 10 (Oct., 1985), pp. 1503-1514 Stable URL: https://www.jstor.org/stable/2443300
- ^ Fecundity in Distylous and Self-Incompatible Homostylous Plants of Mitchella repens (Rubiaceae) Fred R. Ganders Vol. 29, No. 1 (Mar., 1975), pp. 186-188 Published by: Society for the Study of Evolution Stable URL: https://www.jstor.org/stable/2407152
- ^ Alexander Campbell Martin; Herbert Spencer Zim; Arnold L. Nelson (1951). American wildlife & plants: a guide to wildlife food habits; the use of trees, shrubs, weeds, and herbs by birds and mammals of the United States. Courier Dover Publications. pp. 361–. ISBN 978-0-486-20793-3. Retrieved 4 September 2010.
- ^ Marie Harrison (30 March 2006). Groundcovers for the South. Pineapple Press Inc. pp. 76–. ISBN 978-1-56164-347-9. Retrieved 4 September 2010.
- ^ James Howard Miller; Karl V. Miller (May 2005). Forest plants of the Southeast and their wildlife uses. University of Georgia Press. pp. 280–. ISBN 978-0-8203-2748-8. Retrieved 5 September 2010.
- ^ a b c d Wolfram George Schmid (13 September 2002). An encyclopedia of shade perennials. Timber Press. pp. 243–. ISBN 978-0-88192-549-4. Retrieved 4 September 2010.
- ^ William Cullina (18 March 2000). New England Wildflower Society guide to growing and propagating wildflowers of the United States and Canada. Houghton Mifflin Harcourt. pp. 148–. ISBN 978-0-395-96609-9. Retrieved 4 September 2010.
- ^ "Lady Bird Johnson Wildflower Center - the University of Texas at Austin".
- ^ Angier, Bradford (1974). Field Guide to Edible Wild Plants. Harrisburg, PA: Stackpole Books. p. 162. ISBN 0-8117-0616-8. OCLC 799792.
- Mitchelleae
- Berries
- Flora of North America
- Flora of Asia
- Medicinal plants
- Plants described in 1753
- Taxa named by Carl Linnaeus