Acts of Union 1707
| Act of Parliament | |
 Parliament of England | |
| Long title | An Act for a Union of the Two Kingdoms of England and Scotland |
|---|---|
| Citation | 1706 c. 11 |
| Territorial extent | Kingdom of England (inc. Wales); subsequently, Kingdom of Great Britain and United Kingdom |
| Dates | |
| Commencement | 1 May 1707 |
Status: Current legislation | |
| Revised text of statute as amended | |
| Act of Parliament | |
 Parliament of Scotland | |
| Long title | Act Ratifying and Approving the Treaty of Union of the Two Kingdoms of Scotland and England |
|---|---|
| Citation | 1707 c. 7 |
| Territorial extent | Kingdom of Scotland; subsequently, Kingdom of Great Britain and United Kingdom |
| Dates | |
| Commencement | 1 May 1707 |
Status: Current legislation | |
| Revised text of statute as amended | |
| Constitutional documents and events relevant to the status of the United Kingdom and its countries |
|---|
 |
|
show List per year |
The Acts of Union (Scottish Gaelic: Achd an Aonaidh) were two Acts of Parliament: the Union with Scotland Act 1706 passed by the Parliament of England, and the Union with England Act passed in 1707 by the Parliament of Scotland. They put into effect the terms of the Treaty of Union that had been agreed on 22 July 1706, following negotiation between commissioners representing the parliaments of the two countries. By the two Acts, the Kingdom of England and the Kingdom of Scotland—which at the time were separate states with separate legislatures, but with the same monarch—were, in the words of the Treaty, "United into One Kingdom by the Name of Great Britain".[2]
The two countries had shared a monarch since the Union of the Crowns in 1603, when King James VI of Scotland inherited the English throne from his double first cousin twice removed, Queen Elizabeth I. Although described as a Union of Crowns, and in spite of James's acknowledgement of his accession to a single Crown,[3] England and Scotland were officially separate Kingdoms until 1707 (as opposed to the implied creation of a single unified Kingdom, exemplified by the later Kingdom of Great Britain). Prior to the Acts of Union there had been three previous attempts (in 1606, 1667, and 1689) to unite the two countries by Acts of Parliament, but it was not until the early 18th century that both political establishments came to support the idea, albeit for different reasons.
The Acts took effect on 1 May 1707. On this date, the Scottish Parliament and the English Parliament united to form the Parliament of Great Britain, based in the Palace of Westminster in London, the home of the English Parliament.[4] Hence, the Acts are referred to as the Union of the Parliaments.
Political background prior to 1707[]
1603–1660[]
Prior to 1603, England and Scotland had different monarchs; as Elizabeth I never married, after 1567, her heir-presumptive became the Stuart king of Scotland, James VI, who was brought up as a Protestant. After her death, the two Crowns were held in personal union by James, as James I of England, and James VI of Scotland. He announced his intention to unite the two, using the royal prerogative to take the title "King of Great Britain", [5] and give a British character to his court and person.[6]

The 1603 Union of England and Scotland Act established a joint Commission to agree terms, but the English Parliament was concerned this would lead to the imposition of an absolutist structure similar to that of Scotland. James was forced to withdraw his proposals, and attempts to revive it in 1610 were met with hostility.[7]
Instead, he set about creating a unified Church of Scotland and England, as the first step towards a centralised, Unionist state.[8] However, despite both being nominally Episcopalian in structure, the two were very different in doctrine; the Church of Scotland, or kirk, was Calvinist in doctrine, and viewed many Church of England practices as little better than Catholicism.[9] As a result, attempts to impose religious policy by James and his son Charles I ultimately led to the 1639–1651 Wars of the Three Kingdoms.
The 1639–1640 Bishops' Wars confirmed the primacy of the kirk, and established a Covenanter government in Scotland. The Scots remained neutral when the First English Civil War began in 1642, before becoming concerned at the impact on Scotland of a Royalist victory.[10] Presbyterian leaders like Argyll viewed union as a way to ensure free trade between England and Scotland, and preserve a Presbyterian kirk.[11]

Under the 1643 Solemn League and Covenant, the Covenanters agreed to provide military support for the English Parliament, in return for religious union. Although the treaty referred repeatedly to 'union' between England, Scotland, and Ireland, political union had little support outside the Kirk Party. Even religious union was opposed by the Episcopalian majority in the Church of England, and Independents like Oliver Cromwell, who dominated the New Model Army.
