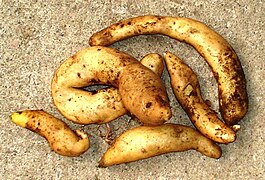Potatoes of Chiloé

The Chiloé Archipelago is home to a wide variety of potatoes. After the Titicaca region of Peru and Bolivia, it is the geographical nucleus where the most different types of potatoes are found. Evidence ranging from historical records, local agriculturalists, and DNA analyses strongly supports the hypothesis that the most widely cultivated variety of potato worldwide, Solanum tuberosum tuberosum, is indigenous to the Chiloé Archipelago, and has been cultivated by the local indigenous people since before the Spanish conquest.[1][2] Contrary to potatoes from Peru and Bolivia the potatoes of Chiloé are adapted to the long-day conditions prevalent in the higher latitude region of southern Chile.[1][3] After the disastrous European Potato Failure in the 1840s strains originating in the Chiloé Archipelago replaced earlier potatoes of Peruvian origin in Europe.[3]
The potatoes of Chiloé are important elements of folk medicine and features in Chilote mythology.[3]
Historian Renato Cárdenas and botanist Carolina Villagrán counted about "300 names used for potatoes grown in Chiloé at different times".[4] Local varieties include Bruja morada,[5] Camota,[6] Chochoca,[3] Clavela lisa,[3] Güencha,[7] Pachacoña,[8] Caballera,[9] Cabrita,[citation needed] Cabra,[10] Michuñe Azul,[5][10] Michuñe negra,[3] Michuñe roja,[5][10] Huicaña,[11] Viscocha.[3]
Some potatoes varieties developed abroad have also been introduced to Chiloé, but not all of these have been successful in adapting, despite their putative high yields.[4] The coraíla variety introduced by Servando Coraíl was dominant in the mid-20th century. Yet cultivation of this foreign variety was discontinued when the cultivar was repeatedly struck by the potato blight in the 1950s and 1960s.[4]
Preservation efforts of the many varieties begun in the 1960s when agronomist Andrés Contreras travelled Chiloé Archipelago in search of small gardens where local elderly women had grown potatoes over many generations.[3] At present Austral University of Chile in Valdivia hosts a gene bank of the potatoes of Chiloé.[3]
Guaitecas Archipelago[]
Some of the potatoes of Chiloé also grow in the wild in Guaitecas Archipelago, although there is some uncertainty as to when and how potatoes arrived there.[12] The Guaitecas Archipelago formed the southern limit of Pre-Hispanic agriculture[13] as noted by the mention of the cultivation of potatoes by a Spanish expedition in 1557.[12] Later during the second voyage of HMS Beagle, Charles Darwin collected potatoes from Guaitecas.[12]
Potatoes grow beside the sea in a herbaceous zone. The wild potatoes that grow in the archipelago are mostly found in its western part. Apparently these potatoes do not reproduce by seeds and rarely produce flowers and fruits.[12] Potatoes grow in zones of disturbance, mainly in the herbaceous zone near the coast that is affected by winter storms.[12]
Guadachos variety
Michuñe Blanca variety
Michuñe Roja variety
References[]
- ^ Jump up to: a b Solano Solis, Jaime; Morales Ulloa, Daniza; Anabalón Rodríguez, Leonardo (July 2007). "Molecular description and similarity relationships among native germplasm potatoes (Solanum tuberosum ssp. tuberosum L.) using morphological data and AFLP markers". Electronic Journal of Biotechnology. 10 (3): 436–443. doi:10.2225/vol10-issue3-fulltext-14. hdl:10925/320. Retrieved 6 December 2009.
- ^ Using DNA, scientists hunt for the roots of the modern potato, January 2008
- ^ Jump up to: a b c d e f g h i Johanson, Mark (August 28, 2020). "Mash hits: the land that spawned the supermarket spud". The Economist. Retrieved September 1, 2020.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c Cárdenas & Villagrán 2005, p. 26.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c Ortiz, Bernardita (September 16, 2019). "El ingrediente: papa chilota". La Tercera (in Spanish). Retrieved September 2, 2020.
- ^ Cárdenas & Villagrán 2005, p. 109.
- ^ Cárdenas & Villagrán 2005, p. 172.
- ^ Cárdenas & Villagrán 2005, p. 263.
- ^ Cárdenas & Villagrán 2005, p. 102.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c Effect of the storage temperature and time on native potato quality
- ^ Cárdenas & Villagrán 2005, p. 186.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c d e Contreras, Andrés; Ciampi, Luigi; Padulosi, Stefano; Spooner, David M. (1993). "Potato germplasm collecting expedition to the Guaitecas and Chonos Archipelagos, Chile, 1990". Potato Research. 36 (4): 309–316. doi:10.1007/BF02361797.
- ^ Bird, Junius (1946). "The Alacaluf". In Steward, Julian H. (ed.). Handbook of South American Indians. Bulletin 143. I. –Bureau of American Ethnology. pp. 55–79.
- Bibliography
- Cárdenas Álvarez, Renato; Villagrán Moraga, Carolina (2005). Chiloé: Botánica de la cotidaniedad (in Spanish).
- Potato cultivars
- Crops originating from Chile
- Agriculture in Chile
- Chiloé Archipelago
- Chilean cuisine
- Indigenous culture of the Southern Cone
- Chile stubs
- Potato stubs