Ter Sami
| Ter Sami | |
|---|---|
| saa´mekiil / са̄мькӣлл | |
| Native to | Russia |
Native speakers | 2 (2010)[1] |
Uralic
| |
| Latin script (historical), Cyrillic script (current) [2] | |
| Language codes | |
| ISO 639-3 | sjt |
| Glottolog | ters1235 |
| ELP | Ter Saami |
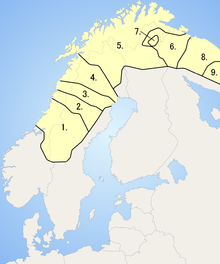 Ter Sámi is number 9 on the map. | |
Ter Sami is the easternmost of the Sámi languages. It was traditionally spoken in the northeastern part of the Kola Peninsula, but now it is a moribund language; in 2004, only ten speakers were left. By 2010, the number of speakers had decreased to two.[1]
History[]

Photo taken in 2006.
In the end of the 19th century, there were six Ter Sámi villages in the eastern part of the Kola Peninsula, with a total population of approximately 450. In 2004, there were approximately 100 ethnic Ter Sámi of whom two elderly persons speak the language; the rest have shifted their language to Russian.[3]
The rapid decline in the number of speakers was caused by Soviet collectivisation, during which its use was prohibited in schools and homes[citation needed] in the 1930s, and the largest Ter Sámi village, Yokanga, was declared "perspectiveless" and its inhabitants were forced to move to the Gremikha military base.[3]
Phonology[]
Consonants[]
| Labial | Alveolar | Post- alveolar |
Palatal | Velar | Glottal | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Plosive | p b | t d | k ɡ | |||
| Affricate | t͡s d͡z | t͡ʃ d͡ʒ | ||||
| Fricative | f v | s z | ʃ ʒ | x | h | |
| Nasal | m | n̥ n | ŋ | |||
| Approximant (Lateral) |
j | |||||
| l̥ l | ||||||
| Trill | r̥ r |
- All consonants except for /j/ may be palatalized [ʲ].
- Consonants /t, d/ can also sound as half-palatalized.
Vowels[]
| Front | Central | Back | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| short | long | short | long | short | long | |
| Close | i | iː | ɨ | ɨː | u | uː |
| Mid | ɛ | o | ||||
| Open | a | aː | ɔ | |||
- After palatalized consonants, /ɛ/ is realized as [e].[4]
Documentation[]
There are no educational materials or facilities in Ter Sámi, and the language has no standardized orthography. The language is incompletely studied and documented; text specimens, audio recordings as well as dictionaries for linguistic purposes exist,[5][6]
The earliest known documentation of Sámi languages is a short Ter Sámi vocabulary collected by the British explorer Stephen Burrough in 1557; the vocabulary was published by Richard Hakluyt.[7]
Writing system[]
A spelling system for Ter Sámi using the Latin alphabet and based on Skolt Sámi was developed in the 1930s. After the Second World War, this was replaced or created by a system using the Cyrillic alphabet, and based on Kildin Sámi.[8]
Example of words in Ter saami[9][]
выэййвэ = head
ныкчым = tongue
кидт = hand
лоннҍт = bird
чадце = water
ке̄ддҍкэ = stone
аббьрэ = rain
толл = fire
Grammar[10][]
Ter saami has 8 cases, Nominative, Genetive, Accusative, Essive, Inessive-Lative, Dative-Illative, Abessive and Cominative.
| case | singular | plural |
|---|---|---|
| Nom | - | change of the main part of word |
| Gen | change of the main part of word | change of the main part of word |
| Acc | change of the main part of word | t |
| Essive | n | n |
| Inessive | s't | n |
| Dative | a, i | t |
| Abessive | ta | ta |
| Cominative | n | k'em, g'em |
Examples of the Genetive
(in the UPA script)
abre' paл = raining cloud
pɛci̮ pal'čemi̮š = slaughter of deer
taja oлmi̮j = German inhabitant
tara parnɛ = Russian boys
Plurals
In the Nominative case the base word changes when a plural is made.
| Word | Meaning | Plural | Meaning |
|---|---|---|---|
| mi̮rr | forest | mi̮r | forests |
| k'iлл | language | k'iл | languages |
| šiɛn'n' | swamp | šiɛn' | swamps |
| tast | star | taast | stars |
The word "ku", meaning: who, which in the cases.
| Case | Singular | Plural |
|---|---|---|
| Nominative | ku | kogg |
| Genetive | konn | kojt |
| Accusative | konn | kojt |
| Essive | kon'n'in | kojn |
| Inessive | kon'n'es't | kojn |
| Dative | kon'n'i | kojt |
| Abessive | konta | kojta |
| Cominative | kon'in | kojgujm |
Notes[]
- ^ Jump up to: a b Sámi Languages Disappearing Barents Observer
- ^ "Ter Sámi alphabet, pronunciation and language". Omniglot.com. Retrieved 27 November 2017.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Tiuraniemi Olli: "Anatoli Zaharov on maapallon ainoa turjansaamea puhuva mies", Kide 6 / 2004.
- ^ Tereškin, Sergej N. (2002). Jokan'gskij dialekt Saamskogo Jazyka. Sankt Petersburg: Rossijskij Gosudarstvennyj pedagogičeskij Universitet imeni.
- ^ Itkonen T. I.: "Koltan- ja kuolanlapin sanakirja", Helsinki: Société Finno-Ougrienne, 1958.
- ^ Itkonen T. I.: "Koltan- ja kuolanlappalaisia satuja", 1931.Memoires de la Société Finno-Ougrienne 60
- ^ Aikio Samuli: "Olbmot ovdal min - Sámiid historjá 1700-logu rádjái". Girjegiisá: Kárášjohka, 1992.
- ^ "Ter Sami alphabet, pronunciation and language". Omniglot.com. Retrieved 16 February 2018.
- ^ "Tersamisk - Allkunne". www.allkunne.no (in Norwegian). Retrieved 2021-01-24.
- ^ Tereškin, Sergej (2002). . Йоганьгский диалект саамского языка. Saint Petersburg.
External links[]
 Media related to Ter Sami language at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Ter Sami language at Wikimedia Commons- Ter saami dictionary
- Die Struktur der Nominalphrase im Tersaamischen (in German)
- Koltan- ja kuolanlapin sanakirja (dictionary in German, contains Ter Saami)
- Koltan- ja kuolanlappalaisia satuja (texts in Kola Saami languages, includes Ter Saami)
- Sámi in Russia
- Eastern Sámi languages
- Languages of Russia
- Endangered Uralic languages
- Endangered languages of Europe