The Scots and English Presbyterians were political conservatives, who increasingly viewed the Independents, and associated radical groups like the Levellers, as a bigger threat than the Royalists. Both Royalists and Presbyterians agreed monarchy was divinely ordered, but disagreed on the nature and extent of Royal authority over the church. When Charles I surrendered in 1646, they allied with their former enemies to restore him to the English throne.[12]
After defeat in the 1647–1648 Second English Civil War, Scotland was occupied by English troops which were withdrawn once the so-called Engagers whom Cromwell held responsible for the war had been replaced by the Kirk Party. In December 1648, Pride's Purge confirmed Cromwell's political control in England by removing Presbyterian MPs from Parliament, and executing Charles in January 1649. Seeing this as sacrilege, the Kirk Party proclaimed Charles II King of Scotland and Great Britain, and agreed to restore him to the English throne.
Defeat in the 1649–1651 Third English Civil War or Anglo-Scottish War resulted in Scotland's incorporation into the Commonwealth of England, Scotland and Ireland, largely driven by Cromwell's determination to break the power of the kirk, which he held responsible for the Anglo-Scottish War.[13] The 1652 Tender of Union was followed on 12 April 1654 by An Ordinance by the Protector for the Union of England and Scotland, creating the Commonwealth of England, Scotland and Ireland.[14] It was ratified by the Second Protectorate Parliament on 26 June 1657, creating a single Parliament in Westminster, with 30 representatives each from Scotland and Ireland added to the existing English members.[15]
1660–1707[]

While integration into the Commonwealth established free trade between Scotland and England, the economic benefits were diminished by the costs of military occupation.[16] Both Scotland and England associated union with heavy taxes and military rule; it had little popular support in either country, and was dissolved after the Restoration of Charles II in 1660.
The Scottish economy was badly damaged by the English Navigation Acts of 1660 and 1663 and England's wars with the Dutch Republic, Scotland's major export market. An Anglo-Scots Trade Commission was set up in January 1668 but the English had no interest in making concessions, as the Scots had little to offer in return. In 1669, Charles II revived talks on political union; his motives were to weaken Scotland's commercial and political links with the Dutch, still seen as an enemy and complete the work of his grandfather James I.[17] Continued opposition meant these negotiations were abandoned by the end of 1669.[18]
Following the Glorious Revolution of 1688, a Scottish Convention met in Edinburgh in April 1689 to agree a new constitutional settlement; during which the Scottish Bishops backed a proposed union in an attempt to preserve Episcopalian control of the kirk. William and Mary were supportive of the idea but it was opposed both by the Presbyterian majority in Scotland and the English Parliament.[19] Episcopacy in Scotland was abolished in 1690, alienating a significant part of the political class; it was this element that later formed the bedrock of opposition to Union.[20]
The 1690s were a time of economic hardship in Europe as a whole and Scotland in particular, a period now known as the Seven ill years which led to strained relations with England.[21] In 1698, the Company of Scotland Trading to Africa and the Indies received a charter to raise capital through public subscription.[22] The Company invested in the Darién scheme, an ambitious plan funded almost entirely by Scottish investors to build a colony on the Isthmus of Panama for trade with East Asia.[23] The scheme was a disaster; the losses of over £150,000[a] severely impacted the Scottish commercial system.[24]
Political motivations[]

The Acts of Union may be seen within a wider European context of increasing state centralisation during the late 17th and early 18th centuries, including the monarchies of France, Sweden, Denmark and Spain. While there were exceptions, such as the Dutch Republic or the Republic of Venice, the trend was clear.[25]
The dangers of the monarch using one Parliament against the other first became apparent in 1647 and 1651. It resurfaced during the 1679 to 1681 Exclusion Crisis, caused by English resistance to the Catholic James II (of England, VII of Scotland) succeeding his brother Charles. James was sent to Edinburgh in 1681 as Lord High Commissioner; in August, the Scottish Parliament passed the Succession Act, confirming the divine right of kings, the rights of the natural heir 'regardless of religion', the duty of all to swear allegiance to that king and the independence of the Scottish Crown. It then went beyond ensuring James's succession to the Scottish throne by explicitly stating the aim was to make his exclusion from the English throne impossible without '...the fatall and dreadfull consequences of a civil war.'[26]
The issue reappeared during the 1688 Glorious Revolution. The English Parliament generally supported replacing James with his Protestant daughter Mary II, but resisted making her Dutch husband William III & II joint ruler. They gave way only when he threatened to return to the Netherlands, and Mary refused to rule without him.[27]
