Varsity Line
| Varsity Line | |
|---|---|
 Bletchley station, at the midpoint of the line, in 1962 | |
| Overview | |
| Status | see East West Rail |
| Owner | Network Rail |
| Locale | South East England |
| Termini | Oxford Cambridge |
| Stations | 13 open 2 planned |
| Service | |
| Type | Heavy rail |
| System | National Rail |
| Operator(s) | Chiltern Railways (Oxford–Bicester) West Midlands Trains (Bletchley–Bedford) |
| History | |
| Opened | 1846–1851 |
| Closed | 1968: Bedford to Cambridge; Oxford–Bletchley (to passengers) 1993: mothballed Claydon Junction–Bletchley (to all traffic) |
| Technical | |
| Number of tracks | 1–2 |
| Track gauge | 1,435 mm (4 ft 8+1⁄2 in) standard gauge |
| hide Varsity Line | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
The Varsity Line (or the Oxford to Cambridge railway line) was the main railway route that once linked the English university cities of Oxford and Cambridge, operated by the London and North Western Railway.
During World War II the line was adopted as a strategic route for freight avoiding London, and additional connections were made to nearby lines to improve the utility of the route. In fact the route was not greatly used for its intended purpose. After the war the line was again scheduled to be developed as a strategic route, but this scheme too was never fully implemented.
Passenger services were withdrawn from most of the line on 1 January 1968, and only the Bletchley–Bedford section remained open for passenger traffic.
In 1987, the section between Oxford and Bicester was reopened, followed in 2015 by a connection to the Chiltern Main Line at Bicester, enabling Chiltern Railways to operate an Oxford to London passenger service. There are funded plans for the entire line to be re-established by the "mid 2020s" (partly on a new route) under a new name – East West Rail.
History[]
The Oxford to Cambridge line, when completed, ran broadly west to east. In the early days there were five intersecting trunk lines running south to north:
- The Great Western Railway at Oxford, with its northward allies;
- the London and Birmingham Railway, forming part of the later West Coast Main Line;
- the Midland Main Line, opened by the Midland Railway, crossing the route at Bedford;
- the East Coast Main Line, opened by the Great Northern Railway, forming a connection at Sandy; and
- the Eastern Counties Railway at Cambridge.
Two other trunk routes, the Great Western Railway's Bicester cut-off and the Great Central Railway main line, were built later. Although a continuous line from Oxford to Cambridge was proposed from time to time, it was actually built by local schemes.
From west to east, these were:
- the Buckinghamshire Railway, from Oxford to Bletchley;
- the Bedford Railway, from Bletchley to Bedford;
- the Bedford and Cambridge Railway, between those points, which adopted the alignment of an earlier private scheme, the Sandy and Potton Railway.
In time, these sections were all incorporated into the London and North Western Railway.
First railway at Bletchley[]
The London and Birmingham Railway opened on 9 April 1838 as far north as Denbigh Hall, about a mile north of Bletchley (which was then a minor village). Initially, passengers alighted here to take a stagecoach on Watling Street to Rugby during construction work on the intervening section, which opened on 17 September 1838,[1] and this temporary terminus was closed. Subsequently and for a time, Wolverton (a few miles further north and on the main road between Oxford and Cambridge via Buckingham and Bedford[2]) took over as an important stop on the line, as a point where engines were changed over and passengers rested.
Bedford Railway[]

In 1836, proposals were put forward to build a line from Cambridge to join the L&BR (still under construction) at Bletchley; the line would have passed through Bedford, but the scheme was not taken forward. The obvious enhancement to the prosperity of Aylesbury following that town's connection to the L&BR changed attitudes, and as time passed, Bedford business interests sought a connection to the main line railway.[3] In 1844 George Stephenson visited Bedford to discuss the matter. At a meeting on 23 April 1844 he set out his proposed scheme, for a line to Bedford joining the L&BR main line at Bletchley. Some opinions had preferred Wolverton as the junction, since Bletchley was not then a settlement of any significance.[4]
A prospectus for the Bedford and London & Birmingham Railway was prepared; the capital was to be £125,000.[4][note 1] On 16 July 1846 the London and Birmingham Railway amalgamated with others, and formed the London and North Western Railway. A proposed extension of the Bedford line on to Cambridge through Hitchin was submitted to Parliament in the 1846 session but failed standing orders. [1][5] The line to Bedford opened on 17 November 1846, when a ceremonial opening took 600 persons from Bedford to Bletchley in a special train. The new line had a connection to the River Great Ouse at Bedford, trailing from the Bletchley direction.[note 2] The Bedford station was not yet ready at the time of opening. The commercial benefit to Bedford, already well served by coastal water-borne commerce over the River Great Ouse, is indicated by the immediate fall of coal prices, from 1s 9d to 11d per cwt.[4] There were four passenger trains each way, Sunday excepted, but this was soon enhanced to five each way, one of which was limited-stop, and two Sunday trains. Immediately on opening the Bedford Railway was absorbed into the London and North Western Railway. The terms were 4% per annum on the capital, plus half of any surplus. The LNWR had subscribed 1,522 of the 2,500 shares.[4]
Buckinghamshire Railway[]
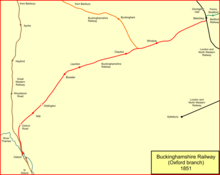

