Sulfine
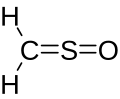
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
Methylidene-λ4-sulfanone | |
| Other names
sulfine
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID
|
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| CH2OS | |
| Molar mass | 62.09 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Sulfinylmethane or sulfine is an organic compound with molecular formula H2CSO. It is the simplest sulfine. Sulfines are chemical compounds with the general structure XY=SO.[1] IUPAC considers the term 'sulfine' obsolete,[2] preferring instead thiocarbonyl S-oxide, despite this the use of the term sulfine still predominates in the chemical literature.
Substituted sulfines[]
The parent sulfine H2CSO is very labile, whereas substituted derivatives are more conveniently isolated. One example is syn-propanethial-S-oxide which is produced from allicin and is responsible for eye-watering effects of cutting onions. Another example is diphenylsulfine, obtained by oxidation of thiobenzophenone:[3]
- (C6H5)2C=S + [O] → (C6H5)2C=S=O

Structure of diphenylsulfine. Selected distances and angles: rS=O = 1.468, rC=S = 1.612 Å, <C=S=O = 113.7°.
See also[]
- Sulfene - related functional group with the formula H2C=SO2
- Ethenone
- Heterocumulene
References[]
- ^ Binne Zwanenburg (1989). "Sulfine Chemistry". Phosphorus, Sulfur, and Silicon and the Related Elements. 43 (1–2): 1–24. doi:10.1080/10426508908040276.
- ^ IUPAC, Compendium of Chemical Terminology, 2nd ed. (the "Gold Book") (1997). Online corrected version: (2006–) "sulfines". doi:10.1351/goldbook.S06108
- ^ G. Rindorf, L. Carlsen (1979). "The crystal and molecular structures of the thiobenzophenone S-oxide and thiobenzophenone". Acta Crystallogr. B35 (5): 1179–1182. doi:10.1107/S0567740879005835.CS1 maint: uses authors parameter (link)
Categories:
- Organosulfur compounds
- Organic compound stubs