In Scotland, conflict over control of the kirk between Presbyterians and Episcopalians and William's position as a fellow Calvinist put him in a much stronger position. He originally insisted on retaining Episcopacy, and the Committee of the Articles, an unelected body that controlled what legislation Parliament could debate. Both would have given the Crown far greater control than in England but he withdrew his demands due to the 1689–1692 Jacobite Rising.[28]
English perspective[]
The English succession was provided for by the English Act of Settlement 1701, which ensured that the monarch of England would be a Protestant member of the House of Hanover. Until the Union of Parliaments, the Scottish throne might be inherited by a different successor after Queen Anne, who had said in her first speech to the English parliament that a Union was 'very necessary'.[29] The Scottish Act of Security 1704 however was passed after the English parliament without consultation with Scotland, had designated Electoress Sophie of Hanover (granddaughter of James I and VI), as Anne's successor, if she died childless. The Act of Security however granted the Parliament of Scotland, the three Estates,[29] the right to choose a successor and explicitly required a choice different from the English monarch unless the English were to grant free trade and navigation. Next the Alien Act 1705 was passed in the English parliament making Scots in England designated as 'foreign nationals' – and blocking about half of all Scottish trade by boycotting exports to England or its colonies, unless Scotland came back to negotiate a Union.[29] To encourage a Union, 'honours, appointments, pensions and even arrears of pay and other expenses were distributed to clinch support from Scottish peers and MPs.'[30]
Scottish perspective[]
The Scottish economy was severely impacted by privateers during the 1688 to 1697 Nine Years' War, and the 1701 War of the Spanish Succession, with the Royal Navy focusing on protecting English ships. This compounded the economic pressure caused by the Darien scheme, and the seven ill years of the 1690s, when between 5–15% of the population died of starvation.[31] The Scottish Parliament was promised financial assistance, protection for its maritime trade, and an end of economic restrictions on trade with England.[32]
The votes of the Court party, influenced by Queen Anne's favourite, the Duke of Queensberry, combined with the majority of the Squadrone Volante, were sufficient to ensure passage of the treaty.[29] Article 15 granted £398,085 and ten shillings sterling to Scotland,[b] a sum known as The Equivalent, to offset future liability towards the English national debt, which at the time was £18 million,[c] but as Scotland had no national debt,[29] most of the sum was used to compensate the investors in the Darien scheme, with 58.6% of the fund allocated to its shareholders and creditors.[33]

The role played by bribery has long been debated; £20,000 was distributed by the Earl of Glasgow,[d] of which 60% went to James Douglas, 2nd Duke of Queensberry, the Queen's Commissioner in Parliament. Another negotiator, Argyll was given an English peerage.[29] Robert Burns is commonly quoted in support of the argument of corruption; "We're bought and sold for English Gold, Such a Parcel of Rogues in a Nation." As historian Christopher Whatley points out, this was actually a 17th-century Scots folk song; but he agrees money was paid, though suggests the economic benefits were supported by most Scots MPs, with the promises made for benefits to peers and MPs,[30] even if it was reluctantly.[34] Professor Sir Tom Devine, agreed that promises of 'favours, sinecures, pensions, offices and straightforward cash bribes became indispensable to secure government majorities'.[35] As for representation going forwards, Scotland was, in the new united parliament only to get 45 MPs, one more than Cornwall, and only 16 (unelected) peers places in the House of Lords.[29]
Sir George Lockhart of Carnwath, the only Scottish negotiator to oppose Union, noted "the whole nation appears against (it)". Another negotiator, Sir John Clerk of Penicuik, who was an ardent Unionist, observed it was "contrary to the inclinations of at least three-fourths of the Kingdom".[36] As the seat of the Scottish Parliament, demonstrators in Edinburgh feared the impact of its loss on the local economy. Elsewhere, there was widespread concern about the independence of the kirk, and possible tax rises.[37]
As the Treaty passed through the Scottish Parliament, opposition was voiced by petitions from shires, burghs, presbyteries and parishes. The Convention of Royal Burghs claimed 'we are not against an honourable and safe union with England', but 'the condition of the people of Scotland, (cannot be) improved without a Scots Parliament'.[38] Not one petition in favour of Union was received by Parliament. On the day the treaty was signed, the carilloner in St Giles Cathedral, Edinburgh, rang the bells in the tune Why should I be so sad on my wedding day?[39] Threats of widespread civil unrest resulted in Parliament imposing martial law.
