Northern Khmer dialect
| Northern Khmer | |
|---|---|
| Surin Khmer, Thai Khmer | |
| พซาคแมร | |
| Pronunciation | /pʰᵊsaː.kʰᵊmɛːr/ |
| Native to | Thailand, Cambodia |
| Ethnicity | Northern Khmer |
Native speakers | 1.4 million, very few monolingual[1] (2006)[2] |
Austroasiatic
| |
Writing system | Thai script (usually oral) |
| Official status | |
Recognised minority language in | native to provinces of Surin, Sisaket, Buriram |
| Regulated by | Royal Society of Thailand |
| Language codes | |
| ISO 639-3 | kxm |
| Glottolog | nort2684 |
Northern Khmer (พซาคแมร; Khmer: ខ្មែរខាងជើង), also called Surin Khmer (Khmer: ខ្មែរសុរិន្ទ), is the dialect of the Khmer language spoken by approximately 1.4 million Khmers native to the Thai provinces of Surin, Sisaket, Buriram and Roi Et as well as those that have migrated from this region into Cambodia.[3]
Northern Khmer differs from the standard language, based on a dialect of Central Khmer, in the number and variety of vowel phonemes, consonantal distribution, lexicon, grammar, and, most notably, pronunciation of syllable-final /r/, giving Northern Khmer a distinct accent easily recognizable by speakers of other dialects. Some speakers of Northern Khmer may understand other varieties of Khmer but speakers of standard Khmer who have not been exposed to Northern Khmer often have trouble understanding Northern Khmer at first. The two varieties are 80–85% cognate on a basic 270-word list.[3] These facts have led some linguists to advocate considering Northern Khmer a separate, but closely related language.[4]
History[]
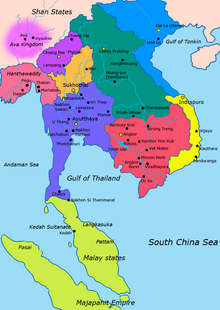
Teal: Lan Xang
Purple: Lanna
Orange: Sukhothai Kingdom
Blue Violet: Ayutthaya Kingdom
Red: Khmer Empire
Yellow: Champa
Blue: Dai Viet
After the fall of the Khmer Empire in the early 15th century the Dongrek Mountains served as a natural border, leaving the Khmer north of the mountains increasingly under the sphere of influence of Lan Xang. The conquests of Cambodia by Naresuan the Great for Ayutthaya furthered the political and economic isolation from Cambodia proper, leading to a dialect that developed relatively independently from the midpoint of the Middle Khmer period.[5]
Subsequently, the Isan area was claimed by the Lao Kingdom of Champasak in 1718 and in 1893, the region became part of the Kingdom of Siam (Thailand) as a result of the Franco-Siamese War. Throughout this period, the Northern Khmer people shared the rural mountainous highlands with the Lao, Thai and various Mon-Khmer groups such as the Kuy, leading to a high degree of multilingualism.[6] These varied influences and unique history have resulted in a distinct accent, with characteristics of the surrounding tonal languages, lexical differences through borrowing from Lao, Kuy and Thai, and phonemic differences in both vowels and distribution of consonants.
