Phang Nga Province
hideThis article has multiple issues. Please help or discuss these issues on the talk page. (Learn how and when to remove these template messages)
|
Phang Nga
พังงา | |
|---|---|
 Similan Islands in Phang Nga Province | |
 Flag  Seal | |
 Map of Thailand highlighting Phang Nga Province | |
| Country | Thailand |
| Capital | Phang Nga |
| Government | |
| • Governor | Chamroen Thipphayaphongthada (since October 2019)[1] |
| Area | |
| • Total | 4,171 km2 (1,610 sq mi) |
| Area rank | Ranked 53rd |
| Population (2018)[3] | |
| • Total | 268,240 |
| • Rank | Ranked 72nd |
| • Density | 64/km2 (170/sq mi) |
| • Density rank | Ranked 68th |
| Human Achievement Index | |
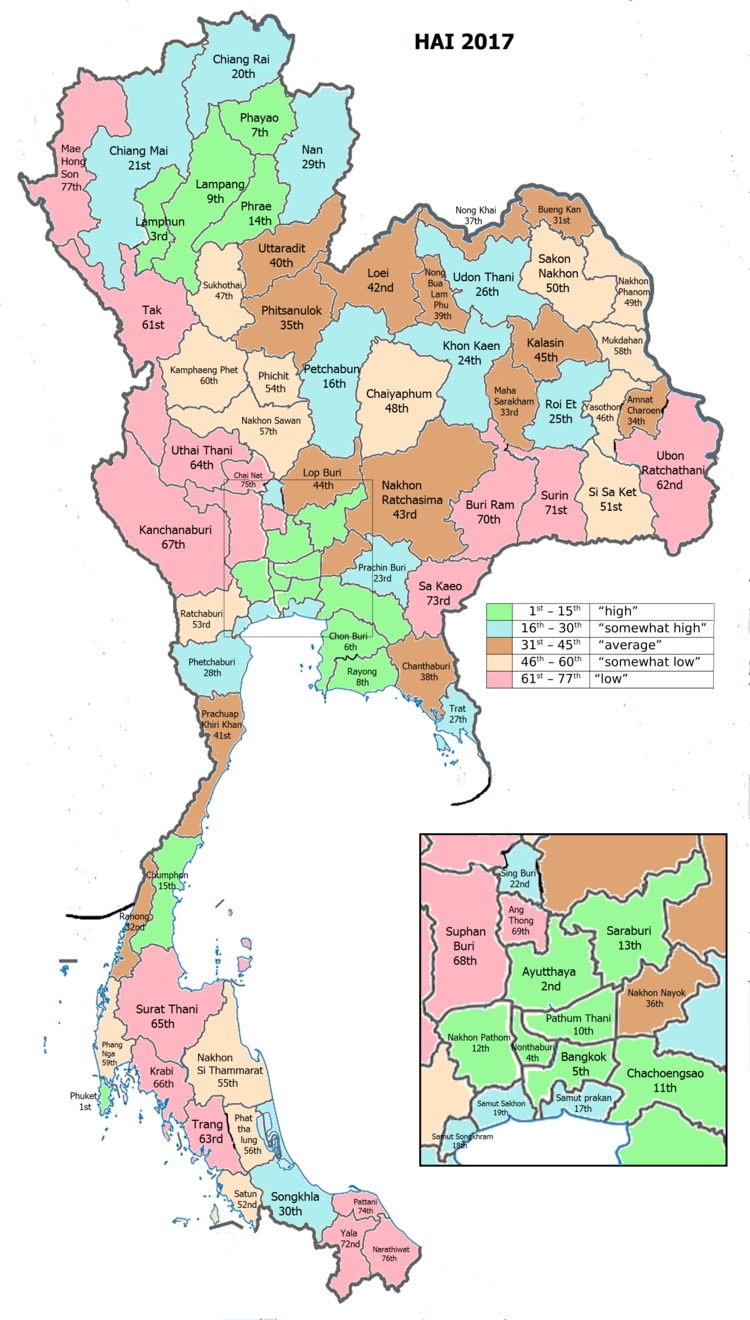
| • HAI (2017) | 0.5649 "somewhat low" Ranked 59th |
| Time zone | UTC+7 (ICT) |
| Postal code | 82xxx |
| Calling code | 076 |
| ISO 3166 code | TH-82 |
| Website | www |
Phang Nga (Thai: พังงา, pronounced [pʰāŋ.ŋāː]) is one of the southern provinces (changwat) of Thailand, on the shore of the Andaman Sea to the west and Phang Nga Bay to the south. Neighboring provinces are (from north, clockwise) Ranong, Surat Thani, and Krabi. To the south is the Phuket Province, connected by the Sarasin Bridge.
Geography[]

