Nosema (microsporidian)
| Nosema | |
|---|---|
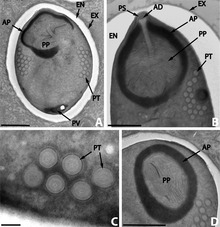
| |
| Nosema podocotyloidis | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Fungi
|
| Division: | |
| Class: | |
| Order: | |
| Family: | |
| Genus: | Nosema Nägeli (1857)
|
Nosema is a genus of microsporidian parasites. The genus, circumscribed by Swiss botanist Karl Wilhelm von Nägeli in 1857, contains 81 species.[1] Most parasitise insects and other arthropods, and the best-known Nosema species parasitise honeybees, where they are considered a significant disease by beekeepers, often causing a colony to fail to thrive in the spring as they come out of their overwintering period. Eight species parasitize digeneans, a group of parasitic flatworms, and thus are hyperparasites, i.e., parasites of a parasite.[2]
Species[]
- Nosema algerae parasitising mosquitoes
- parasitising the Chinese oak silkworm Antheraea pernyi
- Nosema apis parasitising western honey bees
- parasitising the chrysomelid beetle Mesoplatys cincta
- Nosema bombi parasitising bumble bees
- Nosema bombycis causes pébrine in silkworms
- parasitising Laspeyresia molesta (a tortricid moth)
- Nosema ceranae parasitising honey bees and bumble bees
- parasitising the chrysomelid beetle Chaetocnema tibialis
- parasitising the browntail moth Euproctis chrysorrhoea (a lymantrid moth)
- parasitising chrysomelid beetles of genus Nisotra
- parasitising the potato leaf-hopper Empoasca fabae (a cicadellid bug)
- parasitising the chrysomelid beetles Gastrophysa viridula and Leptinotarsa decemlineata
- parasitising the eastern spruce budworm Choristoneura fumiferana (a tortricid moth)
- parasitising the Asian corn-borer Ostrinia furnacalis (a pyralid moth)
- parasitising the chrysomelid beetle Galerucella luteola
- parasitising the chrysomelid beetle Gastrophysa polygoni
- parasitising the crustacean Gammarus duebeni
- parasitising the Colorado potato beetle (Leptinotarsa decemlineata)
- parasitising chrysomelid beetles of genus Nisotra
- parasitising the chrysomelid beetle Oulema melanopus
- parasitising the chrysomelid beetles Phyllotreta atra and Phyllotreta undulata
- parasitising the chrysomelid beetle Polygramma undecimlineata
- parasitising the gypsy moth Lymantria dispar (a lymantrid moth)
- parasitising the red soldier bug Pyrrhocoris apterus (a pyrrhocorid bug)
- parasitising the European corn-borer Ostrinia nubilalis (a pyralid moth)
- parasitising the gypsy moth Lymantria dispar (a lymantrid moth)
- parasitising the diamondback moth, Plutella xylostella (a plutellid moth)
- parasitising the cabbage looper/tiger moth Trichoplusia ni (a noctuid moth)
- parasitising the cinnabar moth Tyria jacobaeae (an arctiid moth)
- parasitising European wasps
Nosema locustae, which parasitises locusts and grasshoppers, and Nosema grylli, which parasitises crickets, have been transferred to Paranosema, or in the former case Antonospora. Nosema algerae, which parasitises anopheline mosquitoes, has been transferred to Brachiola. Nosema kingii, which parasitises fruit flies, and Nosema acridophagus, which parasitises grasshoppers, have been transferred to Tubilinosema.
Studies of DNA sequences imply that the boundaries between the genera Nosema and Vairimorpha are incorrectly drawn.[citation needed]
References[]
- ^ Kirk PM, Cannon PF, Minter DW, Stalpers JA (2008). Dictionary of the Fungi (10th ed.). Wallingford, UK: CAB International. p. 473. ISBN 978-0-85199-826-8.
- ^ Toguebaye, B. S., Quilichini, Y., Diagne, P. M. & Marchand, B. 2014: Ultrastructure and development of Nosema podocotyloidis n. sp. (Microsporidia), a hyperparasite of Podocotyloides magnatestis (Trematoda), a parasite of Parapristipoma octolineatum (Teleostei). Parasite, 21, 44. doi:10.1051/parasite/2014044 PMID 25174849

External links[]
| Wikispecies has information related to Nosema. |
- Microsporidia genera
- Parasites of arthropods
