Tampa Bay Rays
| Tampa Bay Rays | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Established in 1998 | |||||
| |||||
| Major league affiliations | |||||
| |||||
| Current uniform | |||||
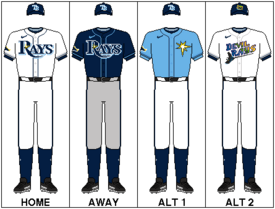 | |||||
| Retired numbers |
| ||||
| Colors | |||||
| Name | |||||
| |||||
| Ballpark | |||||
| |||||
| Major league titles | |||||
| World Series titles (0) | None | ||||
| AL Pennants (2) | |||||
| East Division titles (3) |
| ||||
| Wild card berths (3) | |||||
| Front office | |||||
| Principal owner(s) | Stuart Sternberg | ||||
| President | Brian Auld Matt Silverman | ||||
| General manager | Erik Neander | ||||
| Manager | Kevin Cash | ||||
The Tampa Bay Rays are an American professional baseball team based in St. Petersburg, Florida. The Rays compete in Major League Baseball (MLB) as a member club of the American League (AL) East division. Since its inception, the team's home venue has been Tropicana Field.
Following nearly three decades of unsuccessfully trying to gain an expansion franchise or enticing existing teams to relocate to the Tampa Bay Area, an ownership group led by Vince Naimoli was approved on March 9, 1995. The Tampa Bay Devil Rays began play in the 1998 Major League Baseball season.
Their first decade of play, however, was marked by futility; they finished in last place in the AL East in all but the 2004 season, when they finished second to last.[4] Following the 2007 season, Stuart Sternberg, who had purchased controlling interest in the team from Vince Naimoli two years earlier,[5] changed the team's name from "Devil Rays" to "Rays", now meant to primarily refer to a burst of sunshine rather than a manta ray,[1] though a manta ray logo remains on the uniform sleeves. The 2008 season saw the Tampa Bay Rays post their first winning season, their first AL East championship, and their first American League Pennant (defeating the rival Boston Red Sox in the ALCS), though they lost to the Philadelphia Phillies in that year's World Series. Since then, the Rays have played in the postseason five more times, winning the American League pennant again in 2020 and losing to the Los Angeles Dodgers in that year's World Series.
The Tampa Bay Rays' chief rivals are the Boston Red Sox and the New York Yankees. Regarding the former, there have been several notable on-field incidents.[6] The Rays also have an intrastate interleague rivalry with the National League (NL)'s Miami Marlins (originally the Florida Marlins), whom they play in the Citrus Series.
Through 2020, the Rays' all-time record is 1,726-1,896 (.477).[7]
History[]
Expansion team[]
The prospect of a Major League Baseball team in the Tampa Bay area had been floated as early as 1966, when civic leader and St. Petersburg Times publisher Jack Lake first suggested St. Petersburg as a suitable city for baseball. Local leaders made many unsuccessful attempts to acquire a major league baseball team in the 1980s and 1990s. The Minnesota Twins, Chicago White Sox, Texas Rangers, and Seattle Mariners all considered moving to either Tampa or St. Petersburg before deciding to remain in their current locations. The Florida Suncoast Dome (now named Tropicana Field) was built in St. Petersburg in 1990 with the purpose of luring a major league team. When MLB announced that it would add two expansion teams for the 1993 season, it was widely assumed that one of the teams would be placed in the Dome. However, in addition to the application from St. Petersburg, a competing group applied to field a team in Tampa, prompting much conflict over the bid. The two National League teams were awarded to Denver (Colorado Rockies) and Miami (Florida Marlins) instead.
Tampa-based investor Vince Naimoli, who had almost bought the San Francisco Giants in 1992 before MLB intervention,[8] was finally awarded a new expansion franchise on March 9, 1995. Along with a group from Phoenix (the Arizona Diamondbacks), the new franchise was scheduled to begin play in 1998. Naimoli initially moved to name the team the "Tampa Bay Sting Rays," but the rights to that name were already held by the Maui Stingrays, a short-lived minor league team which wanted $35,000 to buy the name; instead, the team opted for a local variety of the ray, the devil ray.
The Tampa Bay Devil Rays named Chuck LaMar, the former assistant general manager of the Atlanta Braves, as its first general manager; Larry Rothschild, a former pitching coach for the Marlins and Cincinnati Reds, was named the team's first manager on November 7, 1997. In the Expansion Draft on November 18, 1997, the Devil Rays acquired their first player in Tony Saunders. Among the team's 34 other draft picks was future star Bobby Abreu; however, Abreu was dealt to Philadelphia Phillies for Kevin Stocker hours later,[9] in a trade regarded among the worst in MLB history.[10] The team also acquired veteran stars Wade Boggs and Fred McGriff (both Tampa natives), as well as Wilson Álvarez.
1998–2005: The Devil Rays and early struggles[]
The Devil Rays played their first game on March 31, 1998 against the Detroit Tigers at Tropicana Field, before an opening day crowd of 45,369. Wilson Álvarez threw the first pitch and Wade Boggs hit the team's first home run, though the Devil Rays ended up losing 11–6. The next day, the Devil Rays won their first victory, defeating Detroit 11-8, thanks to rookie pitcher (and future All-Star) Rolando Arrojo. Despite briefly being over .500 in their first 19 games (a first for an expansion team in their inaugural season), the team would go on to lose 99 that year, ending with the second-worst record in the league (just above their neighbors, the Marlins, who lost 108).[11]

The Devil Rays continued to struggle in their next few seasons, with many of their veteran players, including the "Hit Show" of sluggers (McGriff, Vinny Castilla, Jose Canseco and Greg Vaughn), being past their prime—though Wade Boggs would mark his 3000th career hit, a home run, against the Cleveland Indians on August 7, 1999.[12] Having led the Devil Rays through two last-place, 69-wins seasons in 1999 and 2000, Rothschild was fired partway through the 2001 season and replaced by Hal McRae. Despite the change, the team continued to decline, and the 2002 season would lead to a franchise-worst 55-106 record, despite the emergence of key players like Aubrey Huff, Toby Hall, and Carl Crawford began to emerge as key players. However, the 2002 season would prove to be the worst in franchise history to date. McRae was moved to a front office position after the season.