The Oxford and Bletchley Junction Railway and the Buckingham and Brackley Junction Railway had both been authorised in 1846,[6] and before construction the two schemes were amalgamated to form the Buckinghamshire Railway, authorised by Act of Parliament on 22 July 1847.[note 3] The new company would form a Y shape from Bletchley to both Oxford and Banbury. The 1847 powers also included an extension to Banbury, connecting to the Oxford and Rugby Railway there. and a southward extension from Verney Junction to join the Aylesbury branch.[6] The scheme was encouraged by the London and North Western Railway, which wished to block northward encroachment from the Great Western Railway, whose area of influence at the time was further south.[4]
The junction that became Verney Junction was known at first as Claydon Junction; the name Verney Junction was given to the station that was later established there. When the World War II link from the Great Central Railway main line was made, the junction there was called Claydon LNE Junction to emphasise the distinction.
Following authorisation of the Buckinghamshire company, the directors determined on 10 November 1847 to press ahead with the Banbury line in preference to the Oxford line. Work started on the last day of 1847. The line opened from Bletchley to Banbury on 1 May 1850 for passenger traffic, and goods trains started on 15 May 1850.[5][6][4]

Opening of the Oxford line (from Claydon Junction, at first as a single track only) followed relatively swiftly: to Islip on 1 October 1850; on to Oxford Road on 2 December 1850. This station was at the crossing of the present-day A4165 road, and therefore near to the modern Oxford Parkway station. Horse omnibuses and carts connected the station with Oxford itself. The line was extended to the company's own station at Oxford on 20 May 1851. It was a single track west of Claydon Junction.[4]
The 1853 passenger timetable shows 4 trains each way daily except Sundays, the first trains each way divided and joined Buckingham portions at Winslow. The journey time Oxford to Bletchley was 75 minutes and a typical journey Oxford to London took about 2 hours 45 minutes.[7]
The company had its own station at Oxford. It was fortunate in finding a site: Rewley Abbey had long since fallen into ruins, and the site was made available. Approaching trains crossed a swing bridge over the Sheepwash Channel to reach it. The junction with Oxford and Rugby Railway at Banbury was not made by the company, and the southwards extension from Verney was abandoned for the time being.[4]
The LNWR provided more than half the capital and worked the line from the beginning, and leased it for 999 years from 1 July 1851 guaranteeing a 4% dividend to the other shareholders. The LNWR absorbed the Buckinghamshire Railway company on 21 July 1879.[6] Early in 1854 the line from Verney Junction to Oxford was doubled, completing double track along the full length of the line. Verney was a junction, but no station was built until 1868, prompted by the construction of the Aylesbury and Buckingham Railway.[4][8]
Wolverhampton to London via Bletchley[]

The Oxford, Worcester and Wolverhampton Railway was authorised as a broad gauge line on 4 August 1845. Its line was to be 89 miles in length, connecting to the Great Western Railway at Wolvercot Junction, just north of Oxford. The cost of the line was heavy, and the estimates fell considerably short, so that the company was constantly short of funds during the construction period. For some time it concentrated its resources on the northern part of the authorised line.[9]
Although the OW&WR had originally been expected to be an ally of the GWR, the friendly relations cooled, and the London and North Western Railway (as owner of the Oxford to Bletchley line) developed good relations with the OW&WR. The LNWR tried to negotiate a takeover of the OW&WR, but this was rejected in Parliament; and in 1852 a direct connection between the LNWR Bletchley line and the OW&WR was also thrown out. In 1853 however the proposed connection (later known as the Yarnton Spur) was approved, and on 4 June 1853 the OW&WR had opened its line as far as Wolvercot Junction, its southern extremity.
The Yarnton Spur was a short double-track line, 1 mile 49 chains (1.61 mi; 2.6 km) in length, from Oxford Road Junction to Yarnton, and it was opened on 1 April 1854. The LNWR at once started operating through passenger services between Euston and Wolverhampton, via Bletchley, Yarnton Spur and the OW&WR. The trains were worked by the LNWR as far as Hanborough, and also from Dudley to Wolverhampton LNWR station via the South Staffordshire curve at Tipton.[9]
The Buckinghamshire Railway connection at Bletchley left in a southward direction, and a west to south chord was brought into use there in October 1854 to permit direct running between Euston and the Buckinghamshire line.[4]
A west to south curve to the Yarnton Spur was opened, allowing direct access from the OW&WR line to the LNWR Oxford station; this was used chiefly for goods traffic, but in the autumn of 1857 local passenger trains used it during a period of exceptionally strained relations between the OW&WR and the GWR.[4]
The service to London over the LNWR ceased by 1 September 1861; the west to south curve at Yarnton was reduced to a through siding only shortly afterwards, and the west to south curve at Bletchley was closed and lifted in 1864.[10][4] Nevertheless, the goods and mineral traffic from the OW&WR line remained considerable; Lawrence, writing in 1910, said that, "In March last, no fewer than 7,500 coal trucks made use of the loop."[11]
Verney Junction[]
There was a junction but no station at Verney Junction until 1868, when the Aylesbury and Buckingham Railway completed their line from Aylesbury to Verney. The Great Western Railway worked the A&BR trains until the company was absorbed by the Metropolitan Railway in 1891, becoming the northern terminus of the Metropolitan Railway. Two Pullman cars worked to Baker Street daily.[8]
Joint station proposed for Bedford[]