Treaty and passage of the 1707 Acts[]

Deeper political integration had been a key policy of Queen Anne from the time she acceded to the throne in 1702. Under the aegis of the Queen and her ministers in both kingdoms, the parliaments of England and Scotland agreed to participate in fresh negotiations for a union treaty in 1705.
Both countries appointed 31 commissioners to conduct the negotiations. Most of the Scottish commissioners favoured union, and about half were government ministers and other officials. At the head of the list was Queensberry, and the Lord Chancellor of Scotland, the Earl of Seafield.[40] The English commissioners included the Lord High Treasurer, the Earl of Godolphin, the Lord Keeper, Baron Cowper, and a large number of Whigs who supported union. Tories were not in favour of union and only one was represented among the commissioners.[40]
Negotiations between the English and Scottish commissioners took place between 16 April and 22 July 1706 at the Cockpit in London. Each side had its own particular concerns. Within a few days, and with only one face to face meeting of all 62 commissioners,[29] England had gained a guarantee that the Hanoverian dynasty would succeed Queen Anne to the Scottish crown, and Scotland received a guarantee of access to colonial markets, in the hope that they would be placed on an equal footing in terms of trade.[41]
After negotiations ended in July 1706, the acts had to be ratified by both Parliaments. In Scotland, about 100 of the 227 members of the Parliament of Scotland were supportive of the Court Party. For extra votes the pro-court side could rely on about 25 members of the Squadrone Volante, led by the Marquess of Montrose and the Duke of Roxburghe. Opponents of the court were generally known as the Country party, and included various factions and individuals such as the Duke of Hamilton, Lord Belhaven and Andrew Fletcher of Saltoun, who spoke forcefully and passionately against the union, when the Scottish Parliament began its debate on the act in on 3 October 1706, but the deal had already been done.[29] The Court party enjoyed significant funding from England and the Treasury and included many who had accumulated debts following the Darien Disaster.[42]
In Scotland, the Duke of Queensberry was largely responsible for the successful passage of the Union act by the Parliament of Scotland. In Scotland, he also received much criticism from local residents, but in England he was cheered for his action. He had personally received around half of the funding awarded by the Westminster Treasury for himself. In April 1707, he travelled to London to attend celebrations at the royal court, and was greeted by groups of noblemen and gentry lined along the road. From Barnet, the route was lined with crowds of cheering people, and once he reached London a huge crowd had formed. On 17 April, the Duke was gratefully received by the Queen at Kensington Palace.[43]
Provisions[]

The Treaty of Union, agreed between representatives of the Parliament of England and the Parliament of Scotland in 1706, consisted of 25 articles, 15 of which were economic in nature. In Scotland, each article was voted on separately and several clauses in articles were delegated to specialised subcommittees. Article 1 of the treaty was based on the political principle of an incorporating union and this was secured by a majority of 116 votes to 83 on 4 November 1706. To minimise the opposition of the Church of Scotland, an Act was also passed to secure the Presbyterian establishment of the Church, after which the Church stopped its open opposition, although hostility remained at lower levels of the clergy. The treaty as a whole was finally ratified on 16 January 1707 by a majority of 110 votes to 69.[44]
The two Acts incorporated provisions for Scotland to send representative peers from the Peerage of Scotland to sit in the House of Lords. It guaranteed that the Church of Scotland would remain the established church in Scotland, that the Court of Session would "remain in all time coming within Scotland", and that Scots law would "remain in the same force as before". Other provisions included the restatement of the Act of Settlement 1701 and the ban on Roman Catholics from taking the throne. It also created a customs union and monetary union.