Lou Piniella, a Tampa native who had previously led the Reds to a World Series, replaced McRae as manager for the 2003 season, winning 63 games. The next year, Piniella's Devil Rays finished with a 70-91 record, just above the Toronto Blue Jays to claim in 4th in the American League East—the first time in franchise history the team was out of last place. Crawford established himself as a breakout star, leading the American League in triples (19) and, for the second year in a row, stolen bases (59). In the 2005 season, Crawford's production at the plate was matched by newcomers Jorge Cantú and Jonny Gomes, though the team was let down by its pitching staff (despite the arrival of Scott Kazmir) and finished 67-95.
Tensions between the owners and management came to a head after the dismal 2005 season. Piniella became frustrated with the ownership group's lack of commitment to the team, stating that they were "not interested about the present" but "about the future." He took issue not only with Naimoli (whose repeated promises of payroll increases had not been met), but with a new group of investors led by Stuart Sternberg.[13] After the 2005 season, Sternberg purchased a controlling interest in the team and released Piniella, buying out the last year of his contract for $2.2 million.[14]
2006–2015: The Rays, Joe Maddon, and first postseason appearances[]
For the 2006 season, Sternberg hired Joe Maddon, formerly of the Anaheim Angels, to replace Piniella as manager. Sternberg also fired LaMar and most of the front office, replacing him with Andrew Friedman (as Executive Vice President of Baseball Operations). Nevertheless, the team continued to struggle for the first two years of Maddon's tenure, finishing 61-101 and 66-96 in 2006 and 2007 season.

The team underwent a massive rebrand prior to the 2008 season, abandoning its nickname and green-white color scheme for a new existence as the Tampa Bay Rays. Dropping the "Devil", the new Rays name referred to a ray of sunshine (for the Sunshine State of Florida), and the team adopted a navy, Columbia blue and gold color scheme. Sternberg finally delivered on his promises to increase the team's payroll, raising it to $43 million (still the lowest payroll in baseball).[15] The team, anchored by Crawford, Kazmir, and pitcher James Shields, was bolstered by new additions of pitchers Matt Garza and David Price (a first round draft pick),[16] outfielder Ben Zobrist, and third base prospect Evan Longoria. The Rays started the season strongly with their best record in franchise history, and became the first team in modern Major League history (since 1900) to hold the best record in the league through Memorial Day, after having the worst record in the league the year before.[17] The Rays briefly fell behind the Boston Red Sox but, with the best home record in Major League Baseball, manage to qualify for at least the AL Wild Card on September 20—the team's first-ever postseason berth.[18] The Rays would ultimately end the season two games above the Red Sox in the AL East, their first divisional title.
The 2008 American League Division Series was the Rays' first playoff series victory, defeating the Chicago White Sox in 4 games. Besting the Red Sox in the American League Championship Series in 7 games, the Rays advanced to the World Series for the first time. However, the team's good fortunes came to an end, and they were defeated four games to one by the Philadelphia Phillies.

Going into the 2009 season, the American League champions again posted a winning record, 84-78, but was unable to return to the postseason, in part due to injuries to Longoria, Akinori Iwamura and Carlos Peña. The Rays performed much better the following year, a season that saw Matt Garza throw the franchise's first no-hitter (against Detroit)[19] They again won the AL East, finishing with the Abest record in the AL, but were eliminated in the ALDS by the Rangers.
The Rays lost veterans like Garza, Peña, and Crawford in the 2010-11 offseason, but nevertheless finished the 2011 season with the AL wild card, having just barely beat out the Red Sox with a 12th-inning walk-off home run by Evan Longoria against the Yankees. The team was again eliminated by the Rangers in the ALDS. The Rays missed out on the postseason the next year despite a 90–72 record, though David Price became the first Rays pitcher to earn the Cy Young Award. The team returned to the postseason in 2013 (after a Game 163 tiebreaker against Texas), in part thanks to new additions Wil Myers and Chris Archer. However, they were again defeated in the ALDS, this time by the eventual World Series champions, the Red Sox.
After 2013's failed championship bid, the Rays entered a period of decline; 2014 saw their first losing record (77-85) since 2007. Price was traded away to the Detroit Tigers, though the Rays received prospect Willy Adames in return.[20] GM Andrew Friedman left Tampa Bay to for a front office role with the Los Angeles Dodgers;[21] this activated an opt-out clause in Maddon's contract, who also opted to leave Tampa Bay despite efforts to resign him.[22] Maddon finished his tenure with a record of 754 wins and 705 losses.[23]
2015–present: The Kevin Cash era[]
The Rays named Kevin Cash as Maddon's successor on December 5, 2014; he would be the youngest manager in league.[24] Cash's first season in 2015 saw strong performances from Chris Archer, who became a Cy Young contender, and center-fielder Kevin Kiermaier, who won his first Gold Glove Award; however the team ended the season with a 80-82 record. The team fared more poorly the next year; they finished last in the AL East for the first time since 2007, winning only 68 games in a season marred by injuries (including to Kiermaier) and a 3-24 stretch between June 16 and July 16. 2017 again saw strong performances from Archer and Alex Cobb (returning from Tommy John surgery the year before), and the team rebounded to match its 2015 record.
The 2017 season also saw Erik Neander take over as general manager from Matthew Silverman, and he would continue the Rays' strategy of aggressive trade moves. Heading into 2018, the Rays traded Evan Longoria, long considered a franchise player, to the Giants, and starter Jake Odorizzi to the Twins.[25] More trades would come as the season went on, as Matt Andriese was dealt to Arizona; Archer was traded to the Pittsburgh Pirates for pitcher Tyler Glasnow, outfielder Austin Meadows, and prospect Shane Baz. Despite the departure of much of their existing rotation, Glasnow and Blake Snell anchored the teams pitching staff; Snell, who lead all AL pitchers in wins (21) and ERA (1.89), won the franchise's second Cy Young Award. The team also pioneered the concept of the "opener," by which the opening pitcher is relieved after only a few outs by a more traditional starting pitcher; the strategy helped the Rays finish the year with the second-best team ERA in the American League. The Rays won 90 games, but lost the AL wild card berth to Oakland by seven games.
Cash led the Rays to his first postseason in 2019, building off an impressive 19-9 start to win 96 games. The pitching staff, anchored by starters Glasnow, Snell, and veteran Charlie Morton as well as relievers Nick Anderson and Diego Castillo, led the American League with a 3.65 ERA. The team defeated Oakland to claim the AL Wild Card spot, but was defeated by the Houston Astros in a five-game ALDS.

