Son preference in China
Son preference in China is a gender preference issue. Preference of sons can be explained by an attitude: a belief that boys have more value than girls; it can be defined as a gender bias as well.[1] This phenomenon in China can be shown in gender sex ratio.[2] Moreover, Chinese son preference can be connected to a variety of reasons. The majority of men are naturally superior to women in terms of physical strength. In the early stage of human evolution, greater physical strength means more sources of food and more survival opportunities in tribal warfare. Majority of investments shows that the financial support that parents receive after their child’s marriage is significantly affected by their child’s gender.[3] This can be one of the reasons that Chinese parents are more willing to have a son. Furthermore, Chinese agrarian society influences sex preference deeply as well. It is obvious that agriculture needs physical strength in a primitive agricultural society. Thus, the long run agriculture society in China can explain this phenomenon. Although the Chinese patriarchal thinking can be traced back thousands of years, with the development of the Chinese economy, this concept potential gradually disintegrates.[4]
History[]
The origin of Chinese son preference can be related to the beginning of Chinese patriarchic society.[5] Agriculture can be a key to understand the Chinese son preference history.[6] For thousands of years in China, most of the Chinese preferred sons rather than daughters because majority of males have more ability to earn more than girls, especially in agrarian economies. When human society enters the patriarchal society from the matriarchal society, men gradually occupy a dominant position in social production. People cannot leave men in hunting, animal husbandry, plowing or even snoring.[7] In most of the religious aspects, males can continue the family line; in financial factor, most of the Chinese older generation believe that girls typically have no responsibility for their parents when they marry.[8] The ethical thoughts of male superiority and female sorrow have existed in the patriarchal society. With the development of feudal ethics, this viewpoint has gradually developed and deepened into the hearts of the people.[7]
Sex selection was operated through ultrasound screenings and abortions during the 1980s and ’90s, but laws and regulations enacted since 2001 have forbidden hospitals from carrying out the procedure.[citation needed]
Reasons[]
Agrarian society[]
The agrarian society is based on producing and maintaining crops and farmland. Agrarian society in China is one of the factors that impact Chinese son preference. Before the globalisation, during Song, Ming and Qing dynasty, China was trapped in an agrarian society period.[9] Obviously, the majority of works in agriculture must utilize males’ strength. Although the expansionary of urbanisation has increased in recent decades in China, agriculture still has impact on gender bias in this country.[10] The Chinese social culture cannot be changed easily. Despite the fact that China has developed its economics rapidly, majority of farmers who move from rural area to urban city still hold the son preference value; in Chinese social culture, sons should take more responsibility to take on households.[11]
Financial security[]
Financial security is a reason that affects sex preference in China. In Chinese social culture, in older generation concepts, once a girl is married with her husband, she will belong to the husbands family, which means she will not have the responsibility to take care of her parents anymore; thus, their parents will have worried who can take care of them if their daughter got married.[12] In general, the majority of traditional Chinese societies culture concept believes that sons can take responsibility for their family, instead of girls.[13] In other words, traditionally, the blood of the family has been inherited by the male side. After the woman married, she joined her husbands family and took care of her in-laws rather than her parents. For a long period of time, "nurturing children to prevent old age" is the iron law of people's trust. In contrast, from several Chinese opinions, raising a daughter becomes a waste. Some Chinese Sociologists even point out from the perspective of society, it is not rational to be patriarchal, but for individuals, this is still a wise choice.[4] In recent years, Chinese population became larger. Therefore, Chinese government advanced the ‘one child policy’ in order to dominate the large population in 1979.[14] With the developing technology, Chinese parents may know their childs sex, they potentially use the sex-selection abortion to make sure they have boys. In Chinese older generations opinions, they potentially will get financial support even if their sons are getting married.[15]
Traditional Chinese folk religion[]

Son preference in rural China has some affect by traditional Chinese folk religion. Such folk religion may overlap with an individual's belief in Buddhism, Taoism, Confucianism, or other traditional Chinese religions.[16] It is widely known that the majority of Chinese hold Confucianism as their core value religion in ancient China; patriarchy is a part of value included by Confucianism. In general, the preference of son basically is strongly command in country which holds Confucianism.[17] Confucianism brings heaved burden on Chinese women. In Chinese traditional confusion families, husband and other family members have more statues than wives. Chinese wives paramount responsibility is to look after and serve the household, including to do all the housework.[18] Furthermore, the ancestor worship underlined by the Chinese folk religion as well.[19] Besides, Chinese ancestor worship emphasizes the filial piety. One of the filial method is to continue the family line in China. Passing on the genealogy is one of the method to continue the family. However, in Chinese old generation concepts, family’s genealogy will be interrupted if they don’t have sons.[20] Moreover, the inability to bear a son can become a potential factor for divorce a some couples.