Status[]
Most, or probably all, speakers of Northern Khmer are bilingual, being also proficient in the national language Thai, which is the sole language of education and mass communication. Usage of Northern Khmer is restricted to the domestic and village domain. In the past, its use was actively disfavored (e.g. by prohibiting speaking Northern Khmer in school classrooms) to boost proficiency in the national language.[7] Only a few (c. 1,000) speakers of Northern Khmer are able to read or write it.[8]
Demographics[]
| Province | Khmer percentage in 1990 | Khmer percentage in 2000 |
|---|---|---|
| Buriram[9] | N/A | 27.6% |
| Chanthaburi[10] | 0.6% | 1.6% |
| Maha Sarakham[11] | 0.2% | 0.3% |
| Roi Et[12] | 0.4% | 0.5% |
| Sa Kaew[13] | N/A | 1.9% |
| Sisaket[14] | 30.2% | 26.2% |
| Surin[15] | 63.4% | 47.2% |
| Trat[16] | 0.4% | 2.1% |
| Ubon Ratchathani[17] | 0.8% | 0.3% |
Phonology[]
Northern Khmer has the typical Mon-Khmer consonant and syllable structure although there is no phonemic phonation.[3] The primary divergences from Central Khmer phonology are in the realizations of some syllable-final consonants and in the vowel inventory.[3] Northern Khmer is also losing the sesquisyllabic pattern of its sister languages.[18] Many dysllables have lost all but the first consonant of the pre-syllable, creating a great number of consonant clusters. In many dialects of Northern Khmer, however, inserting a generic syllable, /-rɔ-/, after an initial consonant is still optional, returning some words to their original sesquisyllabic structure.[18]
Consonants[]
The consonant inventory of Northern Khmer is identical to that of Central Khmer. It is laid out below as reported by Thomas.[19]
| Labial | Dental/Alveolar | Palatal | Velar | Glottal | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Plosive | p, pʰ | t, tʰ | c, cʰ | k, kʰ | ʔ |
| Implosive | ɓ | ɗ | |||
| Nasal | m | n | ɲ | ŋ | |
| Liquid | r l | ||||
| Fricative | (f) | s | h | ||
| Approximant | w | j |
Syllable-initial consonants are pronounced as in Central Khmer. When appearing as a syllable-final, however, the /k/, /ʔ/ and /ŋ/ that would be expected in Central Khmer are often realized as /c/, /k/ and /ɲ/, respectively, in Northern Khmer. Additionally, as mentioned above, syllable-final /r/ which has become silent in all other dialects is markedly pronounced.[19] Clusters often have anaptyxis, the insertion of slight vowel (shown with /ᵊ/).[20]
| Khmer Script | English gloss | Central Khmer (IPA) | Northern Khmer (IPA) |
|---|---|---|---|
| ពាក្យ | word | /piəʔ/ | /piək/ |
| ភ្នែក | eye | /pnɛːk/ | /pᵊnɛːc/ |
| ដឹង | know | /dəŋ/ | /deɲ/ |
| ខ្មែរ | Khmer | /kʰmae/ | /kʰᵊmɛːr/ |
Vowels[]
| Khmer language |
|---|
 |
| Aspects |
|
| Dialects |
|
| Stages |
|
The biggest distinction between Northern Khmer of Thailand and Central Khmer of Cambodia is in the inventory of vowel phonemes. Smalley described 14 pure vowels that occur both long and short.[21]
| Front | Central | Back | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| unrounded | rounded | |||
| Close | /i/ | /ɨ/ | /u/ | |
| Near-close | /ɪ/ | /ʊ/ | ||
| Close-mid | /e/ | /ə/ | /ɤ/ | /o/ |
| Open-mid | /ɛ/ | /ʌ/ | /ɔ/ | |
| Open | /a/ | /ɒ/ | ||
Smalley also described three "vowels with offglides" that he treated as monophthongs, namely /iə/, /ɨə/ and /uə/, for a total of 17 vowel phonemes.[3] All 17 vowels can be short or long. With 14 basic vowel positions, and having more back vowels than front, Northern Khmer is atypical. By contrast, standard Central Khmer only has 9 or 10 basic vowel positions, depending on the analysis.[22][23]
Script[]
Northern Khmer is, for the most part, a spoken language as most speakers are unable to read or write their native tongue[24] due to Thaification policies either enacted or supported by the Thai government. However, recent renewed interest and enthusiasm in Khmer language and culture has resulted in a two-fold increase in the use of Northern Khmer since 1958 and the consequential need for a formalized method of writing the language.[6] Since the Thai language is the medium of public education and, until the 21st century, the media, Khmer is taught at home or by monks in the local Khmer temples, often supported by Khmers in Cambodia or Western nations.[24][25]
In Thailand, Northern Khmer is written in the Thai script.[19] As many sounds occur in Northern Khmer that would be impossible to write according to the rules of Thai orthography, a few innovations are necessary such as using ฮ (initial /h/ in Thai) at the end of words to represent syllable-final /h/ and ญ (initial /j/, final /n/ in Thai) to represent Northern Khmer's palatal nasal /ɲ/. Special diacritics are also sometimes used with the vowels because Northern Khmer has more vowel positions than Thai.[19]
Within Cambodia, Northern Khmer is written in the Khmer script as the words are spelled in standard Khmer, regardless of the Northern Khmer pronunciation. This is seen most often in the context of kantrum music karaoke DVDs which are increasingly popular in Cambodia and with Cambodians overseas.