Despite the postseason defeat, the Rays retained much of their core going into the 2020 season, which had been shortened to 60 games as a result of the COVID-19 pandemic. Despite a 5-7 start, the Rays rebounded to win 35 of their last 48 games, thanks to the rotation, the bullpen (Anderson, Castillo, and Pete Fairbanks), and an offensive breakout from Brandon Lowe. At the end of the regular season, the team posted an AL-best 40-20 record, winning its first divisional title since 2011 and again advancing to the postseason.
The Rays went on to defeat the Yankees in the five-game ALDS, thanks to Mike Brosseau's go-ahead eighth inning home run off Yankees pitcher Aroldis Chapman; during the regular season, Chapman had instigated a bench-clearing altercation by throwing over Brosseau's head. The postseason was dominated by Randy Arozarena, who set new records for postseason home runs (10), hits by a rookie and by any player in a single postseason (29), and total bases (64). In a rematch of 2019, the Rays defeated the Astros in the seven-game ALCS, and went on to meet the Dodgers in the World Series. The Rays won Game 4 of the series in near-miraculous fashion; down 6-7, with two outs in the bottom of the ninth and down in the count 1–2, Brett Phillips singled off LA closer Kenley Jansen for his first career postseason hit, scoring Kiermaier to tie the game, and Arozarena to score the winning run and tie the series at two.[26] Despite the heroics, the Rays lost the next two games to the Dodgers and were defeated in their second bid for a World Series.
Season results[]
The records of the Rays' last five seasons in Major League Baseball.
| American League champions * | Division champions ^ | Wild card berth ¤ |
| MLB season |
Team season |
League[27] | Division[27] | Regular season | Post-season | Awards | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Finish[a] | Wins[b] | Losses | Win% | GB[c] | ||||||
| 2016 | 2016 | AL | East | 5th | 68 | 94 | .420 | 25 | ||
| 2017 | 2017 | AL | East | 3rd | 80 | 82 | .494 | 13 | ||
| 2018 | 2018 | AL | East | 3rd | 90 | 72 | .555 | 18 | Blake Snell (CYA)[28] | |
| 2019 | 2019 | AL | East | 2nd ¤ | 96 | 66 | .593 | 7 | Won ALWC (Athletics) Lost ALDS (Astros) 3–2 |
|
| 2020 | 2020 | AL * | East ^ | 1st | 40 | 20 | .667 | — | Won ALWC (Blue Jays) 2–0 Won ALDS (Yankees) 3–2 Won ALCS (Astros) 4–3 Lost World Series (Dodgers) 4–2 |
Kevin Cash (MOY)[29] |
These statistics are current through the 2020 Major League Baseball regular season.
Rivals[]
AL East[]
Tampa Bay's primary rivals are the Boston Red Sox and the New York Yankees.[30]
Boston Red Sox[]
The Red Sox/Rays rivalry dates back to the 2000 season, when Devil Ray Gerald Williams took exception to being hit by a pitch thrown by Boston pitcher Pedro Martínez and charged the mound, resulting in a game full of retaliations and ejections on both sides.[31] There have been several other incidents between the teams during the ensuing years, including one in 2005 that resulted in two bench-clearing fights during the game and a war of words between then-Devil Rays manager Lou Piniella and then-Boston pitcher Curt Schilling through the media in the following days.[32] The rivalry reached its highest level to date during the 2008 season, including a brawl during a June meeting in Fenway Park[33] and a seven-game American League Championship Series between the teams that ended in the Rays' first ever pennant win.
New York Yankees[]
As a fellow member of the AL East division, the Yankees and Rays play many times each season. There has always been some feeling of a rivalry between the teams because the Yankees make Tampa their spring training home, as well as having a minor league team in the Tampa Tarpons; home and fan loyalty in the Tampa Bay area has historically been divided, especially among transplants from the northeastern U.S.[34] The rivalry became more heated in spring training of 2008, when a home plate collision between Rays outfielder Elliot Johnson and Yankees catcher Francisco Cervelli was followed the next day by spikes-high slide by Yankees outfielder Shelley Duncan into Rays' second baseman Akinori Iwamura, prompting Rays outfielder Jonny Gomes to charge in from his position in right field and knock Duncan to the ground.
In a 2020 incident at Yankee Stadium, Yankee closer Aroldis Chapman threw a 101-mph fastball over the head of Rays batter Mike Brosseau, leading to the ejection of Rays manager Kevin Cash and the clearing of benches. Chapman earned a three-game suspension. In response to the incident, Cash said that, if it continued to happen, the Rays had "a whole damn stable" of pitchers capable of throwing 98 miles an hour. Later that year, the Rays and Yankees would meet in postseason for the first time in the 2020 American League Division Series, which Tampa Bay won in five games; the go-ahead run, in the eighth inning of Game 5, was a home run by Brosseau off of Chapman.
Citrus Series[]
The Rays also have a geographical, interleague rivalry with the Miami Marlins. Tampa Bay currently leads the series, 68–58.[35]
Ballparks[]
Tropicana Field[]

The Rays have played at Tropicana Field since their inception in 1998.[36] The facility, which was originally called the "Florida Suncoast Dome", was built in the late 1980s to attract an MLB team through either relocation or expansion. After St. Petersburg was awarded an expansion franchise in 1995, the dome underwent extensive renovations and naming rights were sold to Tropicana Products, which was based in nearby Bradenton.
Tropicana Field underwent further renovations in 2006 and 2007 after Stu Sternberg gained controlling ownership of the team. Most of the changes sought to improve fans' game-day experience. For the players, the biggest change was the installation of a new Field Turf surface in 2007, which was replaced in turn with a new version of AstroTurf for the 2011 season.
