South End–Groesbeckville Historic District
South End–Groesbeckville Historic District | |
U.S. National Register of Historic Places | |
U.S. Historic district | |
 View south down Clinton Street to German Evangelical Protestant Church, 2011 | |
 | |
| Location | Albany, NY |
|---|---|
| Coordinates | 42°38′23″N 73°45′38″W / 42.63972°N 73.76056°WCoordinates: 42°38′23″N 73°45′38″W / 42.63972°N 73.76056°W |
| Area | 57 acres (23 ha) |
| Built | 1761–1930[2] |
| Architect | Multiple |
| Architectural style | Greek Revival, Stick/Eastlake, Italianate |
| NRHP reference No. | 84002062[1] |
| Added to NRHP | September 13, 1984 |
The South End–Groesbeckville Historic District is located in part of the neighborhood of that name in Albany, New York, United States. It is a 26-block, 57-acre (23 ha) area south of the Mansion and Pastures neighborhoods with a mix of residential and commercial properties. In 1984 it was recognized as a historic district and listed on the National Register of Historic Places.
For several decades after the city's founding in the late 17th century, the South End was undeveloped. In 1761 General Philip Schuyler built his house there. Today it is a National Historic Landmark, the oldest building in the district and the only contributing property in the district individually listed on the National Register.
As the city grew following the opening of the Erie Canal in the early 19th century, development did not reach the South End immediately, save for an early toll road, now South Pearl Street (part of New York State Route 32) built in the first years of the 19th century, which later became the backbone of the South End. Planned streets for the neighborhood were included in Albany's grid pattern as early as 1818. They were built in the middle of the century, and by the 1870s the district had begun growing rapidly, fueled by German immigrants, a group still closely associated with the South End and the first of several waves of immigrants to leave their mark on it. Irish Americans would also consider it theirs even as they dispersed to other parts of the city, and one native of the district, Daniel P. O'Connell, grew up to become boss of the city's Democratic political machine well into the 20th century, using a now-demolished building in the district as his headquarters.[3]
The district is the only large area of Albany predating the 20th century where houses were largely built by the future occupants one at a time, rather than in large sets of speculative houses by developers (as one later historian put it "[it] wasn't planned, it just grew"), resulting in great architectural variety.[2] The hamlet of Groesbeckville in the neighboring Town of Bethlehem, which at the time was just to the south, grew along similar lines and was soon absorbed into the city, the first expansion of Albany's southern boundary. The new neighborhood became the first home for many of the immigrant groups that would populate the city into the 20th century, including African Americans dislocated by urban renewal elsewhere in the city. Today the district remains largely intact (only 13 of the district's 520 buildings, or 2.5 percent, were, at the time of listing, non-contributing) but struggles with the effects of urban decay. A neighborhood association has worked with the city to develop a revitalization plan.
Geography[]
While the South End is generally taken to refer to a large area of Albany, including almost everything south of downtown and Lincoln Park to the city's southern limit,[4] the district covers a smaller 57-acre (23 ha)[2]: 110 area that mostly resembles a slightly bent rectangle, mirroring a bend that once existed in the Hudson River shoreline and marked the city's original southern boundary. It has protrusions at several points, particularly on the east. Within is all the land between Elizabeth and South Pearl (New York State Route 32) streets going north-south and Morton and Second avenues going east-west. The terrain is generally level, since most of the district is on the flood plain of the Hudson River to the east. There are some gentle rises on the west, remnants of the many ravines through which small creeks once flowed to the river.[2]: 2, 265
To the north, separated by a block, are the Mansion and Pastures historic districts, also considered part of the South End in the broader sense, on the west and east respectively of South Pearl. East, Interstate 787 a block east of South Pearl and some modern housing projects divide the South End from Albany's old waterfront, among its buildings the A. Mendelson and Son Company Building, also listed, and the newer facilities of the Port of Albany–Rensselaer to the southeast. Directly south and west of the district are similar blocks of residential buildings, albeit with less historical integrity. North of Morton are some other institutional buildings, including a church and Albany's Criminal Court building.[2]: 2, 120, 265–66
