Protocol pipelining
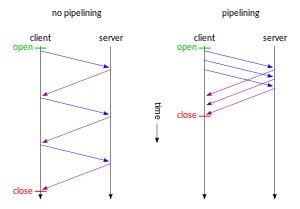
Schema of non-pipelined vs. pipelined connection.
Protocol pipelining is a technique in which multiple requests are written out to a single socket without waiting for the corresponding responses. Pipelining can be used in various application layer network protocols, like HTTP/1.1, SMTP and FTP.
The pipelining of requests results in a dramatic improvement in protocol performance, especially over high latency connections (such as satellite Internet connections). Pipelining reduces waiting time of a process.
See also[]
External links[]
- HTTP/1.1 Pipelining FAQ at mozilla.org
- "Network Performance Effects of HTTP/1.1, CSS1, and PNG" at w3.org
- FTP pipelining
- RFC 2920 SMTP Service Extension for Command Pipelining (STD 60)
Categories:
- Network protocols
- Computer network stubs