Old Age Security
This article has multiple issues. Please help or discuss these issues on the talk page. (Learn how and when to remove these template messages)
|
The Old Age Security (OAS) program is a universal retirement pension available to most residents and citizens of Canada who have reached 65 years old. This pension is supplemented by the Guaranteed Income Supplement (GIS) for seniors with lower incomes, which is added to their monthly OAS payment. Some low-income spouses and survivors of OAS recipients are eligible to receive an income-tested allowance while they are aged 60 to 64.
Legal foundation[]
Old Age Security (OAS) is a monthly payment available to qualifying citizens and permanent residents of Canada who are 65 years old and older. Authorized by Section 94A of the Constitution Act of 1867,[1] the program is defined by the Old Age Security Act (R.S.C., 1985, c. O-9).[2] Implementation is the responsibility of the Minister of Employment and Social Development (ESDC).[3] Administration is performed by Service Canada through offices across Canada.[4]
Payments[]
The pension is paid monthly, on the third business day from the end of the current month. In December the payment is made about one week earlier than it is in all other months. The Government prefers to use Direct Deposit and this has been observed to be consistently executed shortly after midnight Pacific time. This is an unpublished operational detail that ensures all Canadians receive these payments at the same time, regardless of their time zone of residence. There is an official Government of Canada schedule that does not specify the time of day.[5]
Amounts[]
The full OAS payment amount is reviewed at the beginning of each calendar quarter, compared to the Consumer Price Index and increased as appropriate.[6] These reports include the maximum payments for OAS and GIS and the numbers of persons and total dollars for each category of payment.
Enrollment and eligibility[]
Prior to 2013, a person needed to apply to Employment and Social Development Canada (ESDC)[7] and meet the eligibility criteria to receive benefits. Since 2013, the enrollment process has become increasingly automatic as Service Canada are now permitted to use data from Income Tax files.[8] For persons who are not enrolled automatically, a manual application process remains in place.[7]
Eligibility[]
Eligibility for Old Age Security is straightforward for most Canadians. Persons who have lived outside of Canada can refer to official documentation for details including residency requirements and a list of reciprocal agreements with other countries which may allow pooling of residency periods to increase eligibility for Canadian or foreign pension rights.[9]
Pension amounts[]
A complete description of the payment amounts is beyond the scope of this article.[10]
Guaranteed Income Supplement[]
The OAS includes a provision for additional support for low-income seniors. The Guaranteed Income Supplement (GIS)[11] provides an additional payment to seniors whose qualifying incomes (excluding OAS payments) fall below a threshold that depends on the marital status and OAS eligibility of the person and their domestic partner (if they have one).
Single Senior, No Other Income Source[]
By way of an example, in September 2019, a single senior, with no other income could receive a maximum of $1,514.76 per month ($18,177 annually). This combines the basic OAS payment $613.53 and the maximum amount of GIS $916.38. Depending on the province of residence this amount would be increased by a combination of Federal and Provincial tax benefits. For example, in Newfoundland and Labrador (NL), tax benefits could increase this by about $2,122 through the GST credit ($443), NL Income Supplement ($366) and the NL Seniors Benefit ($1,313). The total of $20,299 is close to 100% of Canada's first Official Poverty Line in St. John's Newfoundland and Labrador.
OAS Recovery Tax[]
The OAS is subject to a claw-back, officially named the Old Age Security Pension Recovery Tax that reduces the amount retained by recipients by 15% of taxable income in excess of $75,910 (2018 tax year).[12] For 2018, some of the government documentation appears to state that the maximum income from which the claw-back will be applied is $123,386. This is in fact the base-line case for OAS paid commencing at age 65. The 2018 version of the "Worksheet for the Return" applies the claw-back to the total of OAS and GIS received. This accounts for any cases in which an OAS recipient deferred the pension and received more than the base amount as a result of the deferral.