New ballpark[]
The Rays' current ownership has stated that Tropicana Field does not generate enough revenue and that it is too far from the Tampa Bay Area's population center.[37] In 2007, the team announced a plan to build a covered ballpark at the current site of Al Lang Field on the St. Petersburg waterfront, and a local referendum was scheduled to decide on public financing.[38] However, in the face of vocal opposition, the Rays withdrew the proposal in 2009 and stated they had abandoned all plans for a ballpark in downtown St. Petersburg waterfront, preferring a location nearer the center of Pinellas County or across the bay in Tampa.[39]
Since 2009, local officials, media, and business leaders have explored possibilities for a new stadium for the Rays somewhere in the Tampa Bay area.[40] However, St. Petersburg mayor Bill Foster repeatedly insisted that the Rays honor their use agreement with the city, which runs through 2027 and prohibits the team from entering into talks with other communities, resulting in a protracted stalemate.[citation needed]. Foster was replaced by Mayor Rick Kriseman in 2013.[41]
In October 2014, Sternberg, frustrated with efforts to build a new stadium in the Tampa Bay area, had discussions with Wall Street associates about moving the Rays to Montreal, which has been without a Major League Baseball franchise since the Montreal Expos moved to Washington, D.C. in 2005 to become the Washington Nationals.[42][43] On December 9, 2014, reports surfaced that owner Stuart Sternberg will sell the team if a new stadium is not built.[44]
On February 9, 2018, the team said that Ybor City is their preferred site for a new stadium.[45] However, at the December 2018 Winter Meetings in Las Vegas, Sternberg announced that plans for the proposed stadium in Ybor fell through, meaning the Rays were still on track to play at Tropicana Field until 2027.[46][47] Later in December 2018, the team sent a letter to Mayor Kriseman, foregoing an extension to search for a new stadium outside of the city.[48][49] On June 20, 2019, Major League Baseball's executive council gave the team permission to explore playing early-season home games in the Tampa Bay area and later-season home games in Montreal, with 2024 the earliest prospective date such an arrangement was thought to be feasible.[50][51]
Rays attendance has historically ranked among the lowest compared to all MLB teams including seasons following a playoff berth.[52] Rays attendance at Tropicana Field slightly improved in two seasons following playoff berths between 2008 and 2013 but dropped in two other seasons following playoff berths in the same span.[52] After the Rays earned the best AL record in 2010, average attendance in 2011 dropped by 4,100 per game.[52][53] In 2019 the Rays average attendance was 14,552 per game.[52]
Logo and uniform history[]
1998-2000: Devil Rays rainbow[]
During their first three seasons, the Devil Rays wore traditional white home and gray road uniforms with the text "Devil Rays" (home) and "Tampa Bay" (road) in an unconventional multicolor "rainbow" across the chest. The intended inaugural caps were also unusual: black with a purple brim at home and all black on the road, with both versions featuring a devil ray graphic and no letters at all.[54] However, for most games, the team wore their all-black alternate caps, featuring a smaller ray and the letters "TB" for both home and road games, with the purple-brimmed caps only occasionally seeing use late in the season. During the 1999 and 2000 seasons, the Devil Rays wore an alternate black jersey featuring the same rainbow text as the white and gray uniforms.
2001-2007: Rays greens[]
In 2001, the Devil Rays dropped the multicolor text and de-emphasized purple in favor of more green. They also changed the font on their jersey tops and shortened the name on the home whites to read simply "Rays" while keeping "Tampa Bay" on the road grays.[55]
In 2005, the home uniforms were again tweaked to include still more green. The primary home whites became a sleeveless jersey worn with green sleeved undershirts, and the primary home caps were changed from black to green. In addition, a small ray with a long tail was added under the name "Rays" on the chest of the home jerseys.[56]
2008-present[]
The current Rays primary uniform has been used with little change since the team officially shortened its name from "Devil Rays" to "Rays" for the 2008 season. The home jersey is a traditional white with the name "Rays" in dark blue across the chest and a yellow "sunburst" on the letter "R". The Rays' road uniform is gray, also with a sunburst and the team name across the chest. Both feature dark blue piping and caps featuring a white "TB" logo.[57]
The Rays' first alternate jersey also features the name "Rays" and a yellow sunburst on chest, but is a dark blue material with Columbia blue piping, white characters for the player name, and player numbers that are simply a white outline. This alternate jersey is worn both at home and on the road with either white or gray pants. The Rays' second alternate jersey is similar, but is a light Columbia blue. This second alternate was usually worn only for Sunday home games with white pants, paired since 2018 with an alternate dark blue cap with the team's classic "devil ray" logo; starting with the 2021 season, it has been worn regularly as a standard alternate jersey.
Initially, the dark blue "devil ray" alternate logo was only featured on the right sleeve of the home and away uniforms, but in 2019, the patch was added on both the dark blue and Columbia blue alternates.
"Turn Back the Clock" Nights[]
The Rays staged a "Turn Back the Clock" promotion with a retro theme and throwback uniforms several times early in their existence, and it has become an annual tradition since 2006.[58]
After the 2008 rebrand, the Rays first revisited the Devil Rays name in 2009, wearing the "rainbow" uniforms from their 1998 inaugural season.[58] They returned to the rainbow uniforms in 2018 in honor of the franchise's 20 year anniversary,[59] and have continued to wear them since, in 2019 and 2021, paired with an alternate dark blue hat bearing the throwback "devil ray" logo.
From 2012 to 2017, the Rays sported specially designed 1980 Tampa Bay Rays "faux-back" uniforms that represented what the team might have worn had the franchise existed during the late 1970s and early 80s. These uniforms were patterned after those of the San Diego Padres from the late 1970s, but with the Rays' name (including a circular yellow sunburst) and team colors of gold, navy, and powder blue.[60][61][62] In 2014, the Rays debuted a road version of the fauxback in an interleague game against the Chicago Cubs, this one with gold sleeves instead of navy. This version of the fauxback was later worn for two home games in 2017.[63]
In addition to their own uniforms, the franchise has also worn the uniforms of other historical local teams. The Rays have worn the uniforms of the Tampa Tarpons of the Florida State League (in 1999, 2006, and 2010), the St. Petersburg Pelicans of the Senior Professional Baseball Association (in 2008), the St. Petersburg Saints (in 2000 and 2007) and Tampa Smokers of the Florida International League (in 2011), and the University of Tampa Spartans (in 2000).[58]
The Rays' opponent on Turn Back the Clock night have also occasionally worn throwbacks from the same era as the Rays' retro uniforms. For example, the Houston Astros wore their 1980s "Rainbow Guts" uniforms, the New York Mets wore the road uniforms of their 1969 championship team,[64] the Chicago White Sox wore their red and white home uniforms from the 1970s, and the Baltimore Orioles wore their rare all-orange uniforms from the early 1970s.[65] Perhaps the most memorable such game was on June 23, 2007, when the Devil Rays wore St. Pete Saints uniforms from the early 1950s, and the Los Angeles Dodgers wore the gray road uniforms of the World Series-winning 1955 Brooklyn Dodgers to honor Don Zimmer, who played on that Dodger team and was a senior adviser for the Rays prior to his death. Rays management also gave away a bobblehead at the game featuring a young Zimmer in a Dodgers uniform and an older Zimmer in a Devil Rays uniform.[66]
Team media[]
Radio[]
WDAE (620 AM) has been the flagship station of the Rays radio network since 2009. The play-by-play announcers are Dave Wills and Andy Freed with Neil Solondz serving as the pregame and postgame host. Rich Herrera served as the host during pre- and post-game shows for the Tampa Rays Baseball Radio Network from 2005 to 2011.[67] The (Devil) Rays original radio team consisted of Paul Olden and Charlie Slowes, who broadcast games from 1998 to 2005. Slowes went to the Washington Nationals, where he is now lead announcer, while Olden pursued a photography career before replacing Bob Sheppard as the public address announcer at Yankee Stadium in 2008.[68] Rays games have been aired on WFLA 970 AM (1998–2004) and WHNZ 1250 AM (2005–2008) in the past.