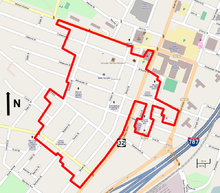
The district boundary follows a combination of lot lines and streets. Its most easily described portion begins at 298 South Pearl Street and follows the west side of that street north for approximately a quarter-mile (500 m) to the north end of the parking lot on the east side between Fourth Avenue and Alexander Street. It turns east then south down St. Ann's Place and across Fourth to exclude the parking lot yet include Public Bath No. 2 and St. Ann's/St. John's Church buildings.[2]: 120
It then turns east, following the church's rear lot line and then crossing Franklin Street to Vine Street including the old Fire Engine No. 5 building. Then it turns north along a rear lot line, taking in "Foley's Row" of houses along Franklin and St. Ann's/St. John's Center on the northeast corner of Fourth and Franklin before returning to Franklin. It follows that street north to turn east again along the lot line in the middle of the block between Plum and Bassett streets, then back south along that same lot's line to Plum. After following the street east for another lot, it turns south to include all the lots on the south side of Plum to Green Street, the easternmost reach of the district.[2]: 120
From there, it goes north up Green and then west along Bassett, returning to its northward course at Franklin. It detours onto property lines to exclude the vacant lot at Franklin and Schuyler Street, then returns to the latter, excluding the modern Giffen Memorial Elementary School building. At the next intersection, it follows South Pearl north to the district's northeastern corner, just short of Morton Avenue.[2]: 120
It follows property lines west and south across that block and Broad Street, excluding some modern government buildings such as a new fire station, Albany's Criminal Court and the local Department of Motor Vehicles office. At Clinton Street it turns north again to return to Morton. It follows this approximately 800 feet (240 m) west to the district's northwestern corner at 84 Morton, on the street's south side two lots east of the Eagle Street intersection.[2]: 120
After another eastward lurch along the back lines of 84 and 86 Morton, it turns south along a side lot line to cross Catherine Street and the next block. At Osborne Street it turns east, following it to the rear line of the properties on the west side of Elizabeth Street. It continues this way for another two blocks, turning back towards Elizabeth at 59, two lots south of Alexander Street.[2]: 120
At Third Avenue it turns west to take in the properties at 76–82 Third, then goes down their side and rear lines to the rear lines of the lots on Elizabeth. It follows them south to the rear lines of the houses on Second Avenue, whereupon it returns to Elizabeth and follows it across the Second intersection. Briefly following Krank Avenue, it then turns along the rear lines along the south side of Second, past Odell and Benjamin to Broad. It turns south along that street and then east to reach the southern end of the district back at 298 South Pearl.[2]: 120
Within this boundary are 520 buildings, all but 13 of which are contributing properties to the district's historic character. Most are two- or three-story vernacular brick or timber frame houses, in a variety of 19th-century styles, particularly Greek Revival, Italianate and Eastlake. The exception is South Pearl, the district's commercial backbone since development began. There are a few institutional buildings, primarily churches but also some schools as well as the fire station, scattered around the district. Some streets and intersections retain their original brick or cobblestone paving.[2]: 2–4
All open space is vacant lots. There are no parks in the district although there are several nearby, such as Lincoln Park to the northwest and Krank Park to the southwest. The baseball fields of Bishop Maginn High School also immediately abut the district on its west.[2]: 265–66
History[]
For most of Albany's early years, from its colonial beginnings to well past independence, the South End was part of the city only politically, its only development being the rough road to the south that went through it. General Philip Schuyler's mid-18th century decision to build a mansion on his lands there was the first development of any kind. Later, after his death, the Erie Canal and its related industrial development brought so many immigrants to the area that the city had to expand its boundaries, making the South End an end in name only.[2]: 109–13
1686–1761: Colonial era[]