The Oxford to Cambridge line crossed under the Midland main line, and there were two separate passenger stations. In November 1855 officers of the Midland Railway and the LNWR met to consider the construction of a joint station at Bedford. It would have been a little to the west of the contemporary LNWR station. The scheme was agreed to be desirable and feasible, but the Midland Railway board declined to approve it, and it foundered.[12]
Sandy and Potton Railway[]

The Great Northern Railway had opened its line from London to Peterborough on 7 June 1850, ultimately giving access to York, and running through Sandy.[13]
The Sandy and Potton Railway was planned by Captain Sir William Peel. He had settled in Potton, and conceived a railway running almost entirely over his own lands, connecting with the Great Northern Railway at Sandy. The length of the line was 3+1⁄2 miles, and an opening ceremony was held in June 1857. The line opened to public goods traffic on 23 June 1857. A Board of Trade inspection took place on 5 November 1857, and this was successful, enabling opening of the line to passengers on 9 November 1857. Peel acquired a locomotive for the line from George England and Co. of Hatcham; it was named Shannon, after the frigate commanded by Peel.[note 4] A locomotive was hired from the GNR on one or two occasions, and passenger rolling stock was supplied by the GNR.[14] The line had cost £15,000 to build.[15][16][note 5]
The GNR had allowed Captain Peel to terminate his line in their Sandy goods yard, on condition that he would remove his works if the GNR required the site.[14][15]
Bedford and Cambridge Railway[]

In 1859 the Cambridge aspirations of several railway companies were competing for Parliamentary approval. A proposed Bedford, Potton and Cambridge Railway was thrown out, but the reverse showed that an alliance with the Great Northern Railway might prove fruitful.
In the 1860 session of Parliament, the Bedford and Cambridge Railway (as it now styled itself) got the Royal Assent on 6 August 1860. The Great Northern Railway hoped to build from Shepreth to this new line near Lords Bridge and gain access to Cambridge, by-passing the hostile, and even spiteful, Eastern Counties Railway.
The Bedford and Cambridge Railway was to take over the Sandy and Potton Railway and use its alignment. The route chosen entered the southern extremity of Cambridge alongside the Eastern Counties route from London, at Cambridge being permitted to use a platform at the ECR station. There was to be a separate LNWR goods station west of Hills Road.[17]
In fact the construction significantly overran cost estimates, and the company had to confer with the LNWR (as prospective lessee) about how to raise the extra cash. The authorised capital had been £240,000, and this had never fully been subscribed, and after opening the estimated cost to complete had risen to £370,175. This at last proved to be accurate. There was acrimony between the companies, but the LNWR underwrote the extra capital, and after considerable further negotiation, the LNWR absorbed the Bedford and Cambridge Railway Company by a share conversion, equating to 4% on the £240,000 original capital.
It opened on 7 July 1862 for passengers, and for goods in October 1862. The Sandy and Potton Railway had been purchased for £20,000. On 1 July 1862 the Eastern Counties Railway was restructured into the Great Eastern Railway.[16][18][14]

The May 1864 working timetable shows four passenger trains running throughout from Cambridge to Bletchley, and one early train from Bedford to Bletchley, and three goods trains. One Sunday passenger train is shown. Most of the passenger trains appear to continue to Oxford and London, probably by through coach attached to other trains.[19]
Working arrangements were made with the LNWR, authorised by Act of 23 June 1864. The company was absorbed by the LNWR on 5 July 1865.[1][6]
The line as constructed was single; double track was later constructed between Sandy and Gamlingay on 20 October 1870, and on to Cambridge on 10 July 1871.[20]
Flat crossing at Bedford[]
The Midland Railway's London extension opened in 1857, at this stage to Hitchin. It crossed the LNWR line at Bedford by a (nearly) 90-degree flat crossing; although it was undesirable, it was considered an appropriate economy measure as compared with a bridge crossing.[note 6]
On 12 March 1875 a collision took place at the location, as an LNWR train was struck by a Midland train. The signals protecting the crossing were not of a modern description; the LNWR train started from the station and approached the crossing, fouling it against the stop signal at danger. One passenger died of injuries, and six persons were injured.[21][22]
Railmotors[]