In 2013, the Rays became the second team to enter into a contract to have games broadcast nationally by Compass Media Networks in a Game of the Week format. The broadcast team utilized during the 2013 season was TJ Rives calling play-by-play and a rotating circuit of analysts in Rob Dibble, Jeff Nelson, and Steve Phillips. 22 Rays games were produced nationally by Compass Media for the 2013 season.
Television[]
Bally Sports Sun, previously known as Fox Sports Sun, broadcasts the Rays' games on television. Through the 2008 season, many games also aired on Ion Television affiliate broadcast stations throughout the state of Florida, with WXPX-TV in Tampa as the flagship. However, after the 2008 season, Fox Sports signed an agreement to become the exclusive local broadcaster of the Rays, and will air 155 games per year through 2016.[69] Fox Sports Florida began broadcasting a portion of the schedule in HD beginning in 2007 after Tropicana Field's broadcast equipment was upgraded for in-house HD production. Most Rays home games are now broadcast in HD.
Dewayne Staats (play-by-play) and former MLB pitcher Brian Anderson (color commentary) are the TV voices of the Rays. For the first 11 seasons of the franchise, Staats teamed with former MLB pitcher Joe Magrane on the Rays' TV broadcasts. Magrane departed after conclusion of the 2008 season to take a position at the MLB Network.[citation needed] Former minors catcher and MLB manager Kevin Kennedy then served as the primary color commentator in 2009 and 2010, with Brian Anderson filling in on some road trips, after which Anderson took over as the everyday commentator from 2011.
Early on, as Staats' first wife was battling cancer, Paul Olden would occasionally fill in for Staats. As a result, Paul Olden ended up calling Wade Boggs' 3,000th hit.[citation needed]
Awards[]
Staats, Magrane, Wills, Olden and Slowes have all been nominated for the Ford C. Frick Award, the broadcasters' path to the Baseball Hall of Fame.
The Rookie[]
The Tampa Bay Devil Rays were featured in the movie, The Rookie, a 2002 drama directed by John Lee Hancock. It is based on the true story of pitcher Jim Morris, who had a brief but famous Major League Baseball career with the team.
Morris was a 35-year-old high school baseball coach who could repeatedly throw a baseball 98 mph (158 km/h), an ability that only a few major leaguers could equal at the time. He was persuaded to try out for professional ballclubs and signed with the Tampa Bay Devil Rays organization. Morris was initially assigned to the minor league Class AA Orlando Rays (now the Montgomery Biscuits), but quickly moved up to the AAA Durham Bulls and was called up to the "Bigs" during the September 1999 roster expansions.
Jim Morris spent parts of two seasons with the Tampa Bay Devil Rays as a reliever, pitching 15 innings in 21 games, with an earned run average of 4.80 and no decisions.
Rays fandom[]

Although widespread support has been slow to build with the lack of success in its first ten seasons, it has taken some cues from the powerhouses of the American League East. Whereas Red Sox fans are referred to as Red Sox Nation, the Orioles fan base is referred to Birdland, and Yankee fans are referred to as Yankees Universe (and the team itself being called the "Evil Empire"), the Rays have adopted the term Rays Republic for their fan base. The team has also had its fair share of notable fans and outrageous fan traditions over the years.
Mascots[]
The Rays have two primary mascots, Raymond and DJ Kitty.
Raymond was introduced during the team's inaugural season in 1998, and is referred to as a "seadog."[70] Raymond interacts with fans throughout the stadium prior to each home game, and can be seen rallying fans throughout games, either by walking through the stands, or climbing on top of the home dugout. After each Rays win at home, Raymond will wave a large "Rays Win" flag in the outfield.
DJ Kitty was introduced in 2010, initially through a video that would play on the scoreboard whenever the game situation called for a rally, in which a large anthropomorphic cat, wearing a Rays jersey, appeared on the screen wielding a turntable similar to those used by rap DJs. Loud music is played over the PA system while the arrival of DJ Kitty is proclaimed on display boards throughout the ballpark. Similarly to Raymond, DJ Kitty will interact with fans and pose for pictures in the stadium prior to each home game, and participates in activities with Raymond, including a mascot race and other between-inning entertainment. The character was created by Rays entertainment director Lou Costanza in an attempt to rally the Rays players and the fans at Tropicana Field.[71]
More Cowbell[]
The Rays' Cowbell was originally a promotional idea thought up by principal owner Stuart Sternberg, who got the idea from the Saturday Night Live sketch. Since then, it has become a standard feature of home games, something akin to the Sacramento Kings of the NBA and the bells their fans ring during games. Road teams have often considered the cowbell a nuisance. The cowbells are rung most prominently when the opposing batter has two strikes, when the opposing fans try to chant, and when the Rays make a good play.[72]
Professional wrestlers[]
Rays games are frequently visited by professional wrestlers, as there are a large number of wrestlers living in the Tampa Bay Area. The Nasty Boys (Brian Knobs and Jerry Sags), Brutus Beefcake, and Hulk Hogan all appear on a semi-regular basis at Rays games. John Cena appears on occasion.