Consequences[]
The sex ratio of birth (SRB) is defined as the ratio of the new born male infants to every 100 girls.[21] It is demonstrated that China has always reported high SRBs during the past decades because of the effect of preference to sons, and there would possibly be a lack of women in the whole society of China for next 20 years, as a shortage of women was estimated to be faced. Interestingly, people in China who are unable to be married or single for a long time are generally called 'guang gun (single)', meaning 'bare branches'.[21][22] According to the reality of male excess female, majority of consequences can be assumed. Firstly, the sexual frustration and psychosocial vulnerability may come together to these males and let them become violent and aggressive.[23] To be clear, the reason is that they can’t through achieve marriage and bear a child to meet the Chinese traditional expectations.[24] Although it just a consumption, this prediction has a good empirical to support: the cross-culture evidences illustrate that majority of criminal planner and murderers were low status and unmarried males.[25] They may turn to anti-social organizations, threatening social stability and security, since they do not behave in current social order.[26] Therefore, male surplus is a trepidation issues which should be concerned. Nevertheless, the evidence is not strong enough to proof the prediction that they are prone on crime though majority of the unmated males are easy to tend to become depression. Furthermore, excess male has stimulate the phonograph industry as well. Majority of data illustrate that the sex industry is experiencing expansionary in current decades.[27][28] However, the consequence of increasing the sex workers as increasing sex ratio can’t be proved. According to some research, the main reason for increasing the sex workers in China can be related to Chinese domestic socioeconomic inequality.[28]
Some positive consequence may affect since high sex ratio on marriage of males in China. Basically, the women status will develop gradually. Clearly, the sex preference may rise the Fertility needs. The mortality rate of girls will decrease as gender discrimination decreases.[29] Minority of article argues that sex imbalance is a way to control Chinese large population.[30] Furthermore, with the decreasing number of women in society, their value will be increased. Thus, their status increases as well. Developing the woman status may let son preference decreased potentially.[31] The issue of women’s rights and patriarchal issues has also become a major concern of the representatives of the Chinese National Committees in 2017. In recent years, the Chinese government has always attached great importance to the rights and interests of women, especially the series of targeted measures taken in recent years to significantly improve the status of women.[32]
Chinese one-child policy[]
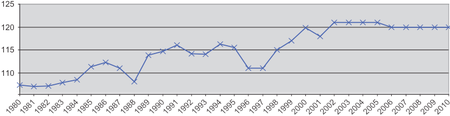

The Chinese one-child policy (instituted from 1979 to 2016) contributed to sex imbalance in China as well. The policy penalized families who had more than one child. The original intention of this policy was to control the growth rate of Chinese large population. Although this policy was introduced as a long term and temporary policy and aimed to reduce the number of family members, this measure was not uniform to some extent. In the early 1980s, the sex ratio of births was 108 (the ratio of male to female was 108:100), slightly higher than the natural level; by 2000, this number had risen to 120, with some provinces such as Anhui, Jiangxi, and Shaanxi reaching 130.[4] Compared to the natural level, this meant 35 million fewer girls were born than would be biologically expected.[4] Although countries like India face similar imbalances, China's gap is the largest, mostly due to the one child policy.[4]
The Chinese government tried to counteract these developments by compensating families who only had a girl and, in some rural areas, allowing them to have a second child if the first was a girl. This however led to further reinforcement of the idea that boys were more valuable.[33]
See also[]
The United Nations proposes improvements in gender equality in China. Son preference in China has also attracted social or international attentions. The gender imbalance in Chinese-born babies is a problem that has plagued China in recent years and has been a concern of the UN Committee on the Elimination of Discrimination against Women. In the conclusion, the Commission made some constructive suggestions. The Committee recommends that China conduct compulsory gender equality education for family planning officials and recommend that China address the tendency to be patriarchal in rural areas and address the root causes of patriarchal attitudes in rural areas. To solve the negative consequences of the one-child policy, the specific recommendations of this committee is to expand the benefit of public in rural areas, especially rural women, by expanding the insurance system and pensions in China. In addition, with efforts of various government departments in China, nowadays, more and more people can treat boys and girls equally.[34]
References[]
- ^ "Son preference". 2018.
- ^ Seager, Joni (2009). The Penguin Atlas of Women in the World. New York: New York: Penguin Group. p. 42.
- ^ Li, Shuzhuo; Feldman, Marcus W.; Jin, Xiaoyi (2004). "Children, Marriage Form, and Family Support for the Elderly in Contemporary Rural China". Research on Aging. 26 (3): 352–384. doi:10.1177/0164027503262477. ISSN 0164-0275. S2CID 145583711.
- ^ a b c d e "中国的性别危机". www.chinadialogue.net. 22 December 2011. Retrieved 2018-11-08.
- ^ Jezebel, Anna. "In Chinese "Matriarchal" Society, Women Do All The Work".
- ^ Wittogel, K. "Agricultural: a key to understand of Chinese society past and present" (PDF).
- ^ a b Branigan, Tanin (2011-11-02). "China's great gender crisis". Support the Guardian.
- ^ Wen, Guanzhong James (2011). "Sex selection". Frontiers of Economics in China. 6 (4): 507–534. doi:10.1007/s11459-011-0145-1. S2CID 56038914.
