Pine Belt (Mississippi)
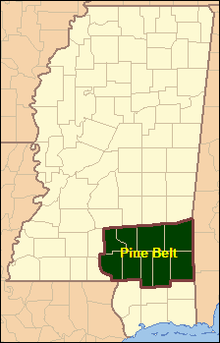
The Pine Belt, also known as the Piney Woods, is a region in Southeast Mississippi. The region gets its name from the longleaf pine trees that are abundant in the region.[1] The Pine Belt includes 9 counties: Covington, Forrest, Greene, Jefferson Davis, Jones, Lamar, Marion, Perry, and Wayne.[2]
History[]
Before the arrival of Europeans, the area that would later become the state of Mississippi was populated by several Native American tribes, including the Natchez and Pascagoula in the Pine Belt.[3][4] The population of these Native Americans declined as a result of armed conflicts with the Europeans, attrition from diseases, or coalescence with other tribes.[4][5]
In 1817, the western portion of the Mississippi Territory was admitted to the Union as the State of Mississippi. Yet, the vast longleaf pine resource in Mississippi's Pine Belt remained mostly undisturbed, because there was no efficient system for transporting cut timber to sawmills for processing into lumber. That changed in the late 1800s, when railroads were built throughout the Pine Belt. These railroads provided an inexpensive means for moving passengers as well as logs and lumber, and opened Mississippi's Pine Belt to both industrial growth and community development. Notable railway construction during this era included the Gulf and Ship Island Railroad; New Orleans and Northeastern Railroad; and the Mobile, Jackson and Kansas City Railroad.[6] The Pine Belt's booming timber industry ended around 1930, when the virgin pine forests were depleted.[6]
As World War I raged in Europe, military training sites were being created throughout the United States.[7] As part of that effort, one of those training sites was established in the Pine Belt south of Hattiesburg in 1917. Over time, that training site transformed into Camp Shelby Joint Forces Training Center.[1] Camp Shelby is the largest state owned military training facility in the United States and covers more than 134,000 acres (54,000 ha).[8][9]
Geography[]
The Pine Belt has a population of 306,417 as of 2019,[10] and an area of about 5,200 mi2 (13,400 km2). In the U.S. House of Representatives, the area is split between Mississippi's 3rd and 4th congressional districts.
Principal cities and towns[]
Education[]
- Universities
- The University of Southern Mississippi
- William Carey University
- Community colleges
- Pearl River Community College
- Jones County Junior College
- Southwest Mississippi Community College
- Copiah-Lincoln Community College
Media[]
- Newspapers, magazines, and journals
- Laurel Leader-Call
- Hattiesburg American
- The Times
- Enterprise-Journal
- Television
Transportation[]
- Airports
- Hattiesburg-Laurel Regional Airport
- Interstates
- Highways
- U.S. Highway 11
- U.S. Highway 49
- U.S. Highway 84
- U.S. Highway 98
Notable people[]
- Bo Diddley
- Brett Favre
- Ray J
- Steve McNair
- Gerald McRaney
- Stevon Moore
- Brandy Norwood
- Walter Payton
- Leontyne Price
- Britney Spears
- Taylor Spreitler
- Sela Ward
- Johnny Welch
See also[]
- Belt regions of the United States
- Mississippi Gulf Coast
References[]
- ^ a b "The Pine Belt | U.S. Congressman Steven Palazzo". palazzo.house.gov. Retrieved 2021-07-17.
- ^ "Regions | Senator Cindy Hyde-Smith". www.hydesmith.senate.gov. Retrieved 2021-07-17.
- ^ "Where Is The Mississippi Pine Belt?". WorldAtlas. Retrieved 2021-07-18.
- ^ a b "MS Archaeology Trails|Indian Tribes of Mississippi". trails.mdah.ms.gov. Retrieved 2021-07-18.
- ^ Barnett, Jim (August 2000). "The Natchez Indians|Mississippi History Now". www.mshistorynow.mdah.ms.gov. Retrieved 2021-07-18.
- ^ a b Howe, Tony (May 2001). "Growth of the Lumber Industry, (1840 to 1930) | Mississippi History Now". web.archive.org. Retrieved 2021-07-18.
- ^ Garamone, Jim (March 29, 2017). "World War I: Building the American Military". U.S. Department of Defense. Retrieved 2021-07-18.
- ^ "Camp Shelby Army Base in Hattiesburg, MS | MilitaryBases.com". Military Bases. Retrieved 2021-07-17.
- ^ "Camp Shelby Joint Forces Training Center". ms.ng.mil. Retrieved 2021-07-17.
- ^ Pine Belt Region vs. Mississippi Comparative Trends Analysis: Population Growth and Change, 1969-2019 at Mississippi Regional Economic Analysis Project
Coordinates: 31°07′22″N 88°56′12″W / 31.122799°N 88.936746°W
- Regions of Mississippi
- Natural history of Mississippi
- Belt regions of the United States