The province is on the west side of the Malay Peninsula, and includes the many islands of the Phang Nga Bay. The most famous one is the so-called James Bond Island, a needle formed limestone rock in the sea, which featured in the 1974 movie The Man with the Golden Gun. Ao Phang Nga (Phang Nga Bay) National Park was established in 1981 to protect the many islands.[5] The Similan Islands and Surin Islands, two of Thailand's main diving destinations, are also part of Phang Nga Province.[6] The total forest area is 1,778 km2 (686 sq mi) or 32.4 percent of provincial area.[7]
Toponymy[]
Phang Nga is the modern Thai transliteration of the archaic Malay word pangan, literally 'jungle'. The phrase orang pangan denotes 'heathen, pagan, primitive people', in reference to a generalised tribe or people typically inhabiting jungle areas of the Malay Peninsula[8] and its offshore islands.
History[]
Phang Nga province originally believed that the name was "Mueang Phu Nga", In the past, Phu Nga city depended on Nakhon Si Thammarat.
Past community[]
From the chronicles it appears that before the Rattanakosin period, Phang Nga was a sub-district with Takua Pa city. Until the reign of King Rama I of Rattanakosin, Phang Nga has been elevated to a city equivalent to the city of Takua Pa and Takua Thung.
Rattanakosin period[]
Phang Nga was officially established in the reign of King Rama II of Rattanakosin in 1809. In that year, The Burmese attacked the towns of Takua Pa, Takua Thung and Thalang, King Rama II ordered to gather immigrants to establish a new community in Phang Nga town at "Kra Phu Nga".
Later in the reign of King Rama III, Phraya Borirak Phuthon (Saeng Na Nakhon) was appointed as the first governor of Phang Nga in 1840, and has dissolved the city of Takua Thung into a district of Phang Nga and later Takua Pa was included as a district of Phang Nga in 1931.
In 1890, King Rama V travelled to Phang Nga and recorded about the state of Phang Nga that is Phang Nga is a beautiful fertile city.
Many years later in 1916, has changed the name of "Phang Nga Town" to "Phang Nga province". Later, when the economic downturn occurred in the reign of King Rama VII, has collapsed Takua Pa, which has status as a province in the district up to Phang Nga.
Symbols[]

The provincial seal shows the Phu Khao Chang mountains in the background, with city hall in front. It also shows a dredge to represent the tin mining in the province.[9]
The provincial slogan is, "Massive mining industry, Ban Klang Nam 'floating house', delightful caves, strangely shaped hills, Jampun flower, rich in resources".[9]
The provincial tree is the (hardy cinnamon), and the provincial flower is .
Administrative divisions[]