The Rays held a "Legends of Wrestling Night" on May 18, 2007, featuring several wrestling matches after the game, an 8–4 loss to the Florida Marlins. Outfielder and wrestling fan Jonny Gomes ran interference for the Nasty Boys during the main event.[73]
A second "Wrestling Night" was held on April 19, 2008, after a 5–0 win over the Chicago White Sox. Gomes participated again, this time making a post-match save for the Nasty Boys.[74]
Team slogans[]
During Joe Maddon's tenure as the Rays manager, he and the team coined several slogans, including the mantra 9=8 for the 2008 season, explained by Maddon as meaning that if nine players play nine innings of hard baseball every day, that team would become one of the eight teams who qualify for the postseason. Prior to 2008 season, the Rays had never had a winning season in franchise history, much less a postseason appearance. The slogan morphed throughout the as the Rays surpassed their previous team record for wins in a single season by more than 30 wins, and ultimately clinched the AL East division title for their first postseason appearance in franchise history. After they clinched their postseason spot, it became 9=4, to represent the teams advancing to the LCS. When they won the ALDS, it became 9=2, for the teams advancing to the World Series. When they won the ALCS, it became 9=1, representing the possible World Series Championship. For the 2009 season, Maddon introduced a new slogan, '09 > '08, to represent that the season would be "greater" than the previous year.
Also while Maddon was the Rays' manager, Rays players and coaches sported mohawk haircuts, nicknamed "rayhawks". The trend started during their 2008 World Series run, and continued for several years until Maddon's departure following the 2014 season.[75]
Roster[]
Tampa Bay Rays roster
| ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Active roster | Inactive roster | Coaches/Other | ||||
|
Pitchers
Bullpen
|
Catchers
Infielders
Outfielders
Designated hitters
|
Pitchers
Infielders
Outfielders
|
Manager
Coaches
60-day injured list
COVID-19 related injured list
| |||
Minor league affiliations[]
The Tampa Bay Rays farm system consists of seven minor league affiliates.[76]
| Level | Team | League | Location | Ballpark |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Triple-A | Durham Bulls | Triple-A East | Durham, North Carolina | Durham Bulls Athletic Park |
| Double-A | Montgomery Biscuits | Double-A South | Montgomery, Alabama | Montgomery Riverwalk Stadium |
| High-A | Bowling Green Hot Rods | High-A Central | Bowling Green, Kentucky | Bowling Green Ballpark |
| Low-A | Charleston RiverDogs | Low-A East | Charleston, South Carolina | Joseph P. Riley Jr. Park |
| Rookie | GCL Rays | Gulf Coast League | Port Charlotte, Florida | Charlotte Sports Park |
| DSL Rays 1 | Dominican Summer League | Boca Chica, Santo Domingo | Tampa Bay Rays Complex | |
| DSL Rays 2 |
Awards, league leaders, and individual records[]
Baseball Hall of Famers[]
| Tampa Bay Rays Hall of Famers | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Affiliation according to the National Baseball Hall of Fame and Museum | |||||||||
|
Florida Sports Hall of Fame[]
| Rays in the Florida Sports Hall of Fame | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| No. | Name | Position | Tenure | Notes |
| 11, 56 | Hal McRae | Coach/Manager | 2001–2002 | Elected mainly on his performance with Kansas City Royals, born in Avon Park |
| 12 | Wade Boggs | 3B | 1998–1999 | Elected mainly on his performance with Boston Red Sox, attended Henry B. Plant High School in Tampa |
| 14 | Lou Piniella | Manager | 2003–2005 | Born in Tampa |
| 22 | Johnny Damon | OF | 2011 | Raised in Orlando |
| 24 | Tino Martinez | 1B | 2004 | Elected mainly on his performance with New York Yankees, born and raised in Tampa, attended University of Tampa |
| 29 | Fred McGriff | 1B | 1998–2001, 2004 | Elected mainly on his performance with Atlanta Braves, born in Tampa |
Retired numbers[]

The Tampa Bay Rays have retired three numbers. These numbers are displayed to the left of the center field scoreboard and "K Counter" on a small wall.
Jackie Robinson's number 42 was retired by all of Major League Baseball.
|
Selected individual franchise single-season records[]
Statistics below are through the end of the 2018 season.
- Highest batting average: .325, Jeff Keppinger (2012)
- Most games: 162, Aubrey Huff (2003), Evan Longoria (2014), and Delmon Young (2007)
- Most hits: 198, Aubrey Huff (2003)
- Highest slugging %: .627, Carlos Peña (2007)
- Most doubles: 47, Aubrey Huff (2003)
- Most triples: 19, Carl Crawford (2004)
- Most home runs: 46, Carlos Peña (2007)
- Most RBIs: 121, Carlos Peña (2007)
- Most stolen bases: 60, Carl Crawford (2009)
- Most wins: 21, Blake Snell (2018)
- Lowest ERA: 1.89, Blake Snell (2018)
- Strikeouts: 252, Chris Archer (2015)
- Complete games: 11, James Shields (2011)
- Shutouts: 4, James Shields (2011)
- Saves: 48, Fernando Rodney (2012)
Team salaries[]
Opening Day payrolls for 25-man roster (since 1998):[77][78][79]
| Opening Day Salary | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Year | Salary | |||
| 2019 | $52,150,800[80] | |||
| 2018 | $67,482,000[81] | |||
| 2017 | $69,982,520 | |||
| 2016 | $57,097,310 | |||
| 2015 | $73,649,584 | |||
| 2014 | $82,035,490 | |||
| 2013 | $51,903,072 | |||
| 2012 | $64,173,500 | |||
| 2011 | $41,053,571 | |||
| 2010 | $71,924,471 | |||
| 2009 | $63,313,034 | |||
| 2008 | $43,820,597 | |||
| 2007 | $24,123,500 | |||
| 2006 | $35,417,967 | |||
| 2005 | $29,679,067 | |||
| 2004 | $29,556,667 | |||
| 2003 | $19,630,000 | |||
| 2002 | $34,380,000 | |||
| 2001 | $56,980,000 | |||
| 2000 | $64,407,910 | |||
| 1999 | $37,812,500 | |||
| 1998 | $25,317,500 | |||
Footnotes[]
- a The Finish column lists regular season results and excludes postseason play.
- b The Wins and Losses columns list regular season results and exclude any postseason play. Regular and postseason records are combined only at the bottom of the list.
- c The GB column lists "Games Back" from the team that finished in first place that season. It is determined by finding the difference in wins plus the difference in losses divided by two.
- d ALDS stands for American League Division Series.
- e ALCS stands for American League Championship Series.
- f CPOY stands for Comeback Player of the Year
- g CYA stands for Cy Young Award.