The Act provided that any "laws and statutes" that were "contrary to or inconsistent with the terms" of the Act would "cease and become void".
Related Acts[]
The Scottish Parliament also passed the Protestant Religion and Presbyterian Church Act 1707 guaranteeing the status of the Presbyterian Church of Scotland. The English Parliament passed a similar Act, 6 Anne c.8.
Soon after the Union, the Act 6 Anne c.40—later named the Union with Scotland (Amendment) Act 1707—united the English and Scottish Privy Councils and decentralised Scottish administration by appointing justices of the peace in each shire to carry out administration. In effect it took the day-to-day government of Scotland out of the hands of politicians and into those of the College of Justice.
On 18 December 1707 the Act for better Securing the Duties of East India Goods was passed which extended the monopoly of the East India Company to Scotland.
In the year following the Union, the Treason Act 1708 abolished the Scottish law of treason and extended the corresponding English law across Great Britain.
Evaluations[]
Scotland benefited, says historian G.N. Clark, gaining "freedom of trade with England and the colonies" as well as "a great expansion of markets". The agreement guaranteed the permanent status of the Presbyterian church in Scotland, and the separate system of laws and courts in Scotland. Clark argued that in exchange for the financial benefits and bribes that England bestowed, what it gained was
of inestimable value. Scotland accepted the Hanoverian succession and gave up her power of threatening England's military security and complicating her commercial relations ... The sweeping successes of the eighteenth-century wars owed much to the new unity of the two nations.[45]
By the time Samuel Johnson and James Boswell made their tour in 1773, recorded in A Journey to the Western Islands of Scotland, Johnson noted that Scotland was "a nation of which the commerce is hourly extending, and the wealth increasing" and in particular that Glasgow had become one of the greatest cities of Britain.[46]
300th anniversary[]

A commemorative two-pound coin was issued to mark the tercentennial—300th anniversary—of the Union, which occurred two days before the Scottish Parliament general election on 3 May 2007.[47]
The Scottish Government held a number of commemorative events through the year including an education project led by the Royal Commission on the Ancient and Historical Monuments of Scotland, an exhibition of Union-related objects and documents at the National Museums of Scotland and an exhibition of portraits of people associated with the Union at the National Galleries of Scotland.[48]
Scottish voting records[]
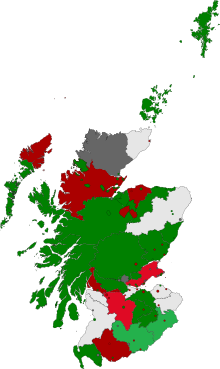
| Commissioner | Constituency/Position | Party | Vote | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| James Graham, 1st Duke of Montrose | Lord President of the Council of Scotland/Stirlingshire | Court Party | Yes | |
| John Campbell, 2nd Duke of Argyll | Court Party | Yes | ||
| John Hay, 2nd Marquess of Tweeddale | Squadrone Volante | Yes | ||
| William Kerr, 2nd Marquess of Lothian | Court Party | Yes | ||
| John Erskine, Earl of Mar | Court Party | Yes | ||
| John Gordon, 16th Earl of Sutherland | Court Party | Yes | ||
| John Hamilton-Leslie, 9th Earl of Rothes | Squadrone Volante | Yes | ||
| James Douglas, 11th Earl of Morton | Yes | |||
