Time in Svalbard
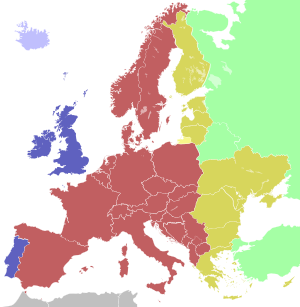
| Western European Time / Greenwich Mean Time (UTC) | |
| Western European Time / Greenwich Mean Time (UTC) | |
| Western European Summer Time / British Summer Time / Irish Standard Time (UTC+1) | |
| Central European Time (UTC+1) | |
| Central European Summer Time (UTC+2) | |
| Eastern European Time / Kaliningrad Time (UTC+2) | |
| Eastern European Time (UTC+2) | |
| Eastern European Summer Time (UTC+3) | |
| Moscow Time / Turkey Time (UTC+3) |
Svalbard, an archipelago in the Arctic Ocean belonging to Norway, observers the same time zone; Central European Time (CET; UTC+01:00) as standard time and Central European Summer Time (CEST; UTC+02:00) during daylight saving time.[1][2] DST begins in the last Sunday of March, and ends in the last Sunday of October.[3]
Since Svalbard is located north of the Arctic Circle, it experiences midnight sun in summer and polar night in winter. At the 74° parallel north, the midnight sun lasts 99 days and polar night 84 days, while the respective figures at 81° are 141 and 128 days.[4] In Longyearbyen, midnight sun lasts from 20 April until 23 August, and polar night lasts from 26 October to 15 February.[5]
History[]
Svalbard became part of Norway on 14 August 1925, and then officially adopted laws of Norway, including same time zone as Norway. Before that there was no official time zone, and due to lack of radios local time was likely kept. Norway adopted a time zone in 1895.
Svalbard introduced DST in 1980, at the same time as the rest of Norway.[6]
Notation[]
IANA time zone database[]
In the IANA time zone database, Svalbard is given one zone in the file zone.tab – Arctic/Longyearbyen. Below is data for Svalbard directly from zone.tab of the IANA time zone database; columns marked with * are the columns from zone.tab itself:[7]
| c.c.* | coordinates* | TZ* | Comments | UTC offset | DST |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SJ | +7800+01600 | Arctic/Longyearbyen | +01:00 | +02:00 |
See also[]
References[]
- ^ Time in Svalbard. TimeAndDate.com. Retrieved 7 May 2021.
- ^ Time changes in Svalbard. WorldData.info. Retrieved 7 May 2021.
- ^ Svalbard at The World Factbook. Central Intelligence Agency (CIA). Retrieved 7 May 2021.
- ^ Torkildsen, Torbjørn; et al. (1984). Svalbard: vårt nordligste Norge (in Norwegian). Oslo: Forlaget Det Beste. pp. 96–97. ISBN 82-7010-167-2.
- ^ "Svalbard". Norwegian Polar Institute. Archived from the original on 15 April 2012. Retrieved 7 May 2021.
- ^ "Daylight Saving Time History in Svalbard". TimeAndDate.com. Retrieved 2021-11-07.
- ^ Europe (2020 edition) at the tz database. Internet Assigned Numbers Authority (IANA). Retrieved 20 May 2021.
External links[]
- Current time in Svalbard at time.is
- Time in Norway
- Svalbard stubs
- Standards and measurement stubs