Neurine
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
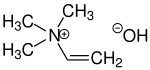
Trimethylvinylammonium hydroxide
| |
| Other names
Vitaloid; N,N,N-Trimethylethenaminium hydroxide
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.006.678 |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C5H13NO | |
| Molar mass | 103.16 |
| Appearance | Syrupy liquid |
| Soluble | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Neurine is an alkaloid found in egg yolk, brain, bile and in cadavers. It is formed during putrefaction of biological tissues by the dehydration of choline. It is a poisonous, syrupy liquid with a fishy odor.
Neurine is a quaternary ammonium salt with three methyl groups and one vinyl group attached to the nitrogen atom. Synthetically, neurine can be prepared by the reaction of acetylene with trimethylamine. Neurine is unstable and decomposes readily to form trimethylamine.
References[]
- Merck Index, 11th Edition, 6393.
Categories:
- Alkaloids
- Quaternary ammonium compounds
- Vinyl compounds