Topaz
| Topaz | |
|---|---|
 Topaz crystal on white matrix | |
| General | |
| Category | Nesosilicate minerals |
| Formula (repeating unit) | Al2SiO4(F,OH)2 |
| Strunz classification | 9.AF.35 |
| Crystal system | Orthorhombic |
| Crystal class | Dipyramidal (mmm) H-M symbol: (2/m 2/m 2/m) |
| Space group | Pbnm |
| Unit cell | a = 4.65 Å, b = 8.8 Å, c = 8.4 Å; Z = 4 |
| Identification | |
| Color | Colorless (if no impurities), white, blue, brown, orange, gray, yellow, yellowish brown, green, pink and reddish pink, red |
| Crystal habit | Prismatic crystal |
| Cleavage | [001] Perfect |
| Fracture | Subconchoidal to uneven |
| Mohs scale hardness | 8 (defining mineral) |
| Luster | Vitreous |
| Streak | White |
| Diaphaneity | Transparent |
| Specific gravity | 3.49–3.57 |
| Optical properties | Biaxial (+) |
| Refractive index | nα = 1.606–1.629 nβ = 1.609–1.631 nγ = 1.616–1.638 |
| Birefringence | δ = 0.010 |
| Pleochroism | Weak in thick sections X = yellow; Y = yellow, violet, reddish; Z = violet, bluish, yellow, pink |
| Ultraviolet fluorescence | Short UV=golden yellow; Long UV=cream |
| References | [1][2][3][4] |
Topaz (/ˈtoʊˌpæz/ TOH-paz) is a silicate mineral of aluminium and fluorine with the chemical formula Al2SiO4(F, OH)2. It is used as a gemstone in jewelry and other adornments. Common topaz in its natural state is colorless, though trace element impurities can make it pale blue, golden brown to yellow orange. Topaz is often treated with heat, or radiation to make it a deep blue, reddish-orange, pale green, pink, or purple.
Topaz is a nesosilicate mineral. It is one of the hardest naturally occurring minerals, and has a relatively low index of refraction. It occurs in many places in the world.
Etymology[]
The name "topaz" is usually derived (via Old French: Topace and Latin: Topazus) from the Greek Τοπάζιος (Τοpáziοs) or Τοπάζιον (Τοpáziοn),[5] from Τοπαζος, the ancient name of St. John's Island in the Red Sea which was difficult to find and from which a yellow stone (now believed to be chrysolite: yellowish olivine) was mined in ancient times; the name topaz was first applied to the mineral now known by that name in 1737.[6] Ancient Sri Lanka (Tamraparni) exported native oriental topazes to Greece and ancient Egypt, which led to the etymologically related names of the island by Alexander Polyhistor (Topazius) and the early Egyptians (Topapwene) – "land of the Topaz".[7][8] Pliny said that Topazos is a legendary island in the Red Sea and the mineral "topaz" was first mined there. Alternatively, the word topaz may be related to the Sanskrit word तपस् "tapas", meaning "heat" or "fire".[5]
History[]
Nicols, the author of one of the first systematic treatises on minerals and gemstones, dedicated two chapters to the topic in 1652.[9] In the Middle Ages, the name topaz was used to refer to any yellow gemstone, but in modern times it denotes only the silicate described above.
Many English translations of the Bible, including the King James Version, mention topaz. However, because these translations as topaz all derive from the Septuagint translation topazi[os], which referred to a yellow stone that was not topaz, but probably chrysolite (chrysoberyl or peridot), topaz is likely not meant here.[10]
An English superstition also held that topaz cured lunacy.[11] The ancient Romans believed that topaz provided protection from danger while traveling.[12] During the Middle Ages, it was believed that attaching the topaz to the left arm protected the owner from any curse and warded off the evil eye. It was also believed that wearing topaz increased body heat, which would enable people to relieve a cold or fever.[13] In Europe during the Middle Ages, topaz was believed to enhance mental powers.[14]
Gemstone[]
Topaz is a gemstone, in cut and polished form, it is used to make jewellery or other adornments. It also has other uses. Orange topaz, also known as precious topaz, is the conventional birthstone for November, the symbol of friendship and the state gemstone of the U.S. state of Utah.[15] Blue topaz is the state gemstone of the US state of Texas.[16]
Characteristics[]