Taxpayers subject to this claw-back have taxable incomes that are greater than the incomes of more than eighty percent of Canadians according to the Canada Revenue Agency.[13] From Table 2, for All of Canada, Item 57 states: Taxable Income Assessed add up the numbers of tax filers in the columns for incomes $70,000 and above (interpolate the number for the range above $75,910 from the range $70,000 to $79,999). Divide this number by the total number of filers in the Grand Total (#) on the line for Item 57.
Tax Benefit and Claw-back Examples 2018 Tax Year[]
Newfoundland and Labrador[]
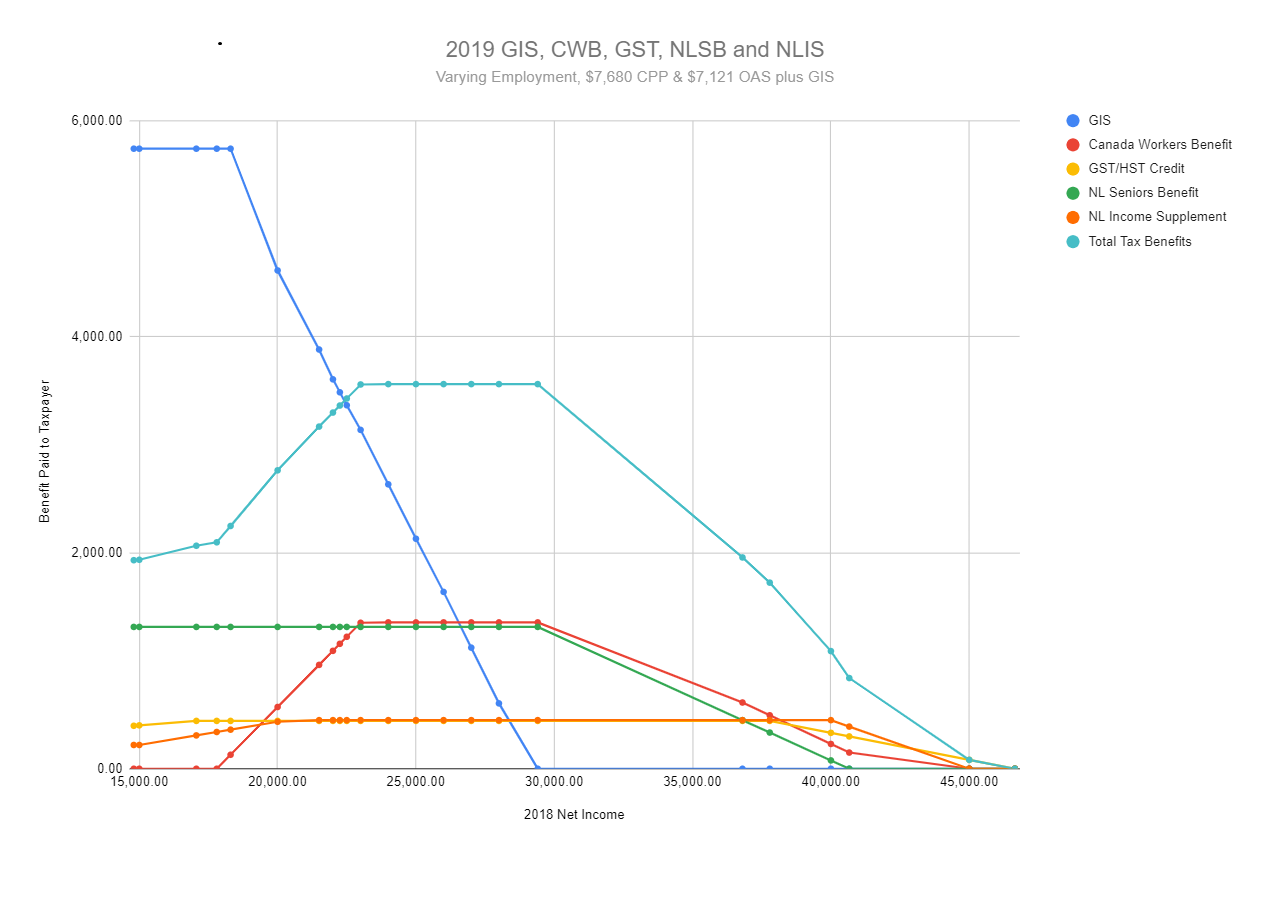
Amounts are additive[]
The benefits can be added which means that claw-backs can combine to produce some steep declines where they overlap. Claw-backs cause a benefit to diminish by a fixed percentage of the amount that "Family Net Income" (FNI) exceeds a fixed threshold. Economists include these declines in the definition of the Marginal Effective Tax Rate (METR). In "The Paycheck Blues", Andre Laurin defines the METR as "The "marginal" effective tax rate (METR) conveys the loss, through additional taxes and diminished benefits, associated with an extra dollar of earnings. For a working parent, it represents the financial penalty that must be paid for working extra hours."[14]
GST credit example[]
The GST credit and claw-back work like this:
- Basic credit is $290 ($580 partner or child), plus $153 per child not counted as a partner by a single parent.
