Tempest (keelboat)
 | |
| Development | |
|---|---|
| Designer | Ian Proctor |
| Location | United Kingdom |
| Year | 1965 |
| No. built | 850 (by 1994) |
| Builder(s) | O'Day Corp. |
| Role | one-design racer |
| Name | Tempest |
| Crew | two |
| Boat | |
| Crew | two |
| Boat weight | 1,021 lb (463 kg) |
| Draft | 3.58 ft (1.09 m) |
| Trapeze | single |
| Hull | |
| Type | monohull |
| Construction | fiberglass |
| LOA | 22.00 ft (6.71 m) |
| LWL | 20.00 ft (6.10 m) |
| Beam | 6.50 ft (1.98 m) |
| Hull appendages | |
| Keel/board type | lifting weighted bulb keel |
| Ballast | 440 lb (200 kg) |
| Rudder(s) | internally-mounted spade-type rudder |
| Rig | |
| Rig type | Bermuda rig |
| Sails | |
| Sailplan | fractional rigged sloop |
| Mainsail area | 164 sq ft (15.2 m2) |
| Jib/genoa area | 82.78 sq ft (7.691 m2) |
| Spinnaker area | 225 sq ft (20.9 m2) |
| Total sail area | 247 sq ft (22.9 m2) |
| Racing | |
| D-PN | 83.4 |
| Former Olympic class | |
The Tempest is a trailerable, one-design racing sailboat that was designed by British naval architect Ian Proctor and first built in 1965.[1][2][3]
Production[]
In the past the design was built by O'Day Corp. and in the United States and by in France. A total of 850 boats had been reported as built by 1994. Today it is built by of Germany and remains in production.[1][3][4]
Design[]


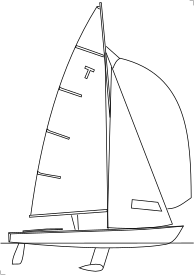
The Tempest is a racing keelboat, built predominantly of fiberglass, with wood trim. It has a fractional sloop rig with aluminum spars. The hull has a spooned raked stem, a plumb transom, an internally mounted spade-type rudder controlled by a tiller and a lifting, weighted, bulb keel. It displaces 1,021 lb (463 kg) and carries 440 lb (200 kg) of lead keel ballast. Construction includes three transverse bulkheads to aid flotation. The boat has a rear deck above the rudder.[1][3]
The boat has a draft of 3.58 ft (1.09 m) with the keel locked in the extended position.[1]
For sailing the design is equipped with a single trapeze, an unusual feature on a keelboat. Jib and mainsail windows for visibility are permitted in the class rules, but the sizes are controlled.[3]
The design has a Portsmouth Yardstick DP-N racing average handicap of 83.4 and an RYA-PN of 942. It is normally raced with a crew of two sailors.[3][5][6]
Operational history[]
The boat was selected as an Olympic class and raced at the 1972 and the 1976 Summer Olympics.[1][3]
The boat is supported by an active class club that organizes racing events, the International Tempest Class Association.[7]
In a 1994 review Richard Sherwood wrote, "the International Class Tempest was an Olympic boat in 1972 and 1976. She is fast. Tempest is a one-design, and class rules are strict ... The mast’s design and material are optional, but the mast may not rotate. Older boats have thicker, stiffer masts and, in addition to the diamond shrouds and spreaders found today, additional swept-back spreaders. Good racing boats are light at the ends and rigid, although this is not necessary in the deck ... Only one person may use the trapeze, and safety equipment is required."[3]
Racing[]
Olympics[]
Reference[8]
| Event | Gold | Silver | Bronze |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1972 Kiel |
Valentin Mankin Vitali Dyrdyra |
Alan Warren David Hunt |
Glen Foster Peter Dean |
| 1976 Montreal |
John Albrechtson Ingvar Hansson |
Valentin Mankin Vladyslav Akimenko |
Dennis Conner Conn Findlay |
World Championships[]
Reference[9]
| Gold | Silver | Bronze | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1967 Weymouth | Reg White |
||
| 1968 Grosse Pointe | |||
| 1969 Riva del Garda | |||
| 1970 Quiberon | John Linville |
Ben Staartjes Cees Kurpershoek |
Falconer Dyson |
| 1971 Marstrand | Glen Foster Peter Dean |
||
| 1972 | not held because of the 1972 Summer Olympics | ||
| 1973 Napoli | Valentin Mankin |