In the early twentieth century, railways sought lower-cost methods of operating passenger trains. The LNWR experimented with a steam railmotor. This was a single passenger coach, designed at Wolverton, with a small integrated steam locomotive. A railmotor was brought to Oxford for trials with a service to Bicester. However, during a trial run on 5 October 1905 the vehicle developed a hot axlebox, and the opening was deferred to the 9th. It was found to be capable of a top speed of 45 mph, and was timed for 30 minutes for the twelve miles to Bicester.
The vehicle had seats for 48 passengers in two saloons, smoking and non-smoking; the transverse seating had reversible backs, to allow passengers to face the direction in which they were going. They were considered by users to be very comfortable at the time. Woodwork was framed teak and the coach was lit electrically. Alighting and departing the vehicle at the ground level platforms of the halts was effected by a set of steps that swung out from the body of the vehicle. The steps were interlocked with the brakes. In 1905 there were six workings between Oxford and Bicester, with one additional on Thursday and Saturday, in each direction.[23]
To facilitate the new service a number of small timber platform halts were built. The halts were unstaffed, as tickets were issued by a Conductor on the train. The first was Summertown Halt, opened on 20 August 1906; by the following January the name had been changed to Port Meadow. The remainder of the halts were opened on 9 October 1905.[4]
From 1 December 1905 a steam railmotor was operated between Bedford and Bletchley also, and several new halts were opened here too. There were three vehicles, one being kept as a maintenance spare. [24]
The six halts were closed from 1 January 1917 because of the war, and reopened on 5 May 1919. The railmotors had limitations: they were underpowered and had limited accommodation, and suffered from reliability problems. They were replaced by auto trains about 1921; in this type of train, a conventional locomotive operated with a coach, specially adapted for the driver to control the train when being propelled from the coach. The auto trains and the halts west of Bicester were finally withdrawn during the General Strike on 25 October 1926; competition from road omnibuses had led to seriously declining usage.[4]
Further east, the system continued: in 1959, the auto-trains were replaced by diesel multiple units, and at this time the remaining stopping points were given raised platforms.[24]
The railmotor halts were, from Oxford to Islip: Summertown Halt, soon to be renamed Port Meadow; Wolvercote; Oxford Road, and between Islip and Bicester: Oddington, Charlton and Wendlebury Halt near Bicester. The eastern section halts were Bow Brickhill, Aspley Guise, Husborne Crawley, Wootton Pillinge, Wootton Broadmead, Kempston Hardwick, and Kempston & Elstow.[4][24]
Grouping of the railways[]
At the beginning of 1923, the main line railways of Great Britain were "grouped" into one or other of four new, large companies, in compliance with the Railways Act 1921. The LNWR and the Midland Railway were constituents of the new London Midland and Scottish Railway. The Great Western Railway absorbed a number of other concerns and continued under the same name. The Great Northern Railway and the Great Eastern Railway were constituents of the new London and North Eastern Railway.[25]
The whole of the Oxford to Cambridge line was thus part of the new LMS. In the 1930s, the major railways adopted a novel form of collaboration in the interest of reducing operating expenses. In 1934 the Stationmaster of the GWR's Oxford General station took over the management of the LMS's Rewley Road station.[citation needed] Cartage lorries in Oxford carried the initials of both companies.[26]
The Micheline railcar[]
In 1931, the Michelin Tyre Company was trying to market an internal combustion (petrol) railcar, which it named the Micheline. It was a ten-wheel articulated vehicle, with pneumatic rubber tyres. It was tried on the line in 1932. Carrying only 24 passengers and with uncertain reliability, it had many of the disadvantages of the steam railmotors, and the trial did not lead to adoption of the system.[note 7][27][28]
Diesel railcar[]
On 12 September 1938, a new diesel railcar design started work on the line. It was a three-car articulated unit, powered by six 125 hp diesel engines; the design was stylish and futuristic, and included central control of sliding passenger doors by the guard. The train was designed at Derby LMS.
Three journeys throughout the Oxford to Cambridge line were undertaken daily, with some short fill-in trips. The journey time Oxford to Cambridge, with three stops, (Bletchley, Bedford and Sandy) was 1 hour 45 minutes, comparing favourably with the 3 hour steam train journey. The runs were not advertised in the ordinary timetables, but only by handbills locally.
The outbreak of World War II prevented further development of this experimental system.[29]
World War II[]
In September 1939, war on Germany was declared by the United Kingdom. Aerial bombardment of UK cities and industrial sites was expected, and it was considered essential to create a trunk route for goods traffic avoiding London, which was expected to be the principal target of bombing. The Cambridge to Oxford route was selected to be the core of this route, because of its intersections with several trunk routes. Where existing connections between railways on the route were inadequate, relatively simple enhancements would resolve the difficulty.
Wragg describes the situation:
The solution was to build what amounted to a railway by-pass of London. Of necessity this was some distance from the capital, both to avoid disruption from heavy air raids, and also to utilise existing lines as far as possible. The start of this massive loop was the old London and North Western line from Cambridge to Oxford…
There were good existing connections in and out of this line at Bedford and Bletchley, but at Sandy and at Oxford time-consuming shunting movements would be necessary, so here again new connections were hastily installed and opened during 1940. There was no link at all at Calvert so a completely new link was created.[30]
In November 1940 Oxford North Junction was created, enabling through running from the Bletchley line towards Oxford GWR station.[31][32] A south-to-east chord line was constructed at Claydon across an area called Shepherd's Furze, connecting the former Great Central Main Line with the line from Bletchley. This link proved a useful connection in addition to its emergency value, and it saw much traffic during the war.
At Bletchley, the old west-to-south curve, removed in 1864, was reinstated, opening on 31 August 1942. . The Bicester Military Railway was built; it served a very large depot for ordnance and equipment. The civilian railway authorities protested at the adverse impact the railway movements to and from the depot would have on the ordinary war effort of the LNWR line, and the Ministry of War Transport agreed to the building of a new 660 wagon capacity yard at Swanbourne, about 3+1⁄2 miles west of Bletchley.[33][34]

