Sukhoi Su-47
This article needs additional citations for verification. (July 2009) |
| Su-47 Berkut | |
|---|---|

| |
| An Su-47 at an airshow in 2008. | |
| Role | Experimental aircraft/Technology demonstrator |
| Manufacturer | Sukhoi |
| Designer | Mikhail Pogosyan |
| First flight | 25 September 1997 |
| Status | Cancelled |
| Primary user | Russian Air Force |
| Number built | 1 |
The Sukhoi Su-47 Berkut (Russian: Сухой Су-47 Беркут, lit. 'Golden Eagle') (NATO reporting name Firkin[1]), also designated S-32 and S-37 (not to be confused with the twin-engined delta canard design[2] offered by Sukhoi in the early 1990s under the designation Su-37) during initial development, was an experimental supersonic jet fighter developed by the JSC Sukhoi Company. A distinguishing feature of the aircraft was its forward-swept wing[3] that gave the aircraft excellent agility and maneuverability. While serial production of the type never materialized, the sole aircraft produced served as a technology demonstrator prototype for a number of advanced technologies later used in the 4.5 generation fighter Su-35 and current fifth-generation jet fighter Su-57.
Development[]
Originally known as the S-37, Sukhoi redesignated its advanced test aircraft as the Su-47 in 2002. Officially nicknamed Berkut (Russian: Беркут) (the Russian name for the golden eagle), the Su-47 was originally built as Russia's principal testbed for composite materials and sophisticated fly-by-wire control systems.
TsAGI has long been aware of the advantages of forward-swept wings, with research including the development of the and study of the captured Junkers Ju 287 in the 1940s. At high angles of attack, the wing tips remain unstalled allowing the aircraft to retain aileron control. Conversely to more conventional rear-swept wings, forward sweep geometrically creates increased angle of incidence of the outer wing sections when the wing bends under load. The wings experience higher bending moments, leading to a tendency for the wings to fail structurally at lower speeds than for a straight or aft-swept wing.
The project was launched in 1983 on order from the Soviet Air Force. But when the USSR dissolved, funding was frozen and development continued only through funding by Sukhoi. Like its US counterpart, the Grumman X-29, the Su-47 was primarily a technology demonstrator for future Russian fighters.
Design[]
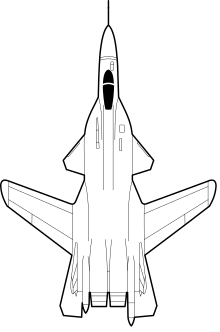
The Su-47 is of similar dimensions to previous large Sukhoi fighters, such as the Su-35. To reduce development costs, the Su-47 borrowed the forward fuselage, vertical tails, and landing gear of the Su-27 family. Nonetheless, the aircraft includes an internal weapons bay, and space set aside for an advanced radar.
Like its immediate predecessor, the Su-37, the Su-47 is of tandem-triple layout, with canards ahead of wings and tailplanes. The Su-47 has two tailbooms of unequal length outboard of the exhaust nozzles. The shorter boom, on the left-hand side, houses rear-facing radar, while the longer boom houses a brake parachute.
Maneuverability[]
The Su-47 has extremely high agility at subsonic speeds, enabling the aircraft to alter its angle of attack and its flight path very quickly while retaining maneuverability in supersonic flight. The Su-47 has a maximum speed of Mach 1.6 at high altitudes and a 9g capability.[4]
The swept-forward wing, compared to a swept-back wing of the same area, provides a number of advantages:[4]
- higher lift-to-drag ratio
- better agility in dogfight situations
- higher range at subsonic speed
- improved stall resistance and anti-spin characteristics
- improved stability at high angles of attack
- a lower minimum flight speed
- a shorter take-off and landing distance
Wings[]
The forward-swept midwing gives the Su-47 its unconventional appearance. A substantial part of the lift generated by the forward-swept wing occurs at the inner portion of the wingspan. This inboard lift is not restricted by wingtip stall and the lift-induced wingtip vortex generation is thus reduced. The ailerons—the wing's control surfaces—remain effective at the highest angles of attack, and controllability of the aircraft is retained even in the event of airflow separating from the remainder of the wings' surface.
A downside of such a forward-swept wing design is that it geometrically produces wing twisting as it bends under load, resulting in greater stress on the wing than for a similar straight or aft-swept wing. This requires the wing be designed to twist as it bends—opposite to the geometric twisting. This is done by the use of composites wing skins laid-up to twist. The plane was initially limited to Mach 1.6.
Thrust vectoring[]
The thrust vectoring (with PFU engine modification) of ±20° at 30°/second in pitch and yaw will greatly support the agility gained by other aspects of the design.
Specifications (Su-47)[]
Data from Jane's All the World's Aircraft 2000–01[5]
General characteristics
- Crew: 1
- Length: 22.6 m (74 ft 2 in)
- Wingspan: 16.7 m (54 ft 9 in)
- Height: 6.4 m (21 ft 0 in)
- Wing area: 56 m2 (600 sq ft)
- Airfoil: 5%
- Gross weight: 25,670 kg (56,593 lb)
- Max takeoff weight: 34,000 kg (74,957 lb)
- Powerplant: 2 × Soloviev D-30F6[6] afterburning turbofan engines, 93.1 kN (20,900 lbf) thrust each engines with 2-dimensional and 3-dimensional thrust-vectoring nozzles planned for testing. dry, 153 kN (34,000 lbf) with afterburner
Performance
- Maximum speed: 2,200 km/h (1,400 mph, 1,200 kn) / M2.21 at altitude
- 1,400 km/h (870 mph; 760 kn) / M1.12 at sea level
- Range: 3,300 km (2,100 mi, 1,800 nmi)
- Service ceiling: 18,000 m (59,000 ft)
- g limits: +9
- Rate of climb: 233[7] m/s (45,900 ft/min)
- Wing loading: 607 kg/m2 (124 lb/sq ft) max (approx.)
- 458 kg/m2 (94 lb/sq ft) normal (approx.)
- Thrust/weight: 0.92 max take-off weight
- 1.21 normal take-off weight
Armament
- provision for conformal weapon storage
Avionics
- provision for mission radar in nose and ECM in tail radomes
Gallery[]