- h MOY stands for Manager of the Year.
- j ROY stands for American League Rookie of the Year.
See also[]
- Baseball awards
- List of MLB awards
- Tampa Bay Rays all-time roster
- Ted Williams Museum and Hitters Hall of Fame (including Tampa Bay Rays exhibit)
References[]
- ^ Jump up to: a b "Time to shine: Rays introduce new name, new icon, new team colors and new uniforms". RaysBaseball.com (Press release). MLB Advanced Media. November 8, 2007. Retrieved June 9, 2019.
- ^ Chastain, Bill (February 7, 2018). "Rays set to celebrate 20th anniversary in '18". RaysBaseball.com. MLB Advanced Media. Retrieved February 8, 2018.
Prominent among those items was the 20th anniversary logo that will appear on the left sleeve of all Rays 2018 regular-season jerseys and caps. The home-plate shaped patch features the number 20, a sunburst and a variation of the original fish -- all in the Rays' modern colors.
- ^ "Rays All-Time Uniforms and Logos". RaysBaseball.com. MLB Advanced Media. Retrieved February 11, 2019.
- ^ "Tampa Bay Rays Team History & Encyclopedia". Baseball-Reference.com.
- ^ "Devil Rays' ownership transfer approved". ESPN. Associated Press. November 17, 2005. Retrieved September 12, 2017.
- ^ Reuter, Joel (June 11, 2013). "Is Red Sox-Rays the Most Underrated Heated Rivalry in Baseball?". Bleacher Report. Retrieved September 12, 2017.
- ^ "Tampa Bay Rays Team History & Encyclopedia". Baseball-Reference.com. Retrieved November 11, 2020.
- ^ Chass, Murray (November 11, 1992). "BASEBALL; Look What Wind Blew Back: Baseball's Giants". The New York Times. Retrieved September 12, 2017.
- ^ "Player Profiles Bobby Abreu". BaseballLibrary.com. Archived from the original on October 12, 2007. Retrieved September 12, 2008.
- ^ "The 30 worst trades in MLB history". December 7, 2015. Archived from the original on December 22, 2015.
- ^ "Franchise Timeline". Tampa Bay Rays.
- ^ Topkin, Marc (August 8, 1999). "3000!". St. Petersburg Times. Retrieved June 18, 2007.
- ^ Topkin, Marc (August 25, 2005). "New owner draws Lou's rap". St. Petersburg Times. Retrieved June 8, 2021.
- ^ "Devil Rays buy out Piniella's final season for $2.2M". Associated Press. September 30, 2005. Retrieved June 8, 2021.
- ^ Rays: Payroll will rise; question is, how much?
- ^ Fitt, Aaron (June 15, 2007). "Price's excellence almost defies words". Baseball America. Retrieved June 30, 2007.
- ^ Foss, Darren (August 17, 2008). "Rays Shine during dream season". Bleacher Report. Retrieved June 8, 2021.
- ^ "Liriano pitches 7 innings as Twins beat Rays 4-1". Archived from the original on September 26, 2008.
- ^ Marc Topkin (July 25, 2010). "Garza has Rays first no-hitter". St. Petersburg Times. Archived from the original on July 30, 2010. Retrieved July 25, 2010.
- ^ Beck, Jason (July 31, 2014). "Tigers land huge Deadline prize in Price". Major League Baseball. Retrieved July 31, 2014.
- ^ "Andrew Friedman named Dodgers' president of baseball operations, Colletti becomes advisor". Major League Baseball. Retrieved October 26, 2015.[permanent dead link]
- ^ Chastain, Bill (October 24, 2014). "Maddon opts out of contract, leaves Rays". Major League Baseball. Retrieved April 10, 2021.
- ^ "Joe Maddon". Baseball Reference. Sports Reference LLC. Retrieved December 15, 2014.
- ^ "'Dynamic' Cash gets call as Rays manager". ESPN. December 5, 2014. Retrieved May 9, 2021.
- ^ Topkin, Marc (December 20, 2017). Tampa Bay Times https://www.tampabay.com/sports/baseball/rays/The-rebuild-begins-in-earnest-Rays-trade-Evan-Longoria-to-Giants_163797009/. Retrieved June 14, 2021. Missing or empty
|title=(help) - ^ Castrovince, Anthony (October 25, 2020). "UNBELIEVABLE! Rays walk off in G4, tie WS". MLB.com. Retrieved October 25, 2020.
- ^ Jump up to: a b "Tampa Bay Rays History & Encyclopedia". Baseball-Reference.com. Retrieved September 28, 2008.
- ^ "Most Valuable Player MVP Awards & Cy Young Awards Winners". Baseball-Reference.com. Retrieved November 14, 2018.
- ^ "Manager of the Year Award Winners". Baseball-Reference.com. Retrieved November 10, 2020.
- ^ Ryan, Bob (October 19, 2008). "Tampa Bay steps up as new rival". The Boston Globe. Retrieved September 12, 2017.
- ^ Topkin, Marc (October 9, 2008). "Rays-Red Sox rivalry dates to 2000". Tampa Bay Times. Retrieved September 12, 2017.
- ^ Cafardo, Nick (April 27, 2005). "Schilling and Piniella exchange barbs". The Boston Globe. Retrieved September 12, 2017.
- ^ Romano, John (October 9, 2008). "Message pitch in Boston helped carry Rays' season". Tampa Bay Times. Retrieved September 12, 2017.
- ^ Cristodero, Damian (March 7, 2005). "Rays: Fans as scarce as wins". St. Petersburg Times. Archived from the original on December 27, 2017. Retrieved September 12, 2017.
- ^ "mcubed.net : MLB : Series records : Miami Marlins against Tampa Bay Rays". Retrieved September 30, 2014.
- ^ "Tampa Bay Rays home". mlb. Retrieved August 21, 2020.
- ^ Sharockman, Aaron; Nohlgren, Stephen (September 5, 2008). "Why replace the Trop?". Tampa Bay Times. Retrieved September 12, 2017.
- ^ Williams, Pete (November 28, 2007). "Rays unveil plans for new stadium". Major League Baseball Advanced Media. Retrieved September 12, 2017.
- ^ Gonzalez, Alden (May 22, 2009). "St. Pete waterfront ballpark a no-go". Major League Baseball Advanced Media. Retrieved September 12, 2017.