When Dutch colonists first established their colonial capital in the mid-17th century, it was clustered around Fort Orange. A stockade enclosed the small village of Beverwijck that grew up around it, delineating the area roughly corresponding to what is today downtown Albany. When the area passed into British control following the Second Anglo-Dutch War, it was renamed Albany. In 1686 the stockaded settlement became a city with the granting of the Dongan Charter, the oldest city charter in continuous use in North America. It fixed Albany's initial municipal boundaries, establishing the southern city limit at the northern tip of what is today Castle Island, corresponding roughly to Gansevoort Street on today's map.[5]
During the first half of the 18th century, the city remained confined to its stockade, on guard against attacks from the French to the north. Just outside the city to the south were common pasturelands owned by the Dutch Reformed Church. Beyond them ran only a road to the south, a route now followed by South Pearl Street.[2]: 109

By the middle of the 18th century, tensions between the British and the French in North America, mirroring those between their parent countries, twice exploded into war. In 1760, during the second of these—the French and Indian War, corresponding to the Seven Years' War in Europe—General Philip Schuyler began accumulating property to the south of the Pastures. The following year he began construction of a house on his land.[2]: 109
1762–1825: Schuyler years[]
Schuyler oversaw the construction from England, where he was tending to military affairs with his mentor, John Bradstreet, and choosing much of the house's interior finishings there. It was a brick Georgian structure, the first full-size structure in that style built in Albany, with many of the latest amenities and designs.[6] Situated on a bluff overlooking the river, city and Schuyler's 80 acres (32 ha), the house he called "The Pasture" was the most elaborate built in Albany at the time, and remained so for many years afterwards.[7]
During the ensuing years of the Revolution Schuyler's mansion was host to some of its notable personalities. After being taken prisoner following the Continental Army's victory at the Battle of Saratoga, British General John Burgoyne and his staff were Schuyler's houseguests. George Washington visited, leading the city to rename the road down to the mansion Washington Street. In 1780, Washington's aide Alexander Hamilton married Schuyler's daughter Elizabeth on the grounds. The following year, even as the Patriot victory loomed, Loyalist forces raided the house in an attempt to kidnap Burgoyne.[8]
Schuyler lived out the remainder of his days there, continuing his public service as both a state and U.S. senator. Upon his death in 1804, the property was subdivided into smaller lots which were gradually sold off by his children. They were largely leased out as pastures since the city did not yet need to expand to that point, and the land east of Washington flooded in the spring. Washington Street nevertheless became part of the Bethlehem Turnpike toll road incorporated that year; by 1818 paper streets in the area had been included in the city's grid plan.[2]: 2
Some development took place along Washington Street north of Alexander in those early years. A few houses, such as the mildly detailed brick house at 395, remain from this time. The earliest hints of the area's future as an immigrant neighborhood began with some Irish settling in that area. Bassett Street was home to a small community of free African Americans, and there was enough of a Jewish presence that a group was meeting for services there in 1838.[2]: 115
1826–1850: Early development[]
The 1825 opening of the Erie Canal began to spur the growth the city had been preparing for. It expanded both north and south of downtown. By 1840 the Pastures had been sufficiently built out, assuming its present character, and development moved to the South End. Over the next 20 years, as Albany's population doubled, many immigrants came to the city for work in the factories that went up along the river. They found housing in the nearby South End. A century later, local historian C.R. Roseberry later described South Pearl Street as
... the main branch Albany put out when it began its serious expansion. It was the city's 19th century street, the street where the Industrial Revolution made itself most cogently felt and ... the city's original melting pot.[2]: 113 [9]
The growth was such that the brickyards that had originally populated the blocks west of Alexander Street due to the quality clay and excellent drainage were gone completely by 1857, replaced by houses.[2]: 113

Like most of the city's other neighborhoods that grew during this period, the new housing of the South End took the form of attached rowhouses. Unlike the other neighborhoods, the construction of those houses was largely paid for by those who intended to live in them, instead of by developers building large groups of speculative housing.[2]: 3 Foley's Row, the timber frame Greek Revival group at 159–169 Franklin Street,[2]: 60 which was almost completely developed by 1850, is a rare example of that type within the district.[2]: 113 Since residents worked and shopped near their houses, the neighborhood was pedestrian-friendly, with narrow streets and small-scale buildings. Along with its bending and non-parallel streets, this has led to it being described as having a European feel.[2]: 3