The Railway Executive also constructed a west-to-north connection at Sandy; it opened in 1942. However it did not prove to have a strategic value in peacetime and was removed after the war.[35][32]
Crump explains the strategic significance:
The combined length of [the Sandy and Claydon curves] cannot have been much more than a mile, but in conjunction with a link joining the Great Western and Southern lines at Staines they provided a route for trains from the Great Northern to run via Sandy, Bletchley, Calvert, High Wycombe, Greenford and Staines on to the Southern. This route would have been of the utmost use if the London junctions had been destroyed. Actually it was only used on a few occasions, and the operating difficulties were considerable.[35]
Bicester Military Railway[]

In the late 1930s, a site at Bicester was selected for a large Ordnance Depot to be road and rail served. Construction of the Depot began in July 1940. The railway part of the site would start from a junction with the Oxford to Bletchley line and encircle the two hills of Graven Hill and Arncott. By the end of 1941 the exchange sidings had been laid, and in 1942 the first troop train entered the depot from Bicester station. The site was heavily used during the war, particularly in the preparations for D-Day.
Since the war, the site has been retained as a base for the Royal Logistic Corps. At its peak there were about 40 single-track miles of layout within the depot.[36][37]
The wartime curves after the war[]
The Oxford connection was useful in peacetime and was retained. The same is true of the Claydon curve, which provided a useful route for certain freight flows, and for empty passenger stock moves. The Bicester and Sandy connections proved less useful, and were removed.
Nationalisation[]
The main line railways of Great Britain were taken into state ownership at the beginning of 1948, pursuant to the Transport Act 1948. The entire line was in the London Midland Region of British Railways at first, but in 1951 the section from just east of Bicester to Oxford was transferred to the Western Region.
Transfer to the GWR station at Oxford[]
The operation of two passenger stations at Oxford was obviously wasteful and the wartime connection allowed trains from the Bletchley direction to run directly into the GWR's Oxford General station.
In October 1951, a complete transfer of passenger operation at Oxford into this (former GWR) station, now named simply Oxford railway station, took place. Most goods workings were transferred to the former GWR Hinksey yard, and Rewley Road station handled only coal and some general goods traffic.[31]
1955 development plan: goods[]

In the first years of British Railways, the organisation was beset with falling demand as costs increased. In 1955 a report, The Modernisation and Re-equipment of British Railways,[38] was published. £1.2 billion would be spent on the project. Subsidiary reports recommended the development of the Oxford to Cambridge line as part of an outer freight ring route from Cambridge to Ashford (Kent) via Oxford, Reading and Tonbridge, keeping freight flows away from London. The cost was to be £15 million. A large marshalling yard was to be built at Swanbourne, and the Bletchley Flyover (a viaduct over the West Coast Main Line beside Bletchley station).
Work on the Swanbourne yard and the Bletchley viaduct started in September 1958. The viaduct was ready in 1962 (it had cost £1.5 million) but work was halted on the marshalling yard.[39][40]
Gerry Fiennes was Chief Operating Officer, British Railways, at the time and wrote that he was convinced marshalling yards should be built in the areas of production and consumption, and not, like Swanbourne, in greenfield sites:
I did stop Swanbourne, Brookthorpe and Walcot [two other green field proposals]. The Bletchley flyover remains as a memorial to those who failed to see that railways must live by concentration and not dispersal. We had … driven … a pretty big nail into Swanbourne’s coffin by refusing to put into it any East Coast traffic. From that moment the writing was on the wall. Swanbourne should have been stopped then.
— Gerry Fiennes[41]
Modernisation and rationalisation[]

