Pterosaur size
Pterosaurs included the largest flying animals ever to have lived. They are a clade of prehistoric archosaurian reptiles closely related to dinosaurs. Species among pterosaurs occupied several types of environments, which ranged from aquatic to forested. Below is a list that comprises the largest pterosaurs known as of 2016.
The smallest known pterosaur is Nemicolopterus with a wingspan of about 25 cm (10 in).[1] The specimen found may be a juvenile or a subadult, however, and adults may have been larger.
Pterosaurs with largest wingspan[]
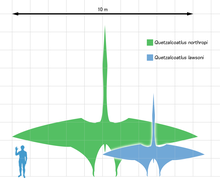
This is a list of pterosaurs with estimated maximum wingspan of more than 5 metres (16 feet):
- Arambourgiania philadelphiae7–13 m (23–43 ft)[2][3]
- Quetzalcoatlus northopi10–11 m (33–36 ft)[4][5]
- Hatzegopteryx thambema 10–11 m (33–36 ft)[4]
- Cryodrakon boreas 10 m (33 ft)[citation needed]
- Undescribed specimen from Mongolia 10 m (33 ft)[6][7]
- Undescribed specimen UNCUYO-LD 350 9.1 m (30 ft)[8]
- Tropeognathus mesembrinus 8.2 m (27 ft)[9]
- Geosternbergia maysei 7.25 m (24 ft)[10]
- Coloborhynchus capito 7 m (23 ft)[11]
- Moganopterus zhuiana 7 m (23 ft)[12]
- Thapunngaka shawi 7 m (23 ft)[13]
- Pteranodon longiceps 6.25 m (20.5 ft)[10]
- Tupuxuara longicristatus 6 m (20 ft)[14]
- Santanadactylus araripensis 5.7 m (19 ft)[15]
- Cearadactylus atrox 5.5 m (18 ft)[15]
- Caulkicephalus trimicrodon 5 m (16 ft)[16]
- Istiodactylus latidens 5 m (16 ft)[15]
- Lacusovagus magnificens 5 m (16 ft)[17]
- Liaoningopterus gui 5 m (16 ft)[citation needed]
- Phosphatodraco mauritanicus 5 m (16 ft)
- Anhanguera sp. 4.5 m (15 ft)[18]
Speculation about pterosaur size and flight[]
Some species of pterosaurs grew to very large sizes and this has implications for their capacity for flight. Many pterosaurs were small but the largest had wingspans which exceeded 9 m (30 ft). The largest of these are estimated to have weighed 250 kilograms (550 lb). For comparison, the wandering albatross has the largest wingspan of living birds at up to 3.5 m (11 ft) but usually weighs less than 12 kilograms (26 lb). This indicates that the largest pterosaurs may have had higher wing loadings than modern birds (depending on wing profile) and this has implications for the manner in which pterosaur flight might differ from that of modern birds.
Factors such as the warmer climate of the Mesozoic or higher levels of atmospheric oxygen have been proposed but it is now generally agreed that even the largest pterosaurs could have flown in today's skies.[19] Partly, this is due to the presence of air sacs in their wing membranes,[20] and that pterosaurs launched into flight using their front limbs in a quadrupedal stance similar to that of modern bats, a method faster and less energy taxing than the bipedal launching of modern birds.[21][22]
See also[]
References[]
- ^ Wang, X.; Kellner, A.W.A.; Zhou, Z.; Campos, D.A. (2008). "Discovery of a rare arboreal forest-dwelling flying reptile (Pterosauria, Pterodactyloidea) from China". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. 105 (6): 1983–1987. Bibcode:2008PNAS..105.1983W. doi:10.1073/pnas.0707728105. PMC 2538868. PMID 18268340.
- ^ Frey, E.; Martill, D.M. (1996). "A reappraisal of Arambourgiania (Pterosauria, Pterodactyloidea): One of the world's largest flying animals". Neues Jahrbuch für Geologie und Paläontologie - Abhandlungen. 199 (2): 221–247. doi:10.1127/njgpa/199/1996/221.
- ^ Pereda-Suberbiola, X., Bardet, N., Jouve, S., Iarochène, M., Bouya, B. and Amaghzaz, M. (2003). "A new azhdarchid pterosaur from the Late Cretaceous phosphates of Morocco." In: Buffetaut, E. and Mazin, J.-M. (eds.), Evolution and Palaeobiology of Pterosaurs. Geological Society of London, Special Publications, 217. p.87
- ^ Jump up to: a b Witton, Mark P.; Martill, David M.; Loveridge, Robert F. (2010). "Clipping the Wings of Giant Pterosaurs: Comments on Wingspan Estimations and Diversity". Acta Geoscientica Sinica. 31 (Supp 1): 79–81.
- ^ Witton, M.P.; Naish, D. (2008). "A Reappraisal of Azhdarchid Pterosaur Functional Morphology and Paleoecology". PLOS ONE. 3 (5): e2271. Bibcode:2008PLoSO...3.2271W. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0002271. PMC 2386974. PMID 18509539.
