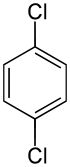
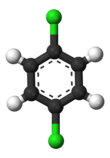
1,4-Dichlorobenzene
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
1,4-Dichlorobenzene | |||
| Other names
1,4-DCB
para-Dichlorobenzene p-Dichlorobenzene p-DCB PDB Paramoth Para crystals Paracide Dichlorocide | |||
| Identifiers | |||
3D model (JSmol)
|
|||
| 1680023 | |||
| ChEBI | |||
| ChEMBL | |||
| ChemSpider | |||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.003.092 | ||
| EC Number |
| ||
| 49722 | |||
| KEGG | |||
PubChem CID
|
|||
| RTECS number |
| ||
| UNII | |||
| UN number | 3077 | ||
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|||
| Properties | |||
| C6H4Cl2 | |||
| Molar mass | 147.00 g·mol−1 | ||
| Appearance | Colorless/white crystals[1] | ||
| Odor | mothball-like[1] | ||
| Density | 1.25 g/cm3, solid | ||
| Melting point | 53.5 °C (128.3 °F; 326.6 K) | ||
| Boiling point | 174 °C (345 °F; 447 K) | ||
| 10.5 mg/100 mL (20 °C) | |||
| Vapor pressure | 1.3 mmHg (20 °C)[1] | ||
| -82.93·10−6 cm3/mol | |||
| Hazards | |||
| Main hazards | Suspected carcinogen | ||
| GHS pictograms |   
| ||
| GHS Signal word | Warning | ||
GHS hazard statements
|
H302, H315, H317, H319, H332, H335, H351, H400, H410 | ||
| P201, P202, P261, P264, P270, P271, P272, P273, P280, P281, P301+312, P302+352, P304+312, P304+340, P305+351+338, P308+313, P312, P321, P330, P332+313, P333+313, P337+313, P362, P363, P391 | |||
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | 
2
2
0 | ||
| Flash point | 66 °C (151 °F; 339 K) | ||
| Explosive limits | 2.5%-?[1] | ||
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |||
LD50 (median dose)
|
500 mg/kg (rat, oral) 2950 mg/kg (mouse, oral) 2512 mg/kg (rat, oral) 2830 mg/kg (rabbit, oral)[2] | ||
LDLo (lowest published)
|
857 mg/kg (human, oral) 4000 mg/kg (rat, oral) 2800 mg/kg (guinea pig, oral)[2] | ||
| NIOSH (US health exposure limits): | |||
PEL (Permissible)
|
TWA 75 ppm (450 mg/m3)[1] | ||
REL (Recommended)
|
Ca[1] | ||
IDLH (Immediate danger)
|
Ca [150 ppm][1] | ||
| Related compounds | |||
Related compounds
|
1,2-Dichlorobenzene 1,3-Dichlorobenzene | ||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |||
| Infobox references | |||
1,4-Dichlorobenzene (1,4-DCB, p-DCB, or para-dichlorobenzene, sometimes abbreviated as PDB or para) is an organic compound with the formula C6H4Cl2. This colorless solid has a strong odor. The molecule consists of a benzene ring with two chlorine atoms (replacing hydrogen atoms) on opposing sites of the ring.
It is used as a disinfectant, pesticide, and deodorant, most familiarly in mothballs in which it is a replacement for the more traditional naphthalene because of naphthalene's greater flammability (though both chemicals have the same NFPA 704 rating). It is also used as a precursor in the production of the chemically and thermally resistant polymer poly(p-phenylene sulfide).[3]
Production[]
p-DCB is produced by chlorination of benzene using ferric chloride as a catalyst:
- C6H6 + 2 Cl2 → C6H4Cl2 + 2 HCl
The chief impurity is the 1,2 isomer. The compound can be purified by fractional crystallization, taking advantage of its relatively high melting point of 53.5 °C; the isomeric dichlorobenzenes and chlorobenzene melt well below room temperature.[3]
Uses[]
Disinfectant, deodorant, and pesticide[]
p-DCB is used to control moths, molds, and mildew.[4] It also finds use as a disinfectant[3] in waste containers and restrooms and is the characteristic smell associated with urinal cakes. Its usefulness for these applications arises from p-DCB's low solubility in water and its relatively high volatility: it sublimes readily near room temperature.[3]
Precursor to other chemicals[]
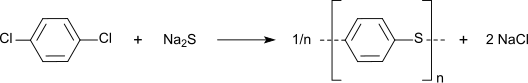
Nitration gives 1,4-dichloronitrobenzene, a precursor to commercial dyes and pigments.[5] The chloride sites on p-DCB can be substituted with hydroxylamine and sulfide groups. In a growing application, p-DCB is the precursor to the high performance polymer poly(p-phenylene sulfide):[6]
Environmental and health effects[]
p-DCB is poorly soluble in water and is not easily broken down by soil organisms. Like many hydrocarbons, p-DCB is lipophilic and will accumulate in fatty tissues if consumed by a person or animal.