If development of passenger business on the line had been envisaged in 1955, that too was suddenly reversed, and in 1959 closure of the entire route was considered. However the introduction of diesel multiple unit passenger trains in that year substantially reduced operating costs, and the closure idea was rescinded. In the Beeching Report of 1963,[42] retention of the line was recommended, with only minor curtailment, but in December 1963 closure was once again put forward, as income was only a little over half of operating expenses. Closure was approved, and most local freight facilities were withdrawn on 18 April 1966.
Following public protest, passenger operation on the central section between Bedford and Bletchley was retained; delay in arranging substitute bus services resulted in the passenger closure of the remainder being deferred to 1 January 1968. The line from Bedford (Goldington Power Station) to the junction at Cambridge was closed completely; the wartime marshalling yard at Swanbourne was closed in March 1967.[43]
The Buckingham branch closed to passengers on 7 September 1964 and to goods on 5 December 1966.[44][45]
On 7 October 1973, the line from Bicester to Oxford was reduced to single track. Following that time, for some years the chief use of the line was as a connection from Aylesbury via Claydon LNE Junction to Bletchley for stone trains, refuse trains from the Bristol area, and empty passenger stock movements.[46]
Revitalisation and renewal, East West Rail[]

After the partial closure, portions of the route continued as the Oxford–Bicester line and the Marston Vale line. Beginning in 2015, work to revitalise and renew the route began; it hoped that by the end of the 2020s the two university cities will be connected by rail again as the East West Rail link.
Varsity line station locations and dates[]
This section needs additional citations for verification. (June 2020) |

