Nicolas Grollier de Servière
Nicolas Grollier de Servière | |
|---|---|
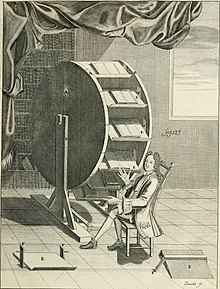 Grollier's reading wheel | |
| Born | 1596 Lyon, France |
| Died | 1689 Lyon, France |
| Occupation | Model maker, inventor and wood turner |
Nicolas Grollier de Servière (1596–1689) was a French inventor and ornamental turner who became well known for creating a series of fantastic machines.
Grollier de Servière, a cousin of Jean Grolier de Servières (1489/90–1565), Treasurer of France and famed bibliophile, was born in Lyon, the fourth son of Antoine Grollier de Servière[1] and in his youth followed a military career that took him to Flanders, Germany, Italy and Constantinople; as an engineer, he specialized in deploying movable bridges in the field. After he retired to his home in Lyon, he worked on ornamental lathe-work and built a series of fantastic models. He displayed his work in a cabinet that he opened to the public once a week and which became famous enough to attract politicians, scholars, artisans and other inventors. It featured model water pumps and Archimedes' screws, siege engines, designs of floating bridges and clocks regulated by balls travelling down inclined planes or along spiral tracks, machines to trace landscape and to convert plan images into perspective, odometers with reducing gears, wheelchairs, many intricate pieces of lathe-work in ivory and wood, and an improved version of Agostino Ramelli's reading wheel that allowed many books to be read by means of a rotating wheel. Eventually even Louis XIV paid a visit to Grollier de Servière.
After his death in 1689, his son Gaspard (1646–1716) and then his grandson Gaspard II (1676–1745) continued to display the contents of the cabinet, and his son published a book cataloguing the curiosities: Recueil d'Ouvrages Curieux de Mathématique et de Mécanique, ou Description du Cabinet de Monsieur Grollier de Servière. Charles Plumier, who visited the cabinet after Nicholas Grollier de Serviere's death, wrote the first book about wood turning, L'Art du Tourneur (The Art of the Turner), in 1701. A model of a water driven pile-driver which Grollier de Servière had built on his grounds was given to Stephen Demainbray in 1754 and is now preserved in the George III Collection in the London Science Museum.
References[]
- ^ Roger Le Roux de Lincy, baron Portalis, 1907. Researches Concerning Jean Grolier: His Life and His Library pp25ff.
- Joseph Connors (1990). "Ars Tornandi: Baroque Architecture and the Lathe". Journal of the Warburg and Courtauld Institutes (III): 217–36. Retrieved 21 November 2006.
- "One of the 17th Century's Most Celebrated and Fantastic Cabinets". Joslin Hall. Archived from the original on March 21, 2006. Retrieved 21 November 2006.
- "The King George III Collection". Science Museum. Archived from the original on November 23, 2005. Retrieved 21 November 2006.
- "Exposition à la Réserve : Livres anciens, rares ou précieux récemment signalés dans le catalogue de la Bibliothèque" (in French). La Réserve: Bibliothèque Sainte-Geneviève. Retrieved 21 November 2006.
- John Powell (Ed.) (2006). Great Events from History: The 18th Century. Salem Press. ISBN 1-58765-279-X. Retrieved 21 November 2006.CS1 maint: extra text: authors list (link)
External links[]
![]() Media related to Nicolas Grollier de Servière at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Nicolas Grollier de Servière at Wikimedia Commons
- 1596 births
- 1689 deaths
- 17th-century French inventors
- 17th-century French engineers
- People from Lyon
- French collectors