| William Cunningham, 12th Earl of Glencairn | Yes | |||
| James Hamilton, 6th Earl of Abercorn | Yes | |||
| John Ker, 1st Duke of Roxburghe | Squadrone Volante | Yes | ||
| Thomas Hamilton, 6th Earl of Haddington | Yes | |||
| John Maitland, 5th Earl of Lauderdale | Yes | |||
| David Wemyss, 4th Earl of Wemyss | Yes | |||
| William Ramsay, 5th Earl of Dalhousie | Yes | |||
| James Ogilvy, 4th Earl of Findlater | Banffshire | Yes | ||
| David Leslie, 3rd Earl of Leven | Yes | |||
| David Carnegie, 4th Earl of Northesk | Yes | |||
| Earl of Belcarras | Yes | |||
| Archibald Douglas, 1st Earl of Forfar | Yes | |||
| William Boyd, 3rd Earl of Kilmarnock | Yes | |||
| John Keith, 1st Earl of Kintore | Yes | |||
| Patrick Hume, 1st Earl of Marchmont | Squadrone Volante | Yes | ||
| George Mackenzie, 1st Earl of Cromartie | Yes | |||
| Archibald Primrose, 1st Earl of Rosebery | Yes | |||
| David Boyle, 1st Earl of Glasgow | Yes | |||
| Charles Hope, 1st Earl of Hopetoun | likely Linlithgowshire | Yes | ||
| Henry Scott, 1st Earl of Deloraine | Yes | |||
| Archibald Campbell, Earl of Illay | Yes | |||
| William Hay, Viscount Dupplin | Yes | |||
| William Forbes, 12th Lord Forbes | Yes | |||
| John Elphinstone, 8th Lord Elphinstone | Yes | |||
| William Ross, 12th Lord Ross | Yes | |||
| James Sandilands, 7th Lord Torphichen | Yes | |||
| Lord Fraser | Yes | |||
| George Ogilvy, 3rd Lord Banff | Yes | |||
| Alexander Murray, 4th Lord Elibank | Yes | |||
| Kenneth Sutherland, 3rd Lord Duffus | Yes | |||
| Robert Rollo, 4th Lord Rollo | Stirlingshire | Yes | ||
| James Murray, Lord Philiphaugh | Lord Clerk Register/Selkirkshire | Yes | ||
| Adam Cockburn, Lord Ormiston | Lord Justice Clerk | Yes | ||
| Sir Robert Dickson of Inverask | Edinburghshire | Yes | ||
| William Nisbet of Dirletoun | Haddingtonshire | Squadrone Volante | Yes | |
| John Cockburn, younger, of Ormestoun | Haddingtonshire | Squadrone Volante | Yes | |
| Sir John Swintoun of that ilk | Berwickshire | Court Party | Yes | |
| Sir Alexander Campbell of Cessnock | Berwickshire | Yes | ||
| Roxburghshire | Squadrone Volante | Yes | ||
| Archibald Douglas of Cavers | Roxburghshire | Court Party | Yes | |
| Roxburghshire | Court Party | Yes | ||
| Mr John Murray of Bowhill | Selkirkshire | Court Party | Yes | |
| Mr John Pringle of Haining | Selkirkshire | Court Party | Yes | |
| William Morison of Prestongrange | Peeblesshire | Court Party | Yes | |
| Alexander Horseburgh of that ilk | Peeblesshire | Yes | ||
| George Baylie of Jerviswood | Lanarkshire | Squadrone Volante | Yes | |
| Sir John Johnstoun of Westerhall | Dumfriesshire | Court Party | Yes | |
| William Dowglass of Dornock | Dumfriesshire | Yes | ||
| Mr William Stewart of Castlestewart | Wigtownshire | Yes | ||
| Mr John Stewart of Sorbie | Wigtownshire | Court Party | Yes | |
| Ayrshire | Court Party | Yes | ||
| Ayrshire | Court Party | Yes | ||
| Mr Robert Stewart of Tillicultrie | Buteshire | Yes | ||
| Sir Robert Pollock of that ilk | Renfrewshire | Court Party | Yes | |
| Mr John Montgomery of Wrae | Linlithgowshire | Yes | ||
| John Halden of Glenagies | Perthshire | Squadrone Volante | Yes | |
| Mongo Graham of Gorthie | Perthshire | Squadrone Volante | Yes | |
| Sir Thomas Burnet of Leyes | Kincardineshire | Court Party | Yes | |
| Aberdeenshire | Squadrone Volante | Yes | ||
| Alexander Grant, younger, of that ilk | Inverness-shire | Court Party | Yes | |
