Xeniidae
| Xeniidae | |
|---|---|

| |
| Heteroxenia fuscescens | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Cnidaria |
| Class: | Octocorallia |
| Order: | Alcyonacea |
| Suborder: | |
| Family: | Xeniidae Ehrenberg, 1828 |
Xeniidae is a family of soft coral in the order Alcyonacea.
Predators[]
Predatory sea slugs of the genus Phyllodesmium are reported to feed on Xeniidae species. Representatives of this family have been observed to provide shelter to juvenile fish.[1]
List of genera[]
The family contains the following genera:[2]
- Anthelia Lamarck, 1816
- Asterospicularia Utinomi, 1951
- Bayerxenia Alderslade, 2001
- Ceratocaulon Jungersen, 1892
- Cespitularia Milne-Edwards & Haime, 1850
- Efflatounaria Gohar, 1939
- Fasciclia Janes, 2008
- Funginus Tixier-Durivault, 1987
- Heteroxenia Koelliker, 1874
- Ingotia Alderslade, 2001
- Ixion Alderslade, 2001* [genus name "Ixion" is preoccupied by Reitter, 1873[3]]
- Orangaslia Alderslade, 2001
- Ovabunda Alderslade, 2001
- Sansibia Alderslade, 2000
- Sarcothelia Verrill, 1928
- Sympodium Ehrenberg, 1834
- Xenia Lamarck, 1816

Cespitularia sp.

Heteroxenia fuscescens
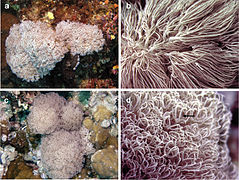


This nudibranch (Phyllodesmium crypticum) mimics Xeniid corals it feeds on

Cerates of a Phyllodesmium rudmani
References[]
- ^ Bos, Arthur R (2016). "Soft corals provide microhabitat for camouflaged juveniles of the Blackspotted wrasse Macropharyngodon meleagris (Labridae)". Marine Biodiversity. 46 (1): 299–301. doi:10.1007/s12526-015-0332x.
- ^ Leen van Ofwegen (2011). "Xeniidae". WoRMS. World Register of Marine Species. Retrieved January 29, 2012.
- ^ "Archived copy". Archived from the original on July 3, 2015. Retrieved November 13, 2012.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link)
External links[]
 Data related to Xeniidae at Wikispecies
Data related to Xeniidae at Wikispecies
Categories:
- Xeniidae
- Alcyoniina
- Cnidarian families
- Octocorallia stubs