This pattern of building, which continued as the neighborhood grew throughout the rest of the century, resulted in a great deal of architectural diversity within individual blocks. For example, the 1895 house at 135 Clinton Street is brick with stone trim, while next door 137, built a quarter-century earlier, is a five-bay brick Italianate rowhouse with arched windows, a decorative cornice and metal sills, and nearby are older frame rowhouses with bracketed cornices next to contemporary brownstones. Despite these differences, many of the rowhouses remain alike in overall form.[2]: 3
The immigrant group most strongly identified with this era were Germans. At late as the early 1850s there were still very few, but more started coming as a consequence of the failed Revolutions of 1848. By the end of the Civil War the South End had many businesses and organizations catering to that population, most notably the 1857 German Evangelical Protestant Church at Alexander and Clinton streets, still a district landmark. Other immigrant groups would come to the South End, but the Germans remained concentrated there for a century.[2]: 114
1851–1885: Melting pot[]
Growth spilled past the city's southern boundary, into Groesbeckville, an unincorporated hamlet of the Town of Bethlehem. It went from almost no residents in 1845 to over a thousand ten years later. Its streets, too, were organized on a grid pattern, but one slightly offset from Albany's, a pattern still visible today. By the 1860s, residents of the hamlet were being listed in Albany's city directory and considered themselves socially and culturally to be part of the city. In 1870 their petition to make this a legal and political reality was accepted and the city's boundary was extended a mile (1.6 km) south, to its present location along the Normans Kill, creating the area of Albany known as the First Ward.[2]: 113

Irish immigrants, too, were settling in the South End. Unlike the Germans, they did not stay in the area; once they grew prosperous, they moved to those areas of the city they could then afford to live in. Even after St. Ann's Church was established as the neighborhood's parish church in 1867, many of the Irish continued to worship at either the Cathedral of the Immaculate Conception north of the Mansion District or St. John's, in the Pastures. But they retained a sentimental attachment to the South End, and Daniel P. O'Connell, boss of the city's Democratic political machine for most of the 20th century, worked out of his father's tavern at Fourth and South Pearl even though he and his family, too, had moved elsewhere in the city.[2]: 115
In the last two decades of the century, Jews from Eastern Europe arrived in the South End. While their synagogues and other cultural institutions were located in other neighborhoods to the north, many were tradesmen who established shops on South Pearl and other streets.[2]: 115 Development that may have been a response to that influx took place primarily to the south and west of the established blocks, in the blocks between Second and Third that had been laid out when they were still Groesbeckville, and the blocks west of Elizabeth Street. As had happened elsewhere in the city when similar areas along the bluff overlooking the river had been developed, the ravines were filled in and the streams that flowed through them diverted or buried in tunnels, a move which lessened the flooding closer to the river.[2]: 114
Italianate rowhouses so defined the neighborhood that the industrial building at 50 Morton Avenue, on the western corner with Elizabeth Street, had its facade along that street done to mimic five rowhouses.[2]: 3 The actual houses built during this era, however, began to break with the Greek Revival and Italianate traditions that had marked their pre-1870s neighbors. Their cornices were less likely to be carved ornately, and their facades featured more bay and oriel windows. Decorative touches characteristic of this era can be seen in the district on South Pearl. The building at 336 has Adamesque wreaths and other classically-inspired detailing while nearby 329 has intricately textured brickwork. Several others on the street have rock-faced lintels or semi-circular attic windows.[2]: 114
1886–1929: Institutions[]
In 1886, following an outbreak of eye disease at an orphanage run by the Daughters of Charity of Saint Vincent de Paul, some of the sisters and the sick children moved into the Schuyler Mansion. The order and the orphanage continued to use it for another 27 years, until the state bought it in 1913[10] for conversion into its present use as a historic site, which it has been since 1917. This institutional use of the district's original building heralded a new era for the South End where most new construction was not residences but larger structures meant for the general welfare.[2]: 5