- ^ Nohlgren, Stephen (March 16, 2010). "ABC Coalition make its Tampa Bay Rays stadium pitch to Pinellas County". Tampa Bay Times. Retrieved September 12, 2017.
- ^ "Rick Kriseman tops Bill Foster in St. Petersburg mayor's race". Tampa Bay Times. Retrieved April 30, 2021.
- ^ Madden, Bill (October 25, 2014). "MLB commish Bud Selig's nightmare is Cubs dream as Joe Maddon leaves Rays". New York Daily News. Retrieved September 12, 2017.
- ^ "Report: Rays owner discussed move to Montreal". TSN. October 26, 2014. Retrieved September 12, 2017.
- ^ "Tampa Bay Rays owner Stuart Sternberg said he will sell team if new stadium not built". Sports Illustrated. December 9, 2014. Retrieved September 12, 2017.
- ^ "Stuart Sternberg: Tampa's Ybor City is top choice for next Rays ballpark".
- ^ Topkin, Marc (December 11, 2018). "Rays say current Ybor stadium project is dead, remain committed to Tampa Bay area – for now". Tampa Bay Times. Times Publishing Company. Retrieved December 12, 2018.
- ^ Lacques, Gabe (December 11, 2018). "Rays' new stadium proposal dead – and clock ticking on alternatives to Tropicana Field". USA Today. Gannett Company. Retrieved December 12, 2018.
- ^ Frago, Charlie; Soloman, Josh (December 18, 2018). "It's official: Tampa Bay Rays tell St. Petersburg they are finished looking elsewhere, for now". Tampa Bay Times. Times Publishing Company. Retrieved December 20, 2018.
- ^ "Rays to St. Pete: Finished looking elsewhere, for now". ESPN. December 19, 2018. Retrieved December 20, 2018.
- ^ Feinsand, Mark (June 20, 2019). "Rays to explore idea of TB-Montreal split season". RaysBaseball.com. MLB Advanced Media. Retrieved June 21, 2019.
- ^ Passan, Jeff (June 20, 2019). "Rays to explore splitting games with Montreal". ESPN.com. ESPN Internet Ventures. Retrieved June 21, 2019.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c d "Rays reach Series, but face familiar question over new park". www.baynews9.com. Retrieved November 23, 2020.
- ^ "Tampa Bay Rays MLB Team History - Major League Baseball - ESPN". ESPN.com. ESPN. Retrieved November 23, 2020.
- ^ "National Baseball Hall of Fame - Dressed to the Nines - Uniform Database". exhibits.baseballhalloffame.org.
- ^ "National Baseball Hall of Fame - Dressed to the Nines - Uniform Database". exhibits.baseballhalloffame.org.
- ^ "National Baseball Hall of Fame - Dressed to the Nines - Uniform Database". exhibits.baseballhalloffame.org.
- ^ "National Baseball Hall of Fame - Dressed to the Nines - Uniform Database". exhibits.baseballhalloffame.org.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c "Q&A: Tampa Bay Rays wear variety of throwback uniforms". Tampa Bay Times.
- ^ "20 ways the Rays will commemorate their 20th anniversary". Tampa Bay Times.
- ^ "Rays Turn Back the Clock with a fake throwback jersey". Tampa Bay Times. June 30, 2012. Retrieved January 27, 2013.
- ^ Matt Moore wins again, Rays cruise past White Sox. Bay News 9 (2013-07-06). Retrieved on 2013-07-23.
- ^ Rays' throwback uniforms to a time when they didn't exist. Content.usatoday.com (2012-06-20). Retrieved on 2013-07-23.
- ^ "Rays Join Cubs' Throwback Weekend With 'Fauxback'". SBNation. August 9, 2014.
- ^ "Lots of fun at the ballpark". Ocala Star-Banner. Retrieved August 1, 2017.
- ^ "Rays will turn back the clock Aug. 13 with Village People". Tampa Bay Times.
- ^ "Rays celebrate Turn Back the Clock Night; Zimmer bobblehead, former Dodgers mates featured at Rays-Dodgers game". Tampa Bay Rays. Archived from the original on March 10, 2012.
- ^ "Rich Herrera" 98.7 The Fan http://tampa.cbslocal.com/2012/08/02/rich-herrera-the-fan-cbs/
- ^ Anthony Mccarron (November 29, 2009). "Paul Olden, public address announcer at Yankee Stadium, gets nod from 'Voice of God' Bob Sheppard". New York: NYDailyNews.
- ^ Maury Brown. "Long Rays Forecast: FSN Florida Signs 8-Year Extension with Tampa Bay". bizofbaseball.com.
- ^ "Rays Mascots". MLB.com. Retrieved August 7, 2021.
- ^ Virginia Johnson (October 7, 2010). "DJ Kitty is the Tampa Bay Rays best kept secret". Bay News 9. Retrieved October 7, 2010.
- ^ FOX. "Tampa Bay news, weather forecast, radar, and sports from WTVT-TV - FOX 13 News - FOX 13 Tampa Bay". FOX13news.
- ^ "Notes: Gomes enjoys Wrestling Night". Tampa Bay Rays.
- ^ "'Wrestling Night' returns to The Trop". Tampa Bay Rays.
- ^ "Mohawk fever spreading among Rays". Major League Baseball. Retrieved June 5, 2016.
- ^ "Tampa Bay Rays Minor League Affiliates". Baseball-Reference. Sports Reference. Retrieved May 14, 2020.
- ^ "Cot's Baseball Contracts: Tampa Bay Rays". mlbcontracts.blogspot.com.
- ^ "Tampa Bay Rays Salaries". USA Today. June 18, 2016.
- ^ Tampa Bay Rays 2013 Player Salaries and Team Payroll – ESPN. Espn.go.com. Retrieved on 2013-07-23.
- ^ Topkin, Marc (March 27, 2019). "Rays 2019 salaries: The $52 million men". Tampa Bay Times. Tampabay.com. Retrieved March 27, 2019.
- ^ Topkin, Marc (March 28, 2018). "Rays salaries: The $67.5 million men". Tampa Bay Times. Tampabay.com. Retrieved September 30, 2018.
External links[]
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Tampa Bay Rays. |
- Tampa Bay Rays
- Major League Baseball teams
- Grapefruit League
- Baseball teams established in 1998
- Professional baseball teams in Florida
- Sports in St. Petersburg, Florida
- 1998 establishments in Florida