Dotti Sibello |
Dyson Lindsay |
| 1974 Medemblik | Uwe Mares |
Krick Heldt |
Mebel Lohmann |
| 1975 Association Island | Giuseppe Milone Roberto Mottola |
John Albrechtson Ingvar Hansson |
Uwe Mares |
| 1976 | not held because of the 1976 Summer Olympics | ||
| 1977 Strömstad | John Albrechtson Ingvar Hansson |
Höss |
Greve |
| 1978 Castelletto | John Albrechtson Ingvar Hansson |
Twelkmeyer Schumacher |
|
| 1979 Hayling Island | Wolf Stadler |
Moncur Lowther | |
| 1980 Medemblik | Haas Jörg |
Greve Pildner | |
| 1981 | no championship | ||
| 1982 Seebrück | |||
| 1983 Weymouth | |||
| 1984 Portorož | |||
| 1985 Medemblik | |||
| 1986 St. Gilgen | |||
| 1987 Portorož | |||
| 1988 Spiez | |||
| 1989 Malcesine | |||
| 1990 Medemblik | |||
| 1991 St. Gilgen | |||
| 1992 Balatonfüred | |||
| 1993 Warnemünde | Vincent Hösch |
||
| 1994 Brunnen | |||
| 1995 Medemblik | |||
| 1996 Villach | |||
| 1997 Hartlepool | |||
| 1998 Malcesine | |||
| 1999 Saint-Raphaël | Werner Meier |
||
| 2000 Travemünde | |||
| 2001 Malcesine | |||
| 2002 Brighton | |||
| 2003 Grandson | |||
| 2004 La Rochelle | |||
| 2005 Attersee | |||
| 2006 Fort-de-France | |||
| 2007 Warnemünde | |||
| 2008 Weymouth | |||
| 2009 Spiez | |||
| 2010 Hoorn | |||
| 2011 Ebensee | |||
| 2012 Quiberon | |||
| 2013 Travemünde | |||
| 2014 Travemünde | |||
European Championships[]
Reference[10]
European championships were only held when a World Championship was held outside the European continent. After 1980 no further European championships were held.
| Event | Gold | Silver | Bronze |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1966 Burnham-on-Crouch |
Keith Musto Ian Winter |
||
| 1968 Alassio |
Carlo Massone |
||
| 1969 Kiel |
|||
| 1972 La Rochelle |
Ben Staartjes Cees Kurpershoek |
Tomasz Holc Rutkowski |
Valentin Mankin Vitaly Dyrdyra |
| 1975 Brunnen |
Uwe Mares |
Dotti Girardi |
Kohler Frey |
| 1976 Alassio |
John Albrechtson Ingvar Hansson |
||
| 1977 Strömstad |
John Albrechtson Ingvar Hansson |
||
| 1978 Kiel |
John Albrechtson Ingvar Hansson |
Twelkmeyer | |
| 1979 Attersee |
See also[]
- List of sailing boat types
References[]
- ^ a b c d e McArthur, Bruce (2020). "Tempest International sailboat". sailboatdata.com. Archived from the original on 18 November 2020. Retrieved 18 November 2020.
- ^ McArthur, Bruce (2020). "Ian Proctor 1918 - 1992". sailboatdata.com. Archived from the original on 18 November 2020. Retrieved 18 November 2020.
- ^ a b c d e f g Sherwood, Richard M.: A Field Guide to Sailboats of North America, Second Edition, pages 116-117. Houghton Mifflin Company, 1994. ISBN 0-395-65239-1
- ^ Mader Bootswerft. "Tempest". mader-boote.de. Archived from the original on 18 November 2020. Retrieved 18 November 2020.
- ^ "Keelboat Classes". US Sailing. Archived from the original on 16 August 2012. Retrieved 31 July 2012.
- ^ "Portsmouth Number List 2011" (PDF). Royal Yachting Association. Archived from the original (PDF) on 11 September 2018. Retrieved 17 September 2012.
- ^ McArthur, Bruce (2020). "International Tempest Class Association". sailboatdata.com. Archived from the original on 18 November 2020. Retrieved 18 November 2020.
- ^ "Sailing Olympic Games - Tempest". sports123.com. Archived from the original on 6 February 2020. Retrieved 18 November 2020.
- ^ "World Championships - Tempest". sports123.com. Archived from the original on 4 November 2011. Retrieved 18 November 2020.
- ^ "European Championships - Tempest". sports123.com. Archived from the original on 5 November 2011. Retrieved 18 November 2020.
External links[]
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Tempest (keelboat). |
- Tempest (keelboat)
- Classes of World Sailing
- Olympic sailing classes
- 1960s sailboat type designs
- Sailboat type designs by British designers
- Sailing yachts
- Two-person sailboats
- Trailer sailers
- Sailboat types built by O'Day Corp.