- ^ James, Wen, Guanzhong (2011). "Why Was China Trapped in an Agrarian Society? An Economic Geographical Approach to the Needham Puzzle [post-print]". Trinity College Digital Repository.
- ^ Simpson, P (2012). "China's urban population exceeds rural for first time ever". The Telegraph.
- ^ Wang, Wendy (2005). "Son preference and educational opportunities of children in China— "I wish you were a boy!"". Gender Issues. 22 (2): 3–30. doi:10.1007/s12147-005-0012-4. ISSN 1098-092X. S2CID 144531015.
- ^ Graham, Maureen J.; Larsen, Ulla; Xu, Xiping (1998). "Son Preference in Anhui Province, China". International Family Planning Perspectives. 24 (2): 72–77. doi:10.2307/2991929. JSTOR 2991929.
- ^ Parish, William L.; Whyte, Martin King (1980-08-15). Village and Family in Contemporary China. University of Chicago Press. ISBN 9780226645919.
- ^ Li, Jiali; Cooney, Rosemary Santana (1993). "Son preference and the one child policy in China: 1979?1988". Population Research and Policy Review. 12 (3): 277–296. doi:10.1007/bf01074389. ISSN 0167-5923. S2CID 153780904.
- ^ Isabelle, Attané. "The Demographic Masculinization of China: Hoping for a Son". Canadian Studies in Population.
- ^ Pike, John. "Traditional Chinese Religion". www.globalsecurity.org. Retrieved 2018-10-18.
- ^ Arnold, Fred; Zhaoxiang, Liu (1986). "Sex Preference, Fertility, and Family Planning in China". Population and Development Review. 12 (2): 221–246. doi:10.2307/1973109. JSTOR 1973109.
- ^ Zhang, Liu. "The Confucian Ethic of Female Subordination and Depression Among Young People in Rural China". ProQuest 1346906003. Cite journal requires
|journal=(help) - ^ "Village context, women's status, and son preference among rural Chinese women". Rural Sociology. 68: 88. ProQuest 199339943.
- ^ "Filial Piety (孝) in Chinese Culture". The Greater China Journal. 2016-03-14. Retrieved 2018-10-18.
- ^ a b "How serious is son preference in China?". ScienceDaily. Retrieved 2018-10-18.
- ^ Hesketh, Therese; Lu, Li; Xing, Zhu Wei (2011-09-06). "The consequences of son preference and sex-selective abortion in China and other Asian countries". CMAJ : Canadian Medical Association Journal. 183 (12): 1374–1377. doi:10.1503/cmaj.101368. ISSN 0820-3946. PMC 3168620. PMID 21402684.
- ^ Barber, N (2000). The sex ratio as a predictor of cross-national variation in violent crime. Cross-Cultural Res.
- ^ Hudson, V. "A surplus of men, a deficit of peace". Int Secur. 26 (5): 38.
- ^ Messner, SF (1991). "The sex ratio, family disruption and rates of violent crime: the paradox of demographic structure". Soc Forces. 69 (3): 693–713. doi:10.2307/2579470. JSTOR 2579470.
- ^ Hudson, V (2002). "A surplus of men, a deficit of peace" (PDF). Int Secur. 26: 5–38. doi:10.1162/016228802753696753. S2CID 57568336.
- ^ Dandona, R; Dandona, L; Kumar, GA; Gutierrez, JP; McPherson, S; Samuels, F; Bertozzi, SM (2016). "Demography and sex work characteristics of female sex workers in India". ASCI FPP Study Team. 6: 5. doi:10.1186/1472-698X-6-5. PMC 1468426. PMID 16615869.
- ^ a b Tucker, JD; Henderson, GE; Wang, TF; Huang, YY; Parish, W; Pan, SM; Chen, XS; Cohen, MS (2005). "Surplus men, sex work, and the spread of HIV in China". AIDS. 19 (6): 539–47. doi:10.1097/01.aids.0000163929.84154.87. PMID 15802971. S2CID 32792732.
- ^ Goodkind, D (1996). "On substituting sex ratio strategies in east Asia: Does prenatal sex selection reduce postnatal discrimination?". Popul Dev Rev. 22 (111): 25. doi:10.2307/2137689. JSTOR 2137689.
- ^ Arnold, F (1987). "The effect of sex preference on fertility and family planning: empirical evidence". Popul Bull UN (23–24): 55. PMID 12315521.
- ^ Branigan, Tania (2011-11-02). "China's great gender crisis". The Guardian. Retrieved 2018-10-18.
- ^ "53.9%受访者称家乡重男轻女现象减轻 农村仍较重-新华网". www.xinhuanet.com. Retrieved 2018-11-08.
- ^ "How serious is son preference in China?". EurekAlert!. Retrieved 2018-11-08.
- ^ "联合国提出中国两性平等方面的改进意见". 联合国新闻 (in Chinese). 2006-09-01. Retrieved 2018-11-08.
- Women in China