| Pronunciation | Thai letter | Transliteration |
| /k/ | ก | k |
| /kʰ/ | ค | kh |
| /ŋ/ | ง | ng |
| /c/ | จ | c |
| /cʰ/ | ช | ch |
| /s/ | ซ | s |
| /ɲ/ | ญ | ny |
| /d/ | ด | d |
| /t/ | ต- -ด |
t |
| /tʰ/ | ท | th |
| /n/ | น | n |
| /b/ | บ | b |
| /p/ | ป- (at the start of words) -บ (at the end of words) |
p |
| /pʰ/ | พ | ph |
| /f/ | ฟ | f |
| /m/ | ม | m |
| /j/ | ย | y |
| /r/ | ร | r |
| /l/ | ล | l |
| /w/ | ว | w |
| /ʔ/ | อ- -∅ |
' |
| /h/ | ฮ | h |
| Pronunciation | Thai diacritic | Transliteration |
| /a/ | อะ อั |
a |
| /a:/ | อา | ā |
| /i/ | อิ | i |
| /i:/ | อี | ī |
| /ɪ/ | อฺิ | œ̆ |
| /ɪ:/ | อฺี | œ |
| /ɯ/ | อึ | ue |
| /ɯ:/ | อื | ue |
| /ɤ/ | อฺึ | eu |
| /ɤ:/ | อฺือ | eu |
| /u/ | อุ | u |
| /u:/ | อู | ū |
| /ʊ/ | อุํ | u |
| /ʊ:/ | อูํ | ū |
| /e/ | เอะ เอ็ |
e |
| /e:/ | เอ | ē |
| /ɛ/ | แอะ แอ็ |
ê |
| /ɛ:/ | แอ | ê |
| /o/ | โอะ ∅ |
o |
| /o:/ | โอ | ō |
| /ɔ/ | เอาะ อ็อ |
ô |
| /ɔ:/ | ออ | ô |
| /ɒ/ | เอฺอะ อ็อฺ |
â |
| /ɒ:/ | ออฺ | â |
| /ə/ | เออะ เอิอ็ |
eu |
| /ə:/ | เออ เอิ |
eu |
| /ʌ/ | เอฺอะ เอฺิอ็ |
ă |
| /ʌ:/ | เอฺอ เอฺิ |
ă |
" ฺ " (the pinthu mark) or " ํ " are used to alter the pronunciation of vowels, similar to the bântăk punctuation mark (a small vertical line on the final consonant of a syllable) in the Khmer alphabet.
See also[]
- Cambodia
- Chrieng Brunh
- Isan
- Khmer language
- Khmer people
- Kantrum
- Northern Khmer people
- Thailand
References[]
- ^ William J. Frawley, ed. (2003). International Encyclopedia of Linguistics. 1 (2nd ed.). Oxford University Press. p. 488.
- ^ Northern Khmer at Ethnologue (18th ed., 2015)
- ^ Jump up to: a b c d e Thomas, David & Wanna, Tienmee; 1984; An Acoustic Study of Northern Khmer Vowels; Mon-Khmer Studies, vol 16–17
- ^ Thomas, David. 1990. "On the 'language' status of Northern Khmer." JLC 9.1:98–106
- ^ de Bernon, Olivier. "Khmer of Surin: Lexical Remarks". 1988.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Smalley, William A. (1988). "Multilingualism in the Northern Khmer Population of Thailand". Language Sciences. 10 (2): 395–408. doi:10.1016/0388-0001(88)90023-X.