| Sir William Mackenzie | Yes | |||
| Mr Aeneas McLeod of Cadboll | Cromartyshire | Yes | ||
| Argyllshire | Court Party | Yes | ||
| Sir James Campbell of Auchinbreck | Argyllshire | Court Party | Yes | |
| James Campbell, younger, of Ardkinglass | Argyllshire | Court Party | Yes | |
| Sir William Anstruther of that ilk | Fife | Yes | ||
| James Halyburton of Pitcurr | Forfarshire | Squadrone Volante | Yes | |
| Alexander Abercrombie of Glassoch | Banffshire | Court Party | Yes | |
| Mr James Dunbarr, younger, of Hemprigs | Caithness | Yes | ||
| Alexander Douglas of Eagleshay | Orkney and Shetland | Court Party | Yes | |
| Sir John Bruce, 2nd Baronet | Kinross-shire | Squadrone Volante | Yes | |
| John Scrimsour | Dundee | Yes | ||
| Lieutenant Colonel John Areskine | Yes | |||
| John Mure | Likely Ayr | Yes | ||
| James Scott | Montrose | Court Party | Yes | |
| Sir John Anstruther, 1st Baronet, of Anstruther | Anstruther Easter | Yes | ||
| James Spittle | Inverkeithing | Yes | ||
| Mr Patrick Moncrieff | Kinghorn | Court Party | Yes | |
| Sir Andrew Home | Kirkcudbright | Squadrone Volante | Yes | |
| Sir Peter Halket | Dunfermline | Squadrone Volante | Yes | |
| Sir James Smollet | Dumbarton | Court Party | Yes | |
| Mr William Carmichell | Lanark | Yes | ||
| Mr William Sutherland | Elgin | Yes | ||
| Captain Daniel McLeod | Tain | Yes | ||
| Sir David Dalrymple, 1st Baronet | Culross | Court Party | Yes | |
| Sir Alexander Ogilvie | Banff | Yes | ||
| Mr John Clerk | Whithorn | Court Party | Yes | |
| John Ross | Yes | |||
| Hew Dalrymple, Lord North Berwick | North Berwick | Yes | ||
| Mr Patrick Ogilvie | Cullen | Court Party | Yes | |
| Kintore | Court Party | Yes | ||
| William Avis | Yes | |||
| Mr James Bethun | Kilrenny | Yes | ||
| Mr Roderick McKenzie | Fortrose | Yes | ||
| John Urquhart | Dornoch | Yes | ||
| Daniel Campbell | Inveraray | Court Party | Yes | |
| Inverurie | Yes | |||
| Mr Robert Dowglass | Kirkwall | Yes | ||
| Inverbervie | Court Party | Yes | ||
| Mr George Dalrymple | Stranraer | Yes | ||
| Mr Charles Campbell | Campbeltown | Yes | ||
| James Hamilton, 4th Duke of Hamilton | No | |||
| William Johnstone, 1st Marquess of Annandale | Annan | No | ||
| Charles Hay, 13th Earl of Erroll | No | |||
| William Keith, 9th Earl Marischal | No | |||
| No | ||||
| Alexander Sinclair, 9th Earl of Caithness | No | |||
| No | ||||
| James Stewart, 5th Earl of Galloway | No | |||
| David Murray, 5th Viscount of Stormont | No | |||
| No | ||||
| William Fraser, 12th Lord Saltoun | No | |||
| No | ||||
| No | ||||
| No | ||||
| Linlithgow | No | |||
| William Hamilton, 3rd Lord Bargany | Queensferry | No | ||
| John Hamilton, 2nd Lord Belhaven and Stenton | No | |||
| Lord Colvill | No | |||
| Patrick Kinnaird, 3rd Lord Kinnaird | No | |||
| Sir John Lawder of Fountainhall | Haddingtonshire | No | ||
| Andrew Fletcher of Saltoun | Haddingtonshire | No | ||
| Sir Robert Sinclair, 3rd Baronet | Berwickshire | No | ||
| Berwickshire | No | |||
| Roxburghshire | No | |||
| Lanarkshire | No | |||
| Lanarkshire | No | |||
| Lanarkshire | No | |||
| Dumfriesshire | No | |||
| Ayrshire | No | |||
| Ayrshire | No | |||
| Dumbartonshire | No | |||
| Dumbartonshire | No | |||
| Sir John Houstoun of that ilk | Renfrewshire | No | ||
| No | ||||
| Linlithgowshire | No | |||
| John Murray of Strowan | No | |||
