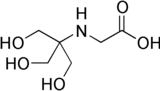
Tricine
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
{[1,3-Dihydroxy-2-(hydroxymethyl)propan-2-yl]amino}acetic acid | |
| Other names
Tricine
N-(Tri(hydroxymethyl)methyl)glycine | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| 1937804 | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.024.721 |
| EC Number |
|
| 3688 | |
| MeSH | tricine |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C6H13NO5 | |
| Molar mass | 179.172 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | White crystals |
| 89.6 g L−1 (at 20 °C) | |
| UV-vis (λmax) | 260 nm |
| Absorbance | 0.03 |
| Related compounds | |
Related compounds
|
Milacemide |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Tricine is an organic compound that is used in buffer solutions. The name tricine comes from tris and glycine, from which it was derived.[1] It is a white crystalline powder that is moderately soluble in water. It is a zwitterionic amino acid that has a pKa1 value of 2.3 at 25 °C, while its pKa2 at 20 °C is 8.15. Its useful buffering range of pH is 7.4-8.8. Along with bicine, it is one of Good's buffering agents. Good first prepared tricine to buffer chloroplast reactions.
Applications[]
Tricine is a commonly used electrophoresis buffer and is also used in resuspension of cell pellets. It has a higher negative (more negative) charge than glycine allowing it to migrate faster. In addition its high ionic strength causes more ion movement and less protein movement. This allows for low molecular weight proteins to be separated in lower percent acrylamide gels. Tricine has been documented in the separation of proteins in the range of 1 to 100 kDa by electrophoresis.[2] The tricine buffer at 25 mmol/L was found to be the most effective buffer among the ten tested for ATP assays using firefly luciferase.[3] Tricine has also been found to be an effective scavenger of hydroxyl radicals in a study of radiation-induced membrane damage.[4]
See also[]
References[]
- ^ Good, N.E., et al., Biochemistry, v. 5, 467 (1966).
- ^ Schaegger, H., and von Jagow, G., "Tricine-sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis for the separation of proteins in the range from 1 to 100 kDa." "Anal. Biochem." 166(2), 368-379.
- ^ Webster, J. J., and Leach, F. R., "Optimization of the firefly luciferase assay for ATP." "J. Appl. Biochem.", 2:469-479.
- ^ Hicks, M., and Gebicki, J. M., "Rate constants for reaction of hydroxyl radicals with Tris, Tricine, and Hepes buffers." "FEBS Lett.", 199(1):92-94.
- Triols
- Buffers
- Amino acid derivatives
- Zwitterions