Second Treaty of Brömsebro (1645)
| Type | Bilateral treaty |
|---|---|
| Signed | 13 August 1645 |
| Location | Brömsebro, Denmark |
| Original signatories | |
| Ratifiers |
|
The Second Treaty of Brömsebro (or the Peace of Brömsebro) was signed on 13 August 1645, and ended the Torstenson War, a local conflict that began in 1643 (and was part of the larger Thirty Years' War) between Sweden and Denmark-Norway. Negotiations for the treaty began in February the same year.
Location[]
The eastern border between the then Danish province of Blekinge and the Swedish province of Småland was formed by the creek Brömsebäck. In this creek lies an islet that was connected to the Danish and Swedish riversides by bridges. On the islet was a stone that was supposed to mark the exact border between the two countries. By this stone, the delegates met to exchange greetings and, at the end of the negotiations, the signed documents.[1] The Danish delegation stayed in Kristianopel while the Swedish side had their accommodation in Söderåkra.[2]
Delegations[]
Sweden's highest ranking representative was Lord High Chancellor Axel Oxenstierna. He was accompanied by, among others, Johan Skytte, who died during the negotiations and was replaced by Ture Sparre.[2]
Corfitz Ulfeldt and Chancellor Christen Thomesen Sehested were the chief negotiators of the Danish delegation.[2]
The French diplomat Gaspard Coignet de la Thuillerie was head mediator and observers from the Hanseatic League, Portugal, Stralsund and Mecklenburg followed the negotiations.[2]
Results[]
The military strength of Sweden ultimately forced Denmark-Norway to give in to Swedish demands.
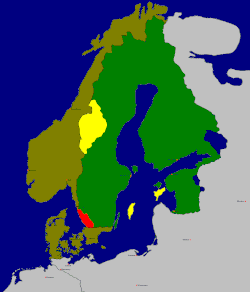
- Denmark-Norway ceded the Norwegian provinces of Jämtland and Härjedalen as well as the Danish Baltic Sea islands of Gotland and Ösel. The Norwegian regions Idre & Särna were conquered by Dalecarlian peasants at the suggestion of the Swedish government. The concession of this region was not formally recognised until 1751.
- The Danish heir to the throne, Frederick II Administrator of the Prince-Bishopric of Verden (1634-1645) and of the Prince-Archbishopric of Bremen (1635-1645), had to resign, with the two prince-bishoprics being occupied by the Swedes.
- Sweden was exempted from the Sound Dues, a toll on foreign ships passing through Danish waters into the Baltic Sea, and Hamburg was exempted from the “Elbe dues”, a toll levied until then on ships to that city by the Prince-Archbishopric of Bremen.
- Sweden received the Danish province of Halland for a period of 30 years as a guarantee of these provisions.
The treaty was to be followed by the Treaty of Roskilde of 1658, which forced Denmark-Norway to further concessions.
See also[]
- dominium maris baltici
- First Treaty of Brömsebro (1541)
- List of Swedish wars
- List of Danish wars
- List of treaties
Notes[]
References[]
- History of the Norwegian People by Knut Gjerset, The MacMillan Company, 1915, Volume I.
- Nordens Historie, ved Hiels Bache, Forslagsbureauet i Kjøbenhavn, 1884.
- The Struggle for Supremacy in the Baltic: 1600-1725 by Jill Lisk; Funk & Wagnalls, New York, 1967.
- Peace treaties of Sweden
- Peace treaties of Denmark
- 1645 in Denmark
- 1645 treaties
- Treaties of the Swedish Empire
- Treaties of Denmark–Norway
- 1645 in Sweden