- Oxford; opened 20 May 1851; later Oxford Rewley Road; closed 1 October 1951, when service diverted to former GWR station.
- Oxford North Junction; convergence from GWR line; from 1940.
- Wolvercote; opened 9 October 1905; close 1 January 1917; reopened 5 May 1919; closed 25 October 1926; in the earliest days the station was named Woolvercot; the nearby GWR station was named Wolvercot.
- Yarnton Loop Junction; diverging junction; 1854 – 1863.
- Oxford Road Junction; convergence of spur from Handborough; 1854 – 1965; renamed Banbury Road Junction about 1950 to avoid confusion with the junction at Reading.
- Oxford Road; opened 2 December 1850 as temporary terminus; closed 20 May 1851, when the line was extended to Oxford; reopened 9 October 1905; closed 1 January 1917; reopened 5 May 1919; closed 25 October 1926.
- Oxford Parkway; opened 25 October 2015
- Islip; opened 1 October 1850; closed 1 January 1968; reopened 13 May 1989
- Oddington; opened 1 October 1850; closed January 1851; reopened 9 October 1905; closed 1 January 1917; reopened 5 May 1919; closed 25 October 1926.
- Charlton; opened 9 October 1905; closed 1 January 1917; reopened 5 May 1919; closed 25 October 1926.
- Wendlebury; opened 9 October 1905; closed 1 January 1917; reopened 5 May 1919; closed 25 October 1926.
- Bicester; opened 1 October 1850; renamed Bicester London Road 1954; closed 1 January 1968; reopened as Bicester Town 11 May 1987; renamed Bicester Village 12 March 2015.
- Gavray Junction; divergence towards Princes Risborough.
- Launton; opened 1 October 1850; closed 1 January 1968.
- Marsh Gibbon and Poundon; opened 2 August 1880; closed 1 January 1968.
- Claydon LNE Junction; trailing junction from Great Central main line; 1940 - .
- Claydon: opened 1 May 1850; closed 1 January 1968.
- Verney Junction; opened 23 September 1868; closed 1 January 1968. Originally Claydon Junction before station opened; converging junction from Buckingham 1856 – 1966; diverging junction to Aylesbury 1868 – 1947.
- Winslow; opened 1 May 1850; closed 1 January 1968.
- Swanbourne; opened October 1851; closed 1 January 1968.
- Bletchley; London and Birmingham Railway station; still open; flyover 1962 - .
- Fenny Stratford; opened 18 November 1846. still open
- Bow Brickhill; opened 1 December 1905; closed 1 January 1917; reopened 5 May 1919; still open.
- Woburn; opened 18 November 1846; renamed Woburn Sands 1860; still open.
- Aspley Guise; opened 1 December 1905; closed 1 January 1917; reopened 5 May 1919; still open.
- Husborne Crawley; opened 1 December 1905; closed 1 January 1917; reopened 5 May 1919; closed 5 May 1941.
- Ridgmont; opened 18 November 1846; still open.
- Lidlington; opened 18 November 1846; still open.
- Marston; opened 18 November 1846; shortly renamed Ampthill; renamed Millbrook 1877; still open.
- Wootton Pillinge; opened 1 December 1850; closed 1 January 1917; reopened 5 May 1919; renamed Stewartby 1935; still open.
- Wootton Broadmead; opened 1 December 1850; closed 1 January 1917; reopened 5 May 1919; closed 5 May 1941.
- Kempston Hardwick; opened 1 December 1905; closed 1 January 1917; reopened 5 May 1919; still open.
- Kempston & Elstow; opened 1 December 1905; closed 1 January 1917; reopened 5 May 1919; closed 5 May 1941.
- Bedford; opened 18 November 1846; relocated 1 August 1862; renamed Bedford St Johns 1924; relocated northwards on line towards Midland Road station 14 May 1984.
- Goldington Siding; connection to Goldington Power Station; closed 1981.
- Willington; opened 1 May 1903; closed 1 January 1968.
- Blunham; opened 7 July 1862; closed 1 January 1968.
- Girtford Halt; opened 1 January 1938; closed 17 November 1940.
- Sandy West Junction; diverging junction to north curve 1940 - ?
- Sandy; Sandy & Potton Railway station; opened 9 November 1857; closed December 1861; reopened by LNWR 7 July 1862 ;closed 1 January 1968.
- Potton; Sandy & Potton Railway station; opened 9 November 1857; closed December 1861. LNWR station opened 7 July 1862; closed 1 January 1968.
- Gamlingay; opened 7 July 1862; closed 1 January 1968.
- Old North Road; opened 7 July 1862; closed 1 January 1968.
- Lords Bridge; opened 7 July 1862; closed 1 January 1968.
- Cambridge; Eastern Counties Railway station; still open.[47][48]
See also[]
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Varsity Line. |
Notes[]
- ^ About £12,000,000 today.
- ^ It was soon made into a complete triangle, avoiding the necessity of providing a turntable for engine turning.
- ^ The first sod of the Buckingham and Brackley Junction Railway had been cut at Buckingham on 20 April 1847.
- ^ There may have been a second engine: Simpson says (volume 2 page 15): Another engine, no 2, Little England, was bought by the LNWR for £350.
- ^ about £1,400,000 today.
- ^ In fact the western apex of the engine turning triangle was crossed by the Midland line, forming a complex permanent way construction.
- ^ Simpson includes a note implying earlier trials of petrol railcars on the line, but does not elaborate: "The text on page 38 is taken from a Micheline Tyre Company booklet selling the idea of the new type of internal combustion railcar. An idea not new to the Oxford line since the LNWR experiment early in the century."