- Family Net Income (FNI): $0 to $9,412, basic credit
- FNI > $9,412 to $17,062: basic credit plus 2% of (FNI - $9,412)
- FNI > $17,062 to $37,789: basic credit plus $153, call this the peak credit
- FNI > $37,789: peak credit minus 5% of (FNI - $37,789)
- FNI > $52,442: credit is zero
Problems settling in to a low-income retirement[]
While the combination of OAS, GIS and Tax Benefits comes close to the Poverty Line, receiving the income will be problematic for many seniors. The official published documentation for the GIS does not clearly indicate a direct path to obtaining the correct payment upon retirement. Furthermore, federal and provincial tax benefits are not generated at the senior's retirement income until the benefit period following the filing of the first full taxation year in retirement. A senior could retire from a position at an income level that claws back tax benefits and find themselves falling short of the combination of GIS and tax benefits that would otherwise lift them up to the poverty line.
The Newfoundland and Labrador example indicates that those tax benefits make up about 10% of this poverty-line target. The GIS maximum payment in 2019, represents more than half of this target with the OAS representing about thirty-six percent of the amount. A low-income part-time job can add up to $5,000 in earnings in 2020 without reducing the GIS and would add another tax benefit, the Canada Workers Benefit, which would pay $520 (26% of employment income over $3,000 to a maximum of $1,355) without requiring high-school algebra. The CWB maximum payment of $1,355, generated at an income of $8,212 but the math should be checked carefully as the addition of $3,212 in income would reduce GIS by 803 (25%) and drive up the worker's income tax.
Invisibly taxed[]
The GIS is described as non-taxable income although it is reported to CRA in box 21 of T4(OAS)[15] from where it is included in Line 236: Net Income which is a critical part of the claw-back implementation used by both Federal and Provincial programs.[16]
Income testing the non-taxable GIS[]
A number of Federal and Provincial Tax Benefits are income-tested using personal information shared by Canada Revenue Agency taken from the T1 Income Tax Form Line 236 - Net Income.[17] This total includes Line 146 - Net Federal Supplements (GIS)[18] and makes the Supplement subject to claw-backs, an implicit tax on income. Notable federal claw-backs include the 12% from the Canada Workers Benefit[19] and 5% from the GST Benefit.[20] Provincial benefit claw-backs are different from province to province. As an example, in Newfoundland and Labrador claw-backs include the NL Low Income Tax Reduction (16%),[21] NL Income Supplement (9%) and the NL Seniors Benefit (11.66%).[22]
Determination of payments[]
Each calendar quarter, Service Canada publishes a set of Tables for five different classes of recipient which determine the amounts payable to eligible persons:[23]
- single
- married (both receiving OAS)
- married (one receiving OAS, one aged less than 60)
- married (one receiving OAS, one aged 60 to 64)
- survivors of OAS recipients (aged 60 to 64)
Estimate of income[]
One common point of confusion is the impression that there is a waiting period between retirement and eligibility for the GIS and the Allowance for spouses aged 60 to 64. The OAS Act stipulates at 14.(2) that anyone who experiences a loss of income (such as through retirement) may file an Estimate of Income with the Minister. The form used to accomplish this (ISP-3041), is not available on the Service Canada web site but can be obtained on paper after discussing one's situation with a Service Canada agent over the phone or in person.