Topaz in its natural state is colorless, often with a greyish cast. It also occurs as a golden brown to yellow which makes it sometimes confused with citrine, a less valuable gemstone.[17] The specific gravity of all shades of topaz, however, means that it is considerably heavier than citrine (about 25% per volume) and this difference in weight can be used to distinguish two stones of equal volume. Also, if the volume of a given stone can be determined, its weight if topaz can be established and then checked with a sensitive scale. Likewise, glass stones are also much lighter than equally sized topaz.
A variety of impurities and treatments may make topaz wine red, pale gray, reddish-orange, pale green, or pink (rare), and opaque to translucent/transparent. The pink and red varieties come from chromium replacing aluminium in its crystalline structure.

Imperial topaz is yellow, pink (rare, if natural) or pink-orange. Brazilian imperial topaz can often have a bright yellow to deep golden brown hue, sometimes even violet. Many brown or pale topazes are treated to make them bright yellow, gold, pink, or violet colored. Some imperial topaz stones can fade on exposure to sunlight for an extended period of time.[18][19] Naturally occurring blue topaz is quite rare. Typically, colorless, gray, or pale yellow and blue material is heat treated and irradiated to produce a more desired darker blue.[19] Mystic topaz is colorless topaz which has been artificially coated via a vapor deposition process giving it a rainbow effect on its surface.[20]
Although very hard, topaz must be treated with greater care than some other minerals of similar hardness (such as corundum) because of a weakness of atomic bonding of the stone's molecules along one or another axial plane (whereas diamonds, for example, are composed of carbon atoms bonded to each other with equal strength along all of its planes). This gives topaz a tendency to break along such a cleavage plane if struck with sufficient force.[21]
Topaz has a relatively low index of refraction for a gemstone, and so stones with large facets or tables do not sparkle as readily as stones cut from minerals with higher refractive indices, though quality colorless topaz sparkles and shows more "life" than similarly cut quartz. When given a typical "brilliant" cut, topaz may either show a sparkling table facet surrounded by dead-looking crown facets or a ring of sparkling crown facets with a dull well-like table.[22]
Localities and occurrence[]
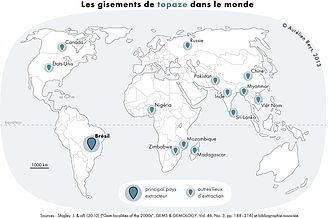
Topaz is commonly associated with silicic igneous rocks of the granite and rhyolite type. It typically crystallizes in granitic pegmatites or in vapor cavities in rhyolite lava flows including those at Topaz Mountain in western Utah and Chivinar in South America. It can be found with fluorite and cassiterite in various areas including the Ural and Ilmensky Mountains of Russia, in Afghanistan, Sri Lanka, Czech Republic, Germany, Norway, Pakistan, Italy, Sweden, Japan, Brazil, Mexico; Flinders Island, Australia; Nigeria and the United States.
Brazil is one of the largest producers of topaz,[23] some clear topaz crystals from Brazilian pegmatites can reach boulder size and weigh hundreds of pounds. The Topaz of Aurangzeb, observed by Jean Baptiste Tavernier weighed 157.75 carats.[24] The American Golden Topaz, a more recent gem, weighed a massive 22,892.5 carats. Large, vivid blue topaz specimens from the St. Anns mine in Zimbabwe were found in the late 1980s.[25] Colorless and light-blue varieties of topaz are found in Precambrian granite in Mason County, Texas[26] within the Llano Uplift. There is no commercial mining of topaz in that area.[27] It is possible to synthesize topaz.[28]