Provincial government[]
Phang Nga is divided into eight districts (amphoes), which are further divided into 48 subdistricts (tambons) and 314 villages (mubans).
|
Local government[]
As of 26 November 2019 there are:[10] one Phang Nga Provincial Administration Organisation (ongkan borihan suan changwat) and 15 municipal (thesaban) areas in the province. Phang Nga and Takua Pa have town (thesaban mueang) status. Further 13 subdistrict municipalities (thesaban tambon). The non-municipal areas are administered by 36 Subdistrict Administrative Organisations - SAO (ongkan borihan suan tambon).[3]
Transportation[]
- Roads: Hwy 4 is the main route that connects all districts in Phang Nga (except Kapong and Ko Yao). Hwy 401 connects Phang Nga to Surat Thani. Hwy 402 connects Phang Nga to Phuket Province. Hwy 4090 connects Muang to Kapong District.
- Railways: There is no rail system in Phang Nga Province. The nearest railway station is at Phunphin, Surat Thani Province.
- Bus: There are frequent buses to Bangkok and other provinces. There are also non air conditioned intra-provincial buses.
- Public transit: songthaews are the most popular mode of public transportation in Phang Nga.
- Motorbike-taxi: These are found mainly in Phang Nga town and are used mainly for very short distances. Charges correspond to distance traveled.
- Airport: There is no airport in Phang Nga Province. The nearest airport is Phuket International Airport.
Human achievement index 2017[]
| Health | Education | Employment | Income |
| 9 | 51 | 76 | 20 |
| Housing | Family | Transport | Participation |

|
 |

|
|
| 70 | 34 | 18 | 26 |
| Province Phang Nga, with an HAI 2017 value of 0.5649 is "somewhat low", occupies place 59 in the ranking. | |||
Since 2003, United Nations Development Programme (UNDP) in Thailand has tracked progress on human development at sub-national level using the (HAI), a composite index covering all the eight key areas of human development. National Economic and Social Development Board (NESDB) has taken over this task since 2017.[4]
| Rank | Classification |
| 1 - 15 | "high" |
| 16 - 30 | "somewhat high" |
| 31 - 45 | "average" |
| 45 - 60 | "somewhat low" |
| 61 - 77 | "low" |
| showMap with provinces and HAI 2017 rankings |
National parks[]
- Ao Phang Nga (Phang Nga Bay) National Park (อุทยานแห่งชาติอ่าวพังงา) was declared a national park in 1981. It has scenic views and features mass limestone formations scattered around in the sea near the shore. The same factors contribute to the density of caves in the area. The park is fertile with mangroves and there are a number of islands in the vicinity.

Phang-nga National Park

Limestone islets in Phang-nga National Park

Sunset in Phang Nga Bay

Karst formations
- Mu Ko Surin National Park (อุทยานแห่งชาติหมู่เกาะสุรินทร์) is an archipelago of five islands: Ko Surin Nuea, Ko Surin Tai, Ko Ri, Ko Khai, and Ko Klang. It was declared a national park on 9 July 1981.[11] The archipelago is in the Andaman Sea, near the Thai-Burmese oceanic border.

- Khao Lak–Lam Ru National Park (อุทยานแห่งชาติเขาหลัก-ลำรู่) was declared a national park in August 1991. The park occupies an area of 150 square kilometers (58 sq mi) and covers Thai Mueang District, Kapong District, Takua Pa District, and Mueang District. The interesting attractions are: Khao Lak (เขาหลัก), which has the Chao Pho Khao Lak Shrine, Laem Pakarang (แหลมปะการัง) which has groves of pine, making it good for camping and relaxation, and Namtok Ton Chong Fa (น้ำตกโตนช่องฟ้า) or Ton Chong Fa Waterfall.[12]
- Khao Lampi–Hat Thai Mueang National Park (อุทยานแห่งชาติเขาลำปี-หาดท้ายเหมือง) The park occupies an area of 18,000 acres (7,300 ha). It was declared a national park on 14 April 1988. Interesting attractions in the park include: Namtok Lampi (น้ำตกลำปี) is a 6-tiered waterfall that runs all year round; Namtok Ton Phrai (น้ำตกโตนไพร), a huge waterfall that runs all year round; and Hat Thai Mueang (หาดท้ายเหมือง), a long beach where the Sea Turtle Festival is held annually.[13]
- Mu Ko Similan National Park (อุทยานแห่งชาติหมู่เกาะสิมิลัน) was declared a national park in 1982.[14] Similan is a group of nine islands. Off-season is 16 May–31 October.[15]

Turtle at Similan

Whale shark at Similan

Phantom Bannerfish at Similan
Gallery[]