There is also a time limit for the filing of the form ISP-3041: "Reduction of Estimated Income after Retirement or Reduction of Pension Income Year 20xx". This is problematic because the existence of the provision and the procedure for exercising the retiring person's right to file it are absent from the seven steps presented on the Service Canada web site.[24]
Canada Pension Plan[]
Old Age Security should not be confused with the Canada Pension Plan, which is a contributory, earnings-related pension paid in addition to the OAS to those who have contributed to it.
See also[]
- Basic income
- Canada Pension Plan / Old Age Security Review Tribunals
- Guaranteed minimum income
References[]
- ^ "The Constitution Act of 1867". Justice Laws Website. Canadian Department of Justice. Retrieved 29 April 2021.
- ^ "Old Age Security Act (R.S.C., 1985, c. O-9)". Justice Laws Website. Canadian Department of Justice. Retrieved 29 April 2021.
- ^ "Employment and Social Development Canada". www.canada.ca. 2020-09-24. Retrieved 2021-08-28.
- ^ "Service Canada". www.canada.ca. 2020-11-12. Retrieved 2021-08-28.
- ^ "Benefits payment dates". www.canada.ca. 2015-05-06. Retrieved 2021-08-28.
- ^ "Statistics related to the Old Age Security Program and the Canada Pension Plan". www.canada.ca. 2016-02-03. Retrieved 2021-08-28.
- ^ a b "Old Age Security: Your application". www.canada.ca. 2015-10-29. Retrieved 2021-08-28.
- ^ "Backgrounder: Old Age Security (OAS) automatic enrolment". www.canada.ca. 2018-01-09. Retrieved 2021-08-28.
- ^ "Canada's international social security agreements". www.canada.ca. 2012-07-25. Retrieved 2021-08-28.
- ^ "Old Age Security: How much you could receive". www.canada.ca. 2015-10-30. Retrieved 2021-08-28.
- ^ "Guaranteed Income Supplement – Overview". www.canada.ca. 2015-10-28. Retrieved 2021-08-28.
- ^ "Old Age Security pension recovery tax". www.canada.ca. 2015-10-30. Retrieved 2021-08-28.
- ^ "Canada Revenue Agency". www.canada.ca. 2020-10-01. Retrieved 2021-08-28.
- ^ Laurin, Andre (2019). "The Paycheck Blues" (PDF). C.D. Howe Institute. p. 1.
- ^ "T4A(OAS), Statement of Old Age Security". www.canada.ca. 2016-12-06. Retrieved 2021-08-28.
- ^ "Line 23600 - Net income". www.canada.ca. 2004-01-23. Retrieved 2021-08-28.
- ^ "Line 23600 - Net income". www.canada.ca. January 23, 2004.
- ^ "Line 14600 - Net federal supplements". www.canada.ca. January 23, 2004.
- ^ "Calculation sheets for the Canada workers benefit advance payments". www.canada.ca. January 4, 2008.
- ^ "GST/HST credit: calculation sheets". www.canada.ca. November 1, 1999.
- ^ "Low Income Tax Reduction".
- ^ "NL Income Supplement and the NL Seniors' Benefit".
- ^ "Table of benefit amounts by marital status and income level". 2002-07-01. Retrieved 2021-08-28.
- ^ "Guaranteed Income Supplement – Overview". www.canada.ca. October 28, 2015.
- 1952 establishments in Canada
- Retirement in Canada
- Pensions in Canada
- Social security in Canada