Topaz Mountain, Utah

Red topaz from Tepetate, Municipio de Villa de Arriaga, San Luis Potosí, Mexico

Facet cut topaz gemstones in various colors

Yellow topaz in stepped kite-shaped cut
See also[]
References[]
- ^ Hurlbut, Cornelius S.; Klein, Cornelis (1985). Manual of Mineralogy (20 ed.). ISBN 0-471-80580-7.
- ^ Anthony, John W.; Bideaux, Richard A.; Bladh, Kenneth W.; Nichols, Monte C., eds. (1995). "Topaz" (PDF). Handbook of Mineralogy. II (Silica, Silicates). Chantilly, VA, US: Mineralogical Society of America. ISBN 978-0-9622097-1-0. Retrieved December 5, 2011.
- ^ Topaz. Mindat.org. Retrieved on 2011-10-29.
- ^ Topaz. Webmineral.com. Retrieved on 2011-10-29.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Harper, Douglas. "topaz". Online Etymology Dictionary.
- ^ Hurlbut & Klein 1985.
- ^ Suckling, Horatio John (1876). Ceylon: A General Description of the Island, Historical, Physical, Statistical. Containing the Most Recent Information. Chapman & Hall. p. 10. Retrieved 28 June 2019.
topaz taprobane.
- ^ "Astrological Magazine". Astrological Magazine. 56 (1–6): 75. 1967. Retrieved 28 June 2019.
- ^ A Lapidary or History of Gemstones, University of Cambridge, 1652.
- ^ Farrington, Oliver (1903) Gems and Gem Minerals. Chicago. p. 119.
- ^ Pettigrew, Thomas Joseph (1844) On Superstitions Connected with the History and Practice of Medicine and Surgery. Philadelphia E. Barrington and G.D. Haswell. p. 70.
- ^ Webster, R. (2012). The encyclopedia of superstitions. Llewellyn Worldwide. p. 256. ISBN 9780738725611.
- ^ Webster 2012, p. 260.
- ^ Simmons, Robert (2005). The book of stones : who they are & what they teach. East Montpelier, VT: Heaven and Earth Pub. p. 403. ISBN 978-0962191039.
- ^ "Utah State gem – Topaz". Pioneer.utah.gov. 16 June 2010. Retrieved 29 October 2011.
- ^ "Texas state gem – Blue Topaz. State gemstone cut – Lone Star cut". state.tx.us. Archived from the original on 2009-03-12.
- ^ Hurrell, Karen; Johnson, Mary L. (15 December 2016). Gemstones: A Complete Color Reference for Precious and Semiprecious Stones of the World. Book Sales. p. 169. ISBN 978-0-7858-3498-4.
- ^ "Imperial topaz". nhm.org. Natural History Museum of Los Angeles County. Archived from the original on 13 May 2009.
- ^ Jump up to: a b "Gemstones & Gemology – Topaz". academic.emporia.edu. Emporia State University.
- ^ "Mystic topaz, consumer information". Farlang.com. 30 October 2008. Retrieved 29 October 2011.
- ^ Newman, Renee (7 January 2015). Gem & Jewelry Pocket Guide: A traveler's guide to buying diamonds, colored gems, pearls, gold and platinum jewelry. BookBaby. p. 104. ISBN 978-0-929975-49-8.
- ^ Dake, H. (16 April 2013). The Art of Gem Cutting – including cabochons, faceting, Sspheres, tumbling, and special techniques. Read Books Limited. p. 105. ISBN 978-1-4474-8480-6.
- ^ "Topaz Guide". Ayana Jewellery. Retrieved November 23, 2016.
- ^ Famous and Notheworthy Topazes Rao Bahadur, A Handbook of Precious Stones, Geological Survey of India
- ^ "Topaz (Blue)". Cape Minerals. Retrieved 7 February 2017.
- ^ Handbook of Texas Online – Mineral Resources and Mining. Tshaonline.org. Retrieved on 2011-10-29.
- ^ Mason, Texas Chamber of Commerce Web site
- ^ http://www.minsocam.org/ammin/AM57/AM57_169.pdf
External links[]
- Topaz from the International Colored Gemstone Association
- Topaz and other minerals found at Topaz Mountain, Juab County, Utah Geological Survey
- . Encyclopædia Britannica. 23 (9th ed.). 1888.
- Aluminium minerals
- Gemstones
- Nesosilicates
- Orthorhombic minerals
- Minerals in space group 62
- Luminescent minerals