Public School No. 17, at Second and Stephen Street, had been the South End's first such building in 1875. Its architecture echoed the Italianate rowhouses around it, with a corbelled cornice and raised basement. The next school, Public School No. 1, went up at Bassett and Franklin in 1889. It made rare use, for both the district and public school buildings, of the Moorish Revival style.[2]: 5
In the first decade of the new century many more large institutional buildings went up. The city built Public Bath No. 2 and Engine House No. 5 on Fourth between South Pearl and Franklin in the 1904–05 period. Across the street, St. Ann's matched it with a large convent in 1908. All these buildings showed at least the influence of the newer Colonial Revival style.[2]: 5 Sometime during this period, the Arts and Crafts-style apartment building at 82–84 Morton went up.[2]: 3 In 1929, the district came full circle when its youngest contributing property, the unrestrained Colonial Revival John B. Howe Branch Library, was built at the northeast corner of Clinton and Schuyler. Its design was meant to complement the Schuyler Mansion across the street.[2]: 5

During this era the demographics of the neighborhood continued their shifts. In the first two decades of the 20th century Italian immigrants began to make their presence felt in the South End. Other than their residence there, they had no lasting impact on the neighborhood since their community and its cultural institutions were concentrated in the Mansion District to the north, where most of Albany's Italian population had settled upon their arrival.[2]: 115–16
1930–present: Preservation and renewal[]
Beginning in 1930, with the Great Depression, the descendants of the original German immigrants who had settled the South End almost a century earlier began moving out. Albany had grown enough by the late 19th century that it began expanding to the west along its streetcar lines and, later, prime automobile routes. Affluent residents of the older neighborhoods close to downtown began moving to these newer, more suburban neighborhoods with their larger lots and detached houses. No statistics have been compiled to support this, but by 1950, it was clear that the Germans were moving out.[2]: 115
In one way the South End remained important to the city. Daniel P. O'Connell, born there in 1885, had served a term as Albany County Assessor from 1919 to 1921. Afterwards, he became chairman of the city's Democratic committee, seeing through its takeover of city government. He soon became boss of a machine that controlled the city until his death in the late 1970s.[11] His family's tavern at Fourth and South Pearl became known as "Little City Hall."[2]
After midcentury, another group of migrants arrived in the neighborhood. Most African Americans who had come to Albany in the Great Migration of the 1920s had settled in Arbor Hill, where the quality houses of the Ten Broeck Triangle that had once been home to the city's wealthy were becoming cheaper as the wealthy moved west or to the suburbs. Thus affected and repopulated, that neighborhood began to suffer from neglect and declined. The city's response was small-scale urban renewal, and black residents displaced by the demolitions that required moved to the South End.[2]: 116
In 1971 O'Connell, advancing in years, had his father's old tavern at Fourth and South Pearl, long the center of city politics, demolished rather than see it bought or rented by someone else.[2] He was slowly ceding control of the Albany machine to Erastus Corning 2nd, whom he had installed as the city's mayor in the late 1940s. His death in 1977 was one of the last breaks with the South End's past. Prominent politicians, including Governor Hugh Carey, attended his funeral at St. Ann's.[12]
By the time Corning died in 1983, the neighborhood had become half African American. Residents formed a neighborhood association to lobby for their interests at City Hall. Urban decay affected the South End, and some buildings had to be demolished or abandoned. In 2007 the city demolished 43–53 Alexander Street after one of the buildings flooded.[13] Four years later, in 2011, Habitat For Humanity proposed an ambitious project to rebuild them as a template for the revitalization of the entire neighborhood.[14]
Significant contributing properties[]
Only one property in the district has so far been listed individually on the National Register, although it is also designated a National Historic Landmark. Among the remaining 519 buildings, 506 (or 97.5 percent of the total) are considered contributing properties. Some of them are notable within the larger context of the district.
