Oligomycin

| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
(1R,4E,5'S,6S,6'S,7R,8S,10R,11R,12S,14R,15S,16R,18E,20E,22R,25S,27R,28S,29R)-22-ethyl-7,11,14,15-tetrahydroxy-6'-[(2R)-2-hydroxypropyl]-5',6,8,10,12,14,16,28,29-nonamethyl-3',4',5',6'-tetrahydro-3H,9H,13H-spiro[2,26-dioxabicyclo[23.3.1]nonacosa-4,18,20-triene-27,2'-pyran]-3,9,13-trione
| |
| Other names
Oligomycin
| |
| Identifiers | |
| |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.014.334 |
| EC Number |
|
| MeSH | Oligomycins |
PubChem CID
|
|
| RTECS number |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C45H74O11 | |
| Molar mass | 791.062 g/mol |
| Hazards | |
| Safety data sheet (SDS) | MSDS at Fermentek |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Oligomycins are macrolides created by Streptomyces that can be poisonous to other organisms.
Function[]
They have use as antibiotics.
Oligomycin A is an inhibitor of ATP synthase. In oxidative phosphorylation research, it is used to prevent state 3 (phosphorylating) respiration. Oligomycin A inhibits ATP synthase by blocking its proton channel (FO subunit), which is necessary for oxidative phosphorylation of ADP to ATP (energy production). The inhibition of ATP synthesis by oligomycin A will significantly reduce electron flow through the electron transport chain; however, electron flow is not stopped completely due to a process known as proton leak or mitochondrial uncoupling.[1] This process is due to facilitated diffusion of protons into the mitochondrial matrix through an uncoupling protein such as thermogenin, or UCP1.
Administering oligomycin to rats can result in very high levels of lactate accumulating in the blood and urine.[2]
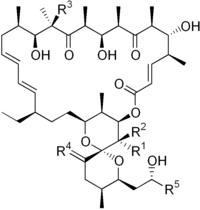
| |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R1 | R2 | R3 | R4 | R5 | |
| Oligomycin A | CH3 | H | OH | H,H | CH3 |
| Oligomycin B | CH3 | H | OH | O | CH3 |
| Oligomycin C | CH3 | H | H | H,H | CH3 |
| Oligomycin D (Rutamycin A) |
H | H | OH | H,H | CH3 |
| Oligomycin E | CH3 | OH | OH | O | CH3 |
| Oligomycin F | CH3 | H | OH | H,H | CH2CH3 |
| Rutamycin B | H | H | H | H,H | CH3 |
| 44-Homooligomycin A | CH2CH3 | H | OH | H,H | CH3 |
| 44-Homooligomycin B | CH2CH3 | H | OH | O | CH3 |
References[]
- ^ Jastroch M, Divakaruni AS, Mookerjee S, Treberg JR, Brand MD (2010). "Mitochondrial proton and electron leaks". Essays in Biochemistry. 47 (1): 53–67. doi:10.1042/bse0470053. PMC 3122475. PMID 20533900.
- ^ Kramer R, Srour A, Khanakah G (1984). "Oligomycin toxicity in intact rats". Models in Toxicology. 15 (5–6): 660–663. doi:10.1007/BF01966788. PMID 6532186. S2CID 7837164.
- ^ Nakata, Masaya; Ishiyama, Takashi; Akamatsu, Shinichi; Hirose, Youichi; Maruoka, Hiroshi; Suzuki, Rika; Tatsuta, Kuniaki (1995). "Synthetic studies on oligomycins. Synthesis of the oligomycin B spiroketal and polypropionate portions". Bulletin of the Chemical Society of Japan. 68 (3): 967–89. doi:10.1246/bcsj.68.967.
- Macrolide antibiotics
- Spiro compounds
- Triketones
- ATP synthase inhibitors