Su-47 next to a Sukhoi Su-35UB at the MAKS-2003 air show.

Sukhoi Su-47 Berkut in the lead, followed by a Su-27SKM (top) and a Su-30MKK (bottom).
See also[]
Related development
- Sukhoi Su-27
- Sukhoi Su-30
- Sukhoi Su-33
- Sukhoi Su-34
- Sukhoi Su-35
- Sukhoi Su-37
- Sukhoi Su-57 / Sukhoi/HAL FGFA
Aircraft of comparable role, configuration, and era
References[]
- ^ "Su-47 / S-37 Berkut". www.globalsecurity.org. Retrieved 2016-01-10.
- ^ Buttler, Tony and Gordon, Yefim. "Soviet Secret Projects: Fighters Since 1945". Midland Publishing, 2005. ISBN 1-85780-221-7.
- ^ Russian Aviation Page: Sukhoi S-37 Berkut (S-32) Archived February 13, 2006, at the Wayback Machine
- ^ Jump up to: a b Su-47 (S-37 Berkut) Experimental Fighter Aircraft – Air Force Technology[unreliable source?]
- ^ Jackson, Paul, ed. (2000). Jane's All the World's Aircraft 2000–01 (91st ed.). Coulsdon, Surrey, United Kingdom: Jane's Information Group. pp. 457–458. ISBN 978-0710620118.
- ^ "Су-47 (С-37) "Беркут" (Russian)". testpilot.ru. Retrieved 29 August 2020.
- ^ "Su-47 (S-37 Berkut) Golden Eagle Fighter". airforce-technology.com. Retrieved 25 March 2020.
Bibliography[]
- Gordon, Yefim (2002). Sukhoi S-37 and Mikoyan MFI: Russian Fifth-Generation Fighter Demonstrators – Red Star Vol. 1. Midland Publishing. ISBN 978-1-85780-120-0.
- Tayor, Michael J. H. (1999). World Aircraft & Systems Directory. Herndon, VA: Brassey's. pp. 78–79.
External links[]
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Sukhoi Su-47. |
- 1990s Soviet and Russian experimental aircraft
- 1990s Soviet and Russian fighter aircraft
- Abandoned military aircraft projects of Russia
- Aircraft first flown in 1997
- Canard aircraft
- Forward-swept-wing aircraft
- Relaxed-stability aircraft
- Sukhoi aircraft
- Twinjets