National Historic Landmark[]

- Schuyler Mansion, 32 Catherine Street. Philip Schuyler built this seven-by-four-bay Georgian mansion in what was then undeveloped woodland near the city's south boundary in 1761. He chose most of its interior finishes personally on extended trips to England. During the Revolutionary War, Schuyler had captured British general John Burgoyne and his staff as houseguests; George Washington would later pay a visit. After a period of use as an orphanage it has been a state historic site since 1917.[6][7]
Other contributing properties[]
- Apartment Building at 82–84 Morton Avenue: One of the few residential structures in the district built in the early 20th century, this Arts and Crafts three-story brick structure features projecting bays on either side with multipaned casement windows. The two main entrances in the center feature double doors in an arched entryway.[2]: 3, 65
- Building at 395 South Pearl Street: This three-story three-bay building of brick laid in Flemish bond with a projecting cornice, remodeled storefront and stone lintels dates to 1832, making it one of the few survivors from the district's pre-immigration era.[2]: 91, 112
- Building at 465 South Pearl Street: A historical marker out front at the Second Avenue intersection commemorates the 1885 birth of Daniel P. O'Connell, boss of the city's political machine that thrived late into the 20th century, in this four-story, four-bay brick Italianate commercial-residential building that was probably built in 1875.[2]: 95, 115 Uncle Dan's Diner, in the ground floor, takes its name from his nickname.[15][16]
- Building at 80 Morton Avenue: The three-story, three-bay yellow brick structure dating to the early 20th century shows some Georgian Revival influence. Its facade features stone quoins, splayed voussoir lintels on the one-over-one double-hung sash, and a wooden bracketed cornice.[2]: 64

- Engine Co. No. 5, 88 Fourth Avenue: This former firehouse was built in 1905 to house horse-drawn firefighting vehicles.[2]: 5, 54 It is an ornate two-story three-by-five-bay brick building on a sandstone foundation with stone trim.[2]: 54 On the north (front) facade are the original hinged wooden doors. Today it is the Outreach Center for St. John's/St. Ann's across the street.[17]
- Foley Row, 159–169 Franklin Street: This row of six attached Greek Revival gabled timber frame houses, each three bays wide with brick foundations, simple wooden lintels and clapboard siding, dates to 1851. It is one of the few groups of properties in the districts built speculatively by a developer rather than the ultimate residents.[2]: 113
- German Evangelical Protestant Church and Rectory, 76–78 Clinton Street. The spire of this 1857 Gothic Revival brick and stone church is a symbol of the South End and the early German immigrant population. To its south is the 1926 rectory, also brick, two stories high and four bays wide. Its west (front) facade features stone trim, strips of casement windows on both stories and an oblique peak along the roof parapet in which a stone cross has been set.[3][2]: 4, 115
- Jared Holt Wax Works, 111 Broad Street: A curved parapet reaching 8 feet (2.4 m) above the roofline at its center is the decorative highlight of this brick industrial building from the last years of the 19th century.[2]: 19 It has recently been converted into housing.[18]

- John A. Howe Branch Library, 105 Schuyler Street: The Georgian Revival style was used for this 1929 building to complement the nearby Schuyler Mansion.[2]: 5 It is a one-story, nine-bay structure of brick in Flemish bond on a raised basement, set off by a stone water table with a projecting central entrance pavilion, narrow arched Palladian windows set with 12-over-23 double-hung sash, separated by pilasters topped by scroll-carved stones. On the roof is a stone balustrade with carved pineapple finials. Inside are many of the original oak finishings and furniture. The children's room has a fireplace with stone tiles telling the story of Rip Van Winkle.[2]: 71
- Mt. Calvary Baptist Church, 58 Alexander Street: Built in the late 1860s, this is one of the last wood frame churches in the city of Albany.[2]: 5 It is a two-story clapboard-sided building with a gabled roof that slopes slightly at either side of, creating broad overhanging eaves along the side elevations. On the north (front) face, it is met at the corners by slightly projecting wooden pilasters, suggesting a lingering Greek Revival influence. The lancet arched windows are complemented by a gabled front entrance porch. Atop is a small conical steeple with a wooden cross at its peak.[2]: 13

- Mount Zion Baptist Church, 86 Schuyler Street: South End resident Charles Heidrich designed and built this Victorian Gothic structure in 1893.[2]: 70 The brick structure has stone trim and two octagonal front turrets flanking a central bell tower, echoed by a gabled central portion on the second story with stained glass rosette window and a gabled hood over the main entrance supported by two smooth round Ionic columns on either side.[2]: 13
- Public Bath No. 2, 90 Fourth Avenue: Adjacent to the Engine Co. 5 firehouse, it was built at the same time. It is a two-story buff brick and stone building with a pediment along the bracketed cornice over its main entrance and round-arched windows. Above the entrance is a recessed porch; inside it retains much of its original heating system and other features.[2]: 54 It was closed at the end of 2010 after mayor Gerald Jennings vetoed a budget amendment to keep it open, the first such action in his 17 years on the job at that time.[19]
- Public School No. 1, 71–77 Bassett Street: This 21⁄2-story 15-bay brick former school building, dating to 1889, uses the Moorish Revival style, one of its rare appearances in Albany.[2]: 15 It is most evident in the recessed main entry, with a Middle Eastern-style segmented arch surrounded by glass tiles with the school sign and gate of ornate iron,[2]: 15 considered some of the best architectural detailing in the city.[3]: 5