References[]
- ^ Jump up to: a b c Robin Leleux, A Regional History of the Railway of Great Britain: volume 9: the East Midlands, David & Charles, Newton Abbot, 1976, ISBN 9780715371657, pages 17 to 27
- ^ Eleanor Chance, Christina Colvin, Janet Cooper, C J Day, T G Hassall, Mary Jessup and Nesta Selwyn (1979). "Communications". A History of the County of Oxford: Volume 4, the City of Oxford. Victoria History of the Counties of England. p. 284–295. Retrieved 13 October 2019.CS1 maint: uses authors parameter (link)
- ^ Bill Simpson, Oxford to Cambridge Railway: volume two: Bletchley to Cambridge, Oxford Publishing Company, Poole, 1983, ISBN 0 86093 121 8, pages 7 to 18
- ^ Jump up to: a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o Bill Simpson, Oxford to Cambridge Railway: Volume One: Oxford to Bletchley, Oxford Publishing Co, Headington, 1981, ISBN 0-86093-120-X, pages 7 to 15
- ^ Jump up to: a b David Gould, The London and Birmingham Railway, 150 years on, David & Charles, Newton Abbot, 1987, ISBN 0-7153-8968-8, page 15
- ^ Jump up to: a b c d e Malcolm Reed, The London and North Western Railway: A History, Atlantic Transport Publishers, Penryn, 1996, ISBN 978-0906899663, pages 45 and 46
- ^ Bradshaw's Railway Guide, 1853, part reproduced in Simpson, volume 1, page 12
- ^ Jump up to: a b Simpson, volume 1, pages 97 and 99
- ^ Jump up to: a b John Boynton, The Oxford, Worcester and Wolverhampton Railway, Mid England Books, Kidderminster, 2002, ISBN 0 954 0839 0 3
- ^ Reed, pages 65 and 66
- ^ J T Lawrence, From Oxford to Cambridge by the London and North Western Railway, Railway Magazine, October 1910, page 321
- ^ E G Barnes, The Rise of the Midland Railway, George Allen and Unwin Limited, London, 1966, page 153
- ^ Awdry, pages 134-135
- ^ Jump up to: a b c John Wrottesley, The Great Northern Railway: volume 1: Origins and Development, Harpur Collins, 1978, pages 143 and 144
- ^ Jump up to: a b Simpson, volume 2, pages 15 and 16
- ^ Jump up to: a b Leleux, page 28
- ^ Reed, pages 80 to 82
- ^ D I Gordon, A Regional History of the Railways of Great Britain,: volume 5: the Eastern Counties, David and Charles, Newton Abbot, 1968, revised 1977, ISBN 0 7153 7431 1, page 147
- ^ Simpson, volume 2, page 28
- ^ Simpson, volume 2, page 18
- ^ Barnes, page 148
- ^ Board of Trade accident Report dated 18 March 1875, available at [1]
- ^ Simpson, volume 1, pages 60 and 62; original timetable reproduced on page 62
- ^ Jump up to: a b c Simpson, volume 2, pages 33 to 35
- ^ D C Robinson, Railway Amalgamation in Great Britain, The Railway Gazette, 1923
- ^ Simpson, volume 1 page 24
- ^ Simpson, volume 1, pages 37 and 38
- ^ Colin G Maggs, Branch Lines of Buckinghamshire, Sutton Publishing, Stroud, 2000, ISBN 0 7509 1749 0, page 110
- ^ Simpson, volume 2, pages 80 to 82
- ^ David Wragg, Wartime on the Railways, History Press, Stroud, 2006, new edition 2012, ISBN 978 0 7524 8612 3
- ^ Jump up to: a b Simpson, volume 1, page 132
- ^ Jump up to: a b R T Munns, Milk Churns to Merry-go-round: A Century of Train Operation, David and Charles, Newton Abbot, 1986, ISBN 978-0715386668
- ^ Ernest R Lawton and Maurice W Sackett, Bicester Military Railway, Oxford Publishing Company, 1992, ISBN 978-0-86093-467-7, page 17
- ^ Simpson, volume 1, pages 18 and 19
- ^ Jump up to: a b Norman Crump, By Rail to Victory: The Story of the LNER in Wartime, published by the LNER, York, 1947
- ^ Simpson, volume 1, pages 68 to 71
- ^ Lawton and Sackett, pages 11 to 20
- ^ The Modernisation and Re-equipment of British Railways, British Transport Commission, London, 1955
- ^ T R Gourvish, British Railways: 1948 – 1973: A Business History, Cambridge University Press, 1986, ISBN 0 521 26480 4, pages 290 and 703
- ^ Maggs, page 105
- ^ G F Fiennes (1973). "7. Chief Operating Officer, B.R.". I tried to run a Railway (Revised ed.). London: Ian Allan Ltd. ISBN 9780711004474.
- ^ The Reshaping of British Railways, British Railways Board, London, 1963
- ^ Gordon, pages 148 and 149
- ^ Gould, page 15
- ^ Simpson, volume 1, page 15
- ^ Simpson, volume 1, pages 134 and 136
- ^ Michael Quick, Railway Passenger Stations in England Scotland and Wales—A Chronology, The Railway and Canal Historical Society, 2002
- ^ Col M H Cobb, The Railways of Great Britain A Historical Atlas, Ian Allan Publishing, 2003, ISBN 978-0711030022
Further reading[]
- Jenkins, Stanley C. (2013). Oxford, Bletchley & Bedford Line Through Time. Amberley Publishing. ISBN 9781445617480.
- Simpson, Bill. The Oxford To Cambridge Railway: Forty Years On 1960–2000. Witney: Lamplight Publications. ISBN 1-899246-05-3. OCLC 54047797.
- Adlam, Lance; Simpson, Bill (2008). A Triumph of Restoration - Oxford Rewley Road Station. Lamplight Publications. ISBN 978-1899246212.
- "The Oxford-Cambridge Closure Case". Modern Railways. Shepperton: Ian Allan. December 1964. pp. 398–401.
External links[]
Coordinates: 51°58′05″N 0°49′05″W / 51.968°N 0.818°W
- Railway lines in the East of England
- Rail transport in Bedfordshire
- Rail transport in Buckinghamshire
- Rail transport in Cambridgeshire
- Rail transport in Oxfordshire
- Transport in Oxford
- Rail transport in Milton Keynes
- Rail transport in Cambridge
- 1846 establishments in England