The United States Department of Health and Human Services (DHHS) and the International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC) have determined that p-DCB may reasonably be anticipated to be a carcinogen.[7] This has been indicated by animal studies, although a full-scale human study has not been done.[8]
The United States Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) has set a target maximum contaminant level of 75 micrograms of p-DCB per liter of drinking water (75 μg/L),[9] but publishes no information on the cancer risk.[10] p-DCB is also an EPA-registered pesticide.[11] The United States Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) has set a maximum level of 75 parts of p-DCB per million parts air in the workplace (75 ppm) for an 8-hour day, 40-hour workweek.[12][13]
Under California's Proposition 65, p-DCB is listed as "known to the State to cause cancer".[14] A mechanism for the carcinogenic effects of mothballs and some types of air fresheners containing p-DCB has been identified in roundworms.[15]
See also[]
References[]
- ^ Jump up to: a b c d e f g NIOSH Pocket Guide to Chemical Hazards. "#0190". National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH).
- ^ Jump up to: a b "p-Dichlorobenzene". National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH). 4 December 2014. Retrieved 6 March 2015.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c d Rossberg, M.; Lendle, W.; Pfleiderer, G.; Tögel, A.; Dreher, E. L.; Langer, E.; Rassaerts, H.; Kleinschmidt, P.; Strack (2006). "Chlorinated Hydrocarbons". Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry. Weinheim: Wiley-VCH. doi:10.1002/14356007.a06_233.pub2.
- ^ "National Pesticide Information Center – Mothballs Case Profile" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 22 June 2010. Retrieved 10 August 2009.
- ^ K. Hunger. W. Herbst "Pigments, Organic" in Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim, 2012. doi:10.1002/14356007.a20_371
- ^ Fahey, D. R.; Ash, C. E. (1991). "Mechanism of poly(p-phenylene sulfide) growth from p-dichlorobenzene and sodium sulfide". Macromolecules. 24 (15): 4242. doi:10.1021/ma00015a003.
- ^ Preamble to the IARC Monographs Archived 9 August 2016 at the Wayback Machine definition of "Group 2B: Possibly carcinogenic to humans", the International Agency for Research on Cancer classification of this chemical
- ^ "ToxFAQs for Dichlorobenzenes". Toxic Substances Portal. Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry. Retrieved 24 May 2013.
- ^ "Consumer Factsheet on: PARA-DICHLOROBENZENE (p-DCB)". 28 November 2006. Archived from the original on 6 October 2009. Retrieved 10 August 2009.
- ^ Standards, US EPA, OAR, Office of Air Quality Planning and. "1,4-Dichlorobenzene (para-Dichlorobenzene) – Technology Transfer Network Air Toxics Web site | US EPA". www3.epa.gov. Retrieved 24 March 2016.
- ^ "Reregistration Eligibility Decision for Para-dichlorobenzene" (PDF). December 2008. Archived from the original (PDF) on 26 September 2009. Retrieved 10 August 2009.
- ^ "Chemical Sampling – p-Diclorobenzine". United States Department of Labor. Occupational Safety & Health Administration. Retrieved 23 March 2016.
- ^ "Common Name: 1,4-DICHLOROBENZENE" (PDF). New Jersey Department of Health and Senior Services. December 2005. Retrieved 24 March 2016.
- ^ Proposition 65 Archived 29 July 2019 at the Wayback Machine, Office of Environmental Health Hazard Assessment
- ^ Kokel, David (14 May 2006). "The nongenotoxic carcinogens naphthalene and para-dichlorobenzene suppress apoptosis in Caenorhabditis elegans". Nature Chemical Biology. 2 (6): 338–345. doi:10.1038/nchembio791. PMID 16699520.
External links[]
- International Chemical Safety Card 0037
- Mothball sniffing warning issued, BBC News, 27 July 2006
- NIOSH Pocket Guide to Chemical Hazards, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
- Organochloride insecticides
- IARC Group 2B carcinogens
- Chloroarenes