- Public School No. 17, 43 Second Avenue: No longer in use, this three-story ten-by-four-bay brick structure is built into the slope at the top of Stephen Street, revealing its brownstone foundation at the north and east sides. Brick pilasters rise to the corbelled flat roof with unusual projecting round arches. Along the south facade are two gabled entrance porches whose arches have radiating stone voussoirs.[2]: 78 } When built in 1875 it was the first major institutional building in the South End.[2]: 5
- St. John's/St Ann's Church Complex, 88 Fourth Avenue. The Gothic brick church with stone trim, a gabled side tower and an arcaded eastern porch is the oldest of these three, dating to 1867. In the decade after it, the neighboring Victorian Gothic rectory was built, probably after a fire destroyed the original one. It is brick with stone courses, recessed windows and an entrance tower with peaked roof in polychrome slate. Completing the set is the St. John's Center, also in brick with stone trim, built as a convent in 1908.[2]: 50
- Sunrise Tavern, 48 Delaware Street. The 1930 construction date of this two-story brick commercial-residential building makes it the youngest contributing property in the district.[2]: 2 It features a corner entry on the half-timbered storefront (now a church) with a corner entry for traffic on Elizabeth Street. The second floor of the north facade has an oriel window.[2]: 46
- Warehouse at 50 Morton Avenue. The east facade of this industrial building, dating to 1885, was decorated to look like five Italianate rowhouses.[2]: 3 They all have bracketed wooden cornices, ornate cast iron window and door hoods and recessed doors. The interior has its original freight elevator and open spaces.[2]: 63
Preservation and revitalization[]
The South End's decline in the later years of the 20th century has been met with efforts to reverse it. A neighborhood association has been formed to lobby for improvements in housing and the overall quality of life.[20] In 1978 the South End Improvement Corporation was established as a non-profit by a community housing activist to work toward similar goals by rehabilitating houses.[21]
In the early 21st century the city and all stakeholders collaborated to create a comprehensive plan for the South End, Mansion and Pastures neighborhoods. It was released in 2007, under the name Capitol South Plan: SEGway for the Future. "SEG" stood for the plan's three steps: stabilize, energize and grow the area.[22]
It gave a seven-year timetable for implementing the plan. The first phase, stabilization, referred to measures that could be accomplished quickly such as renovating housing, improving residents' educational attainment and taking measures to reduce crime. It was expected to take two years. After that, the neighborhood would be energized by investing strategically to make it a more desirable place to live. The final stage, growth, would involve major investments. "Each of the plan's recommendations build upon each other, with the foundation being what can be done within the next two years to benefit the current residents of the South End."[22]: ii–iv
In 2009 the city issued a progress report. Among the accomplishments it listed were the renovations to the Howe Branch Library and revitalization projects that included 20 homes built by Habitat for Humanity Capital District, which planned to concentrate its efforts at the intersection of Stephen Street and Third Avenue. The Capital District Transportation Authority had also extended a bus route serving the South End with stops at both nearby hospitals, increasing residents' access to jobs there.[23]
A decade later, the district and other neighborhoods near it still had problems. Federal money the city had hoped to use had not been forthcoming, and one in three Black residents—in an area 67 percent Black—still lived in poverty. The area's 10.4 percent building vacancy rate was almost triple that of the city of Albany as a whole.[24]
"This whole area was supposed to be redeveloped", Carolyn McLaughlin, a resident and former president of the city council, recalled to the Albany Times Union at the end of 2018, as she stood on the corner of Morton and South Pearl. She was particularly dismayed by the failure to turn that intersection into a public square, which would have been a "focal point" for the neighborhood.[24] Business owners in the area said the neighborhood's biggest problem was its image as a ghetto. "I think there's been a terrible misperception that the South End is a bad neighborhood," said Darius Shahinfar, the city treasurer.[25]
To begin that process, the city believes it should first help the South End's existing businesses and solicit investment from those who have already successfully developed and redeveloped in the area.[24] One goal would be to bring a supermarket back to the area, considered by residents to be a food desert.[25] A Rite Aid drugstore that offset that issue somewhat closed in October 2018 despite local protests, and a supermarket opened in the 1970s closed in less than a decade and is now a state Department of Motor Vehicles office. Albany Mayor Kathy Sheehan said it was a challenge to attract retailers to the South End since the neighborhood is not only poor but ill-suited to the kind of big-box stores that have come to dominate the sector.[24]
See also[]
References[]
- ^ "National Register Information System". National Register of Historic Places. National Park Service. March 13, 2009.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r s t u v w x y z aa ab ac ad ae af ag ah ai aj ak al am an ao ap aq ar as at au av aw ax ay az ba bb bc bd be bf bg bh bi bj bk bl bm bn bo J. Botch; Lucy A. Breyer & C.L. Sweet (January 1984). "National Register of Historic Places Registration: South End-Groesbeckville Historic District". U.S. National Archives. Retrieved October 23, 2020.
