Ngas language
| Ngas | |
|---|---|
| Native to | Nigeria |
| Region | Plateau State |
Native speakers | 400,000 (1998)[1] |
Afro-Asiatic
| |
| Language codes | |
| ISO 639-3 | anc |
| Glottolog | ngas1240 |
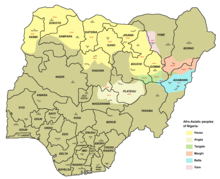 Ethnic territories (tan) of the Ngas-speaking people (Angas) in Nigeria | |
Ngas, or Angas, is an Afro-Asiatic language spoken in Plateau State, Nigeria. Dialects are Hill Angas and Plain Angas.[1] Retired General Yakubu Gowon is a prominent Nigerian who is of Ngas extraction.
Neighbouring languages[]
Bəlnəŋ, an A3 West Chadic language closely related to Angas, was discovered by Roger Blench in 2016. It is spoken by about 500 people in the single village of Langung, which is surrounded by Tal villages in the east and Miship villages in the west (Blench 2017).[2]
Speakers of Sur, a Plateau language, are surrounded by Ngas speakers, but Sur nevertheless continues to be a well-maintained language.[3]
The Ngas language has also undergone extensive influence from Tarok.[4]
Writing system[]
| a | b | ɓ | c | d | ɗ | dy | e | ə | f | g | h | ḥ | i | j | k | l |
| m | n | ṇ | ny | o | p | r | s | sh | t | u | v | w | y | z | ẓ | ʼ |
Notes[]
- ^ Jump up to: a b Ngas at Ethnologue (18th ed., 2015)
- ^ Blench, Roger. 2017. Current research on the A3 West Chadic languages.
- ^ Blench, Roger. 2004. Tarok and related languages of east-central Nigeria.
- ^ Longtau, Selbut (25–26 March 2004). Some Historical Inferences from Lexical Borrowings and Traditions of Origins in the Tarokoid/Chadic Interface. International Symposium on Endangered Languages in Contact: Nigeria’s Plateau Languages. Hamburg: Asien-Afrika-Institut, Universität Hamburg.
- ^ Hartell 1993.
Further reading[]
- Donald A. Burquest. 1971. A Preliminary Study of Angas Phonology. Zaria: Institute of Linguistics.
- Donald A. Burquest. 1973. A Grammar of Angas. University of California at Los Angeles, PhD dissertation.
Categories:
- Languages of Nigeria
- West Chadic languages
- West Chadic language stubs
- Nigeria stubs
