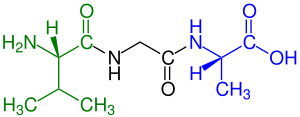Tripeptide
A tripeptide is a peptide derived from three amino acids joined by two or sometimes three peptide bonds.[1] As for proteins, the function of peptides is determined by the consistuent amino acids and their sequence. The simplest tripeptide is glycylglycylglycine. In terms of scientific investigations, the dominant tripeptide is glutathione (γ-L-Glutamyl-L-cysteinylglycine), which serves many roles in many forms of life.[2]
Examples[]
- (pGlu-Gln-Ala-OH) is a peptide with immunological activity that is isolated from the Japanese marine alga, Eisenia bicyclis, which more commonly is known as Arame
- GHK-Cu (glycyl-L-histidyl-L-lysine) is a human copper binding peptide with wound healing and skin remodeling activity, which is used in anti-aging cosmetics and more commonly referred to as copper peptide
- Lactotripeptides (Ile-Pro-Pro and Val-Pro-Pro) found in milk products, act as ACE inhibitors
- Leupeptin (N-acetyl-L-leucyl-L-leucyl-L-argininal) is a protease inhibitor that also acts as an inhibitor of calpain
- Melanostatin (prolyl-leucyl-glycinamide) is a peptide hormone produced in the hypothalamus that inhibits the release of melanocyte-stimulating hormone (MSH)
- Ophthalmic acid (L-γ-glutamyl-L-α-aminobutyryl-glycine) is an analogue of glutathione isolated from crystalline lens
- (y-glutamyl-alanyl-glycine) is an analogue of glutathione (L-cysteine replaced by L-alanine) isolated from crystalline lens
- Thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH, thyroliberin or protirelin) (L-pyroglutamyl-L-histidinyl-L-prolinamide) is a peptide hormone that stimulates the release of thyroid-stimulating hormone and prolactin by the anterior pituitary
- ACV (δ-(L-α-aminoadipyl)-L-Cys-D-Val) is a key precursor to penicillin and cephalosporin.
See also[]
References[]
- ^ Nelson, David L.; Cox, Michael M. (2005). Principles of Biochemistry (4th ed.). New York: W. H. Freeman. ISBN 0-7167-4339-6.
- ^ Guoyao Wu, Yun-Zhong Fang, Sheng Yang, Joanne R. Lupton, Nancy D. Turner (2004). "Glutathione Metabolism and its Implications for Health". Journal of Nutrition. 134: 489-492. doi:10.1093/jn/134.3.489.CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link)
Categories:
- Peptides
- Protein stubs