- ^ Vail, Peter (2007). "Thailand's Khmer as 'invisible minority': Language, ethnicity and cultural politics in north-eastern Thailand". Asian Ethnicity. 8 (2): 111–130. doi:10.1080/14631360701406247. S2CID 144401165.
- ^ Northern Khmer dialect at Ethnologue (22nd ed., 2019)
- ^ "burirum.xls" (PDF). Retrieved 2017-03-08.
- ^ http://web.nso.go.th/pop2000/finalrep/chanburifn.pdf
- ^ "mahakam.xls" (PDF). Retrieved 2017-03-08.
- ^ http://web.nso.go.th/pop2000/finalrep/roietfn.pdf
- ^ (PDF) http://web.nso.go.th/pop2000/finalrep/sakaeofn.pdf. Retrieved 2017-03-08. Missing or empty
|title=(help) - ^ (PDF) http://web.nso.go.th/pop2000/finalrep/srisaketfn.pdf. Retrieved 2017-03-08. Missing or empty
|title=(help) - ^ (PDF) https://web.archive.org/web/20120215221927/http://web.nso.go.th/pop2000/finalrep/surinfn.pdf. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2012-02-15. Retrieved 2017-03-08. Missing or empty
|title=(help) - ^ http://web.nso.go.th/pop2000/finalrep/tratfn.pdf
- ^ (PDF) http://web.nso.go.th/pop2000/finalrep/ubonfn.pdf. Retrieved 2017-03-08. Missing or empty
|title=(help) - ^ Jump up to: a b Phon-ngam, Prakorb; 1992; The Problem of Aspirates in Central Khmer and Northern Khmer Archived 2016-03-04 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ Jump up to: a b c d Thomas, Dorothy; Popularizing the Northern Khmer Orthography: Sociolinguistics in Action Workshop in Northern Khmer Orthography, Surin; Mon-Khmer Studies Journal. 16–17: 255–265
- ^ พจนานุกรมเขมร (สุรินทร์)-ไทย-อังกฤษ, Khmer (Surin)-Thai-English Dictionary (1978) [1]
- ^ Smalley, William A.; 1976; The Problem of Vowels: Northern Khmer; Canberra; Pacific Linguistics C-43; pp 25–42.
- ^ Huffman, Franklin. 1970. Cambodian System of Writing and Beginning Reader. Yale University Press. ISBN 0-300-01314-0
- ^ Wayland, Ratree. "An Acoustic Study of Battambang Khmer Vowels." The Mon-Khmer Studies Journal. 28. (1998): 43–62.
- ^ Jump up to: a b "VOA Khmer News, Radio, TV". voanews.com. Archived from the original on 25 February 2011. Retrieved 19 April 2018.
- ^ Isara, Choosri; 2008; THE USE OF NORTHERN KHMER IN COMMUNITY RADIO PROGRAMS IN THAILAND[permanent dead link]; Mahidol University, Bangkok, Thailand
Further reading[]
- Thanan Čhanthrupant, and Chātchāi Phromčhakkarin. Photčhanānukrom Khamen (Surin)-Thai-Angkrit = Khmer (Surin)-Thai-English Dictionary. [Bangkok, Thailand]: Indigenous Languages of Thailand Research project, Chulalongkorn University Language Institute, 1978.
- Suwilai Prēmsīrat, and Sōphanā Sīčhampā. Kānphatthanā rabop kānkhīan Phāsā Khamēn Thin Thai Khrōngkān Phatthanā Phāsā Phư̄nbān phư̄a ʻAnurak Sinlapawatthanatham Phư̄nbān læ Phalit Sư̄ Tāng Tāng = Formulating Thai-based northern Khmer orthography : for the recording and preservation of local culture and for the producing of educational materials. [Bangkok]: Sathāban Wičhai Phāsā læ Watthanatham phư̄a Phatthanā Chonnabot, Mahāwitthayālai Mahidon, 1990. ISBN 9745868302
External links[]
- Languages of Cambodia
- Languages of Thailand
- Khmer language