Undulipodium
This article includes a list of general references, but it remains largely unverified because it lacks sufficient corresponding inline citations. (April 2010) |
An undulipodium (a Greek word meaning "swinging foot") or a 9+2 organelle is a motile filamentous intracellular projection of eukaryotic cells. It is basically synonymous to flagella and cilia which are differing terms for similar molecular structures used on different types of cells, and usually correspond to different waveforms.
The name was coined to differentiate from the analogous structures present in prokaryotic cells. It is structurally a complex of microtubules along with motor proteins.[1][2]
The usage of the term was early supported by Lynn Margulis, especially in support of endosymbiotic theory.[3] The eukaryotic cilia are structurally identical to eukaryotic flagella, although distinctions are sometimes made according to function and/or length.[4] The Gene Ontology database does not make a distinction between the two, referring to all undulipodium as "motile cilium".[5]
Structure[]
Undulipodia use a whip-like action to create movement of the whole cell, such as the movement of sperm in the reproductive tract, and also create water movement as in the choanocytes of sponges.[citation needed]
Motile (or secondary) cilia are more numerous, with multiple cilia per cell, move in a wave-like action, and are responsible for movement in organisms such as ciliates and platyhelminthes, but also move extracellular substances in animals, such as the ciliary escalator found in the respiratory tract of mammals and the corona[clarification needed] of rotifers.
Primary cilia function as sensory antennae,[6] but are not undulipodia as primary cilia do not have the rotary movement mechanism found in motile cilia.
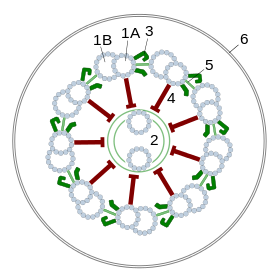
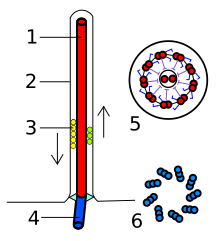
Undulipodia are an extension of the cell membrane containing both cytoplasm and a regular arrangement of microtubules known as an axoneme. At the base of the extension lies a structure called the kinetosome or basal body which is attached via motor proteins to the microtubules. The kinetosome mediates movement through a chemical reaction, causing the microtubules to slide against one another and the whole structure to bend.[citation needed]
Usage[]
Biologists such as Margulis strongly advocate the use of the name, because of the apparent structural and functional differences between the cilia and flagella of prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. They argue that the name flagella should be restricted only to prokaryotic organelles, such as bacterial flagella and spirochaete axial filaments.[7] However, the term is not generally endorsed by most biologists because it is argued that the original purpose of the name does not sufficiently differentiate the cilia and flagella of eukaryotic from those of prokaryotic cells. For example, the early concept was the trivial homology of flagella of flagellates and pseudopodia of rhizopods. The consensus terminology is the use of cilium and flagellum for all purposes.[1][8]
See also[]
References[]
- ^ Jump up to: a b Hülsmann N (1992). "Undulipodium: End of a useless discussion". European Journal of Protistology. 28 (3): 253–257. doi:10.1016/S0932-4739(11)80231-2. PMID 23195228.
- ^ Margulis L, Lovelock JE. "CP-2156 Life In The Universe: Atmospheres and Evolution". history.nasa.gov. Retrieved 8 July 2013.
- ^ Sagan L (1967). "On the origin of mitosing cells". J Theor Biol. 14 (3): 255–274. doi:10.1016/0022-5193(67)90079-3. PMID 11541392.
- ^ Haimo LT, Rosenbaum JL (December 1981). "Cilia, flagella, and microtubules". J. Cell Biol. 91 (3 Pt 2): 125s–130s. doi:10.1083/jcb.91.3.125s. PMC 2112827. PMID 6459327.
- ^ "Term Details for "motile cilium" (GO:0005929)". AmiGO 2.
Synonyms: motile cilia, microtubule-based flagellum, motile primary cilia, motile primary cilium, motile secondary cilium, nodal cilium
- ^ Satir P, Christensen ST (June 2008). "Structure and function of mammalian cilia". Histochem. Cell Biol. 129 (6): 687–93. doi:10.1007/s00418-008-0416-9. PMC 2386530. PMID 18365235.
- ^ Margulis L (1980). "Undulipodia, flagella and cilia". Biosystems. 12 (1–2): 105–108. doi:10.1016/0303-2647(80)90041-6. PMID 7378551.
- ^ Corliss JO (1980). "Objection to "undulipodium" as an inappropriate and unnecessary term". Biosystems. 12 (1–2): 109–110. doi:10.1016/0303-2647(80)90042-8. PMID 7378552.
- Cell anatomy
- Cell movement