Mu Ko Similan National Park

Limestone islets in Phangnga Bay

Limestone islets in Phangnga Bay, Ao Phangnga National Park

Emerald lagoon in Phang Nga Bay

Cardisoma carnifex at Similan Islands

Dolphins at Surin Island

Khao Lampi–Hat Thai Mueang National Park

View from Similan Island to Andaman Sea

Mai-Ngam beach, Surin Islands National Park
References[]
- ^ "ประกาศสำนักนายกรัฐมนตรี เรื่อง แต่งตั้งข้าราชการพลเรือนสามัญ" [Announcement of the Prime Minister's Office regarding the appointment of civil servants] (PDF). Royal Thai Government Gazette. 136 (Special 242 Ngor). 15. 28 September 2019. Retrieved 24 November 2019.
- ^ Advancing Human Development through the ASEAN Community, Thailand Human Development Report 2014, table 0:Basic Data (PDF) (Report). United Nations Development Programme (UNDP) Thailand. pp. 134–135. ISBN 978-974-680-368-7. Archived from the original (PDF) on 1 August 2019. Retrieved 17 January 2016, Data has been supplied by Land Development Department, Ministry of Agriculture and Cooperatives, at Wayback Machine.CS1 maint: postscript (link)
- ^ Jump up to: a b "รายงานสถิติจำนวนประชากรและบ้านประจำปี พ.ศ.2561" [Statistics, population and house statistics for the year 2018]. Registration Office Department of the Interior, Ministry of the Interior (in Thai). 31 December 2018. Retrieved 20 June 2019.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Human achievement index 2017 by National Economic and Social Development Board (NESDB), pages 1-40, maps 1-9, retrieved 14 September 2019, ISBN 978-974-9769-33-1
- ^ "Ao Phang-nga National Park". Department of National Parks (DNP) Thailand. Archived from the original on 20 October 2014. Retrieved 26 May 2015.
- ^ "About Phang Nga". Tourism Authority of Thailand (TAT). Retrieved 16 December 2018.
- ^ "ตารางที่ 2 พี้นที่ป่าไม้ แยกรายจังหวัด พ.ศ.2562" [Table 2 Forest area Separate province year 2019]. Royal Forest Department (in Thai). 2019. Retrieved 6 April 2021, information, Forest statistics Year 2019CS1 maint: postscript (link)
- ^ Mid 19th century; earliest use found in Thomas Newbold (1807–1850), army officer in the East India Company and oriental scholar. Malay: pangan, a tract of forest (Oxford Dictionaries).
- ^ Jump up to: a b "Symbol of Phang Nga". OSM Andamnan: The Office of Strategy Management for Southern Province Cluster. Retrieved 26 May 2015.
- ^ "Number of local government organizations by province". dla.go.th. Department of Local Administration (DLA). 26 November 2019. Retrieved 10 December 2019.
33 Phang Nga: 1 PAO, 2 Town mun., 13 Subdistrict mun., 36 SAO.
- ^ "Mu Ko Surin National Park". Department of National Parks (DNP) Thailand. Archived from the original on 26 May 2015. Retrieved 26 May 2015.
- ^ "Khao Lak-Lam Ru National Park". Department of National Parks (DNP) Thailand. Archived from the original on 20 April 2013. Retrieved 26 May 2015.
- ^ "Khao Lampi–Hat Thai Mueang National Park". Department of National Parks (DNP) Thailand. Archived from the original on 26 May 2015. Retrieved 26 May 2015.
- ^ "Mu Ko Similan National Park". Department of National Parks (DNP) Thailand. Archived from the original on 26 May 2015. Retrieved 26 May 2015.
- ^ "Mu Koh Similan National Park". Tourism Authority of Thailand (TAT). Retrieved 26 May 2015.
External links[]
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Phang Nga Province. |
 Phang Nga travel guide from Wikivoyage
Phang Nga travel guide from Wikivoyage- Provincial website
- Phang Nga Province
- Provinces of Thailand
- Andaman Sea
- Southern Thailand