Propyl gallate
| |
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
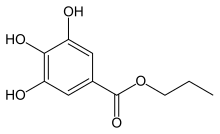
Propyl 3,4,5-trihydroxybenzoate
| |
| Other names
Gallic acid, propyl ester
n-Propyl gallate E310 | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.004.090 |
| EC Number |
|
| E number | E310 (antioxidants, ...) |
| MeSH | Propyl+Gallate |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C10H12O5 | |
| Molar mass | 212.20 g/mol |
| Appearance | White crystalline powder |
| Melting point | 150 °C (302 °F; 423 K) |
| Boiling point | Decomposes |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Propyl gallate, or propyl 3,4,5-trihydroxybenzoate is an ester formed by the condensation of gallic acid and propanol. Since 1948, this antioxidant has been added to foods containing oils and fats to prevent oxidation.[1] As a food additive, it is used under the E number E310.
Description[]
Propyl gallate is an antioxidant. It protects against oxidation by hydrogen peroxide and oxygen free radicals.
Uses[]
Propyl gallate is used to protect oils and fats in products from oxidation; it is used in foods, cosmetics, hair products, adhesives, and lubricants.
It is used as a triplet state quencher and an antioxidant in fluorescence microscopy.[2]
Biological effects[]
A 1993 study in fat rodents found little or no effect on carcinogenesis by propyl gallate.[3]
A 2009 study found that propyl gallate acts as an estrogen antagonist.[4]
References[]
- ^ "Final Report on the Amended Safety Assessment of Propyl Gallate". International Journal of Toxicology. 26 (suppl. 3): 89–118. 2007. doi:10.1080/10915810701663176. ISSN 1091-5818. PMID 18080874. S2CID 39562131.
- ^ Jerker Widengren; Andriy Chmyrov; Christian Eggeling; Per-Åke Löfdahl & Claus A. M. Seidel (2007). "Strategies to Improve Photostabilities in Ultrasensitive Fluorescence Spectroscopy". The Journal of Physical Chemistry A. 111 (3): 429–440. doi:10.1021/jp0646325. PMID 17228891.
- ^ Hirose, Masao, et al. "Modification of carcinogenesis by α-tocopherol, t-butylhydro-quinone, propyl gallate and butylated hydroxytoluene in a rat multi-organ carcinogenesis model." Carcinogenesis 14.11 (1993): 2359-2364.
- ^ Alessio Amadasi; Andrea Mozzarelli; Clara Meda; Adriana Maggi; Pietro Cozzini (2009). "Identification of Xenoestrogens in Food Additives by an Integrated in Silico and in Vitro Approach". Chem. Res. Toxicol. 22 (1): 52–63. doi:10.1021/tx800048m. PMC 2758355. PMID 19063592.
- Antioxidants
- Carboxylate esters
- Food antioxidants
- Pyrogallols
- E-number additives