- ^ Tsuihiji, T., B. Andres, P. M. O'Connor, M. Watabe, K. Tsogtbaatar, and B. Mainbayar (2017). Gigantic pterosaurian remains from the Upper Cretaceous of Mongolia. Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology. doi: 10.1080/02724634.2017.1361431.
- ^ "Ancient Winged Terror Was One of the Largest Animals to Fly". 2017-10-31.
- ^ Leonardo D. Ortiz David, Bernardo J. González Riga & Alexander W. A. Kellner (2017). Discovery of the largest pterosaur from South America. Cretaceous Research (advance online publication); doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cretres.2017.10.004
- ^ Kellner, A. W. A.; Campos, D. A.; Sayão, J. M.; Saraiva, A. N. A. F.; Rodrigues, T.; Oliveira, G.; Cruz, L. A.; Costa, F. R.; Silva, H. P.; Ferreira, J. S. (2013). "The largest flying reptile from Gondwana: A new specimen of Tropeognathus cf. T. Mesembrinus Wellnhofer, 1987 (Pterodactyloidea, Anhangueridae) and other large pterosaurs from the Romualdo Formation, Lower Cretaceous, Brazil". Anais da Academia Brasileira de Ciências. 85 (1): 113–135. doi:10.1590/S0001-37652013000100009. PMID 23538956.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Benton, S.C. (1994). "The Pterosaurs of the Niobrara Chalk". The Earth Scientist. 11 (1): 22–25.
- ^ Martill, D.M.; Unwin, D.M. (2011). "The world's largest toothed pterosaur, NHMUK R481, an incomplete rostrum of Coloborhynchus capito (Seeley 1870) from the Cambridge Greensand of England". Cretaceous Research. 34: 1–9. doi:10.1016/j.cretres.2011.09.003.
- ^ Lü Junchang; Pu Hanyong; Xu Li; Wu Yanhua; Wei Xuefang (2012). "Largest Toothed Pterosaur Skull from the Early Cretaceous Yixian Formation of Western Liaoning, China, with Comments On the Family Boreopteridae". Acta Geologica Sinica. 86 (2): 287–293. doi:10.1111/j.1755-6724.2012.00658.x.
- ^ Timothy M. Richards; Paul E. Stumkat; Steven W. Salisbury (2021). "A new species of crested pterosaur (Pterodactyloidea, Anhangueridae) from the Lower Cretaceous (upper Albian) of Richmond, North West Queensland, Australia". Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology. doi:10.1080/02724634.2021.1946068.
- ^ Unwin, David M. (2006). The Pterosaurs: From Deep Time. New York: Pi Press. p. 246. ISBN 0-13-146308-X.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c Wellnhofer, P. (1991). The Illustrated Encyclopedia of Pterosaurs. New York: Barnes and Noble Books. pp. 124. ISBN 0-7607-0154-7.
- ^ Steel, L.; Martill, D.M.; Unwin, D.M.; Winch, J. D. (2005). "A new pterodactyloid pterosaur from the Wessex Formation (Lower Cretaceous) of the Isle of Wight, England". Cretaceous Research. 26 (4): 686–698. doi:10.1016/j.cretres.2005.03.005.
- ^ Witton, M.P. (2008). "A new azhdarchoid pterosaur from the Crato Formation (Lower Cretaceous, Aptian?) of Brazil". Palaeontology. 51 (6): 1289–1300. doi:10.1111/j.1475-4983.2008.00811.x.
- ^ Aureliano, T.; Ghilardi, A.; Duque, R.; Barreto, A. (2014). "ON THE OCCURRENCE OF PTEROSAURIA IN EXU, PERNAMBUCO (LOWER CRETACEOUS ROMUALDO FORMATION, ARARIPE BASIN), NORTHEASTERN BRAZIL". Estudos Geológicos. 24 (2): 15–27. doi:10.18190/1980-8208/estudosgeologicos.v24n2p15-27.
- ^ Witton, Mark P. (2013). Pterosaurs: Natural History, Evolution, Anatomy. Princeton University Press. ISBN 0691150613.
- ^ Claessens, Leon P. A. M.; O'Connor, Patrick M.; Unwin, David M. (February 18, 2009). "Respiratory Evolution Facilitated the Origin of Pterosaur Flight and Aerial Gigantism". PLOS ONE. 4 (3): e4497. Bibcode:2009PLoSO...4.4497C. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0004497. PMC 2637988. PMID 19223979.
- ^ Fox, Stuart (May 1, 2009). "How Giant Pterosaurs Took Flight". Scientific American. Retrieved July 11, 2014.
- ^ Witton, Mark P. (2013). Pterosaurs: Natural History, Evolution, Anatomy. Princeton University Press. ISBN 0691150613.
External links[]
- Pterosaurs
- Animal size