- ^ a b c "O Albany's South End: A Walking Tour" (PDF). New York State Writers' Institute. 2006. Retrieved September 8, 2012.
- ^ "South End". City of Albany Department of Development and Planning. 2007. Retrieved September 8, 2012.
- ^ "City Limits". New York State Museum. June 2008. Retrieved September 10, 2012.
- ^ a b Greiff, Constance M.; Schuyler Mansion National Historic Landmark (791 KB), National Park Service; July 26, 1985; p. 6, retrieved September 10, 2012.
- ^ a b "Schuyler Mansion". New York State Museum. June 2008. Retrieved September 10, 2012.
- ^ "Schuyler Mansion State Historic Site". Frommer's. 2012. Archived from the original on January 4, 2013. Retrieved September 10, 2012.
- ^ Roseberry, C.R. (June 23, 1949). "South End, Cross Section of America". Albany Times Union.
- ^ "History". St. Catherine's Center for Children. Archived from the original on August 3, 2012. Retrieved September 12, 2012.
- ^ O'Grady, Timothy (2010). Divine Magnetic Lands: A Journey in America. New York, NY: Random House. p. 77. ISBN 9781407092904. Retrieved September 13, 2012.
- ^ "O'Connell Eulogized At Rite As Man Of Feeling, Warmth". The Daily Gazette. Schenectady, NY. March 3, 1977. Retrieved September 14, 2012.
- ^ O'Brien, Tim (September 15, 2007). "Where there once was blight: hope". Albany Times Union. Retrieved September 14, 2012.
- ^ Carleo-Evangelist, Jordan (April 26, 2011). "Overdue renaissance on Alexander Street". Albany Times Union. Retrieved September 14, 2012.
- ^ Norder, Akum (January 7, 2011). "Uncle Dan's: diner food, with a helping of history". All Over Albany. Retrieved October 24, 2020.
- ^ Weaver Jr., Warren (March 1, 1977). "Daniel P. O'Connell Is Dead at 91; Old‐Time Albany Democratic Boss". The New York Times. Retrieved October 24, 2020.
- ^ "St. John's/St. Ann's Outreach Center". St. John's/St. Ann's Roman Catholic Church. Retrieved September 18, 2012.
- ^ "Jared Holt Mews". Albany Housing Authority. Retrieved October 24, 2020.
- ^ Lee, Stephanie (December 30, 2010). "Pool fans make splash on last day". Albany Times Union. Retrieved September 21, 2012.
- ^ "About SENA". South End Neighborhood Association. January 2008. Retrieved September 23, 2012.
- ^ "Mission + Vision". 2020. Retrieved October 25, 2020.
- ^ a b "Capitol South Plan: SEGway for the Future" (PDF). Philip Preiss Shapiro Architects. July 2007. Retrieved September 30, 2012.
- ^ City of Albany, "The Revitalization of the South End: Progress Report, 2007–2009" (PDF). City of Albany. December 2009. Retrieved October 25, 2020.
- ^ a b c d Moench, Mallory; Fries, Amanda (December 29, 2018). "South End community vigor aims to revive Albany neighborhood". Albany Times-Union. Retrieved October 25, 2020.
- ^ a b "Big plans announced to revitalize Albany's South End". WNYT-TV. March 5, 2019. Retrieved October 25, 2020.
External links[]
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to South End-Groesbeckville Historic District. |
- Historic districts on the National Register of Historic Places in New York (state)
- Buildings and structures in Albany, New York
- National Register of Historic Places in Albany, New York


