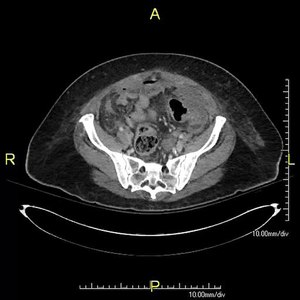
Stercoral perforation
| Stercoral perforation | |
|---|---|
| Axial CT cine clip showing loculated fluid, free intraperitoneal fluid, extraluminal gas, and focal discontinuity of the wall of the sigmoid colon with stool in the defect consistent with stercoral perforation. The person was a heavy opioid user |
Stercoral perforation is the perforation or rupture of the intestine's walls by its internal contents, such as hardened feces or foreign objects. Hardened stools may form in prolonged constipation or other diseases which cause obstruction of transit, such as Chagas disease, Hirschprung's disease, toxic colitis, hypercalcemia, and megacolon.[1]
Symptoms can include abdominal distension, pain, and nausea.[1]
Stercoral perforation is a rare and very dangerous, life-threatening situation, as well as a surgical emergency, because the spillage of contaminated intestinal contents into the abdominal cavity leads to peritonitis, a rapid bacteremia (bacterial infection of the blood), with many complications.
See also[]
- Gastrointestinal perforation
- Stercoral ulcer, which can lead to stercoral perforation
References[]
Categories:
- Gastrointestinal tract disorders
- Gross pathology
- Pathology stubs