| Aberdeenshire | No | |||
| Nairnshire | No | |||
| Fife | No | |||
| Fife | No | |||
| No | ||||
| Mr Patrick Lyon of Auchterhouse | Forfarshire | No | ||
| Mr James Carnagie of Phinhaven | Forfarshire | No | ||
| Forfarshire | No | |||
| Kirkcudbrightshire | No | |||
| Kirkcudbrightshire | No | |||
| Caithness | No | |||
| Sir Henry Innes, younger, of that ilk | Elginshire | No | ||
| Ross-shire | No | |||
| Robert Inglis | Edinburgh | No | ||
| Alexander Robertson | Perth | No | ||
| Walter Stewart | No | |||
| Glasgow | Court Party | No | ||
| Alexander Edgar | Haddington | No | ||
| Alexander Duff | Banffshire | No | ||
| Francis Molison | Brechin | No | ||
| Walter Scott | Jedburgh | No | ||
| Robert Scott | Selkirk | No | ||
| Robert Kellie | Dunbar | No | ||
| John Hutchesone | Arbroath | No | ||
| Archibald Scheills | Peebles | No | ||
| Mr John Lyon | Forfar | No | ||
| George Brodie | Forres | No | ||
| George Spens | Rutherglen | No | ||
| Sir David Cuningham | Lauder | No | ||
| Mr John Carruthers | Lochmaben | No | ||
| George Home | New Galloway | No | ||
| John Bayne | Dingwall | No | ||
| Mr Robert Fraser | Wick | No | ||
| Total Ayes | 106 | |||
| Total Noes | 69 | |||
| Total Votes | 175 | |||
| Sources: Records of the Parliament of Scotland, Parliamentary Register, p.598 | ||||
See also[]
- Acts of Union 1800 (King of Great Britain with Kingdom of Ireland)
- Kingdom of Ireland
- English independence
- History of democracy
- List of treaties
- MacCormick v Lord Advocate
- Parliament of the United Kingdom
- Political union
- Real union
- Scottish independence
- Unionism in Scotland
- Welsh independence
Notes[]
References[]
- ^ The citation of this Act by this short title was authorised by section 1 of, and Schedule 1 to, the Short Titles Act 1896. Due to the repeal of those provisions, it is now authorised by section 19(2) of the Interpretation Act 1978.
- ^ Article I of the Treaty of Union
- ^ "House of Commons Journal Volume 1: 31 March 1607". Retrieved 27 October 2020.
- ^ Act of Union 1707, Article 3
- ^ Larkin & Hughes 1973, p. 19.
- ^ Lockyer 1998, pp. 51–52.
- ^ Lockyer 1998, pp. 54–59.
- ^ Stephen 2010, pp. 55–58.
- ^ McDonald 1998, pp. 75–76.
- ^ Kaplan 1970, pp. 50–70.
- ^ Robertson 2014, p. 125.
- ^ Harris 2015, pp. 53–54.
- ^ Morrill 1990, p. 162.
- ^ Constitution.org
- ^ The 1657 Act's long title was An Act and Declaration touching several Acts and Ordinances made since 20 April 1653, and before 3 September 1654, and other Acts
- ^ Parliament.uk Archived 12 October 2008 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ MacIntosh 2007, pp. 79–87.
- ^ Whatley 2001, p. 95.
- ^ Lynch 1992, p. 305.
- ^ Harris 2007, pp. 404–406.
- ^ Whatley 2006, p. 91.
- ^ Mitchison 2002, pp. 301–302.
- ^ Richards 2004, p. 79.
- ^ Mitchison 2002, p. 314.
- ^ Munck 2005, pp. 429–431.
- ^ Jackson 2003, pp. 38–54.
- ^ Horwitz 1986, pp. 10–11.
- ^ Lynch 1992, pp. 300–303.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c d e f g h i MacPherson, Hamish (27 September 2020). "How the Act of Union came about through a corrupt fixed deal in 1706". The National. Retrieved 27 September 2020.
- ^ Jump up to: a b "Ratification, October 1706 – March 1707". www.parliament.uk. Retrieved 27 September 2020.
- ^ Cullen 2010, p. 117.
- ^ Whatley 2001, p. 48.
- ^ Watt 2007, p. ?.
- ^ Whatley 1989, pp. 160–165.
- ^ Devine, T. M. (Thomas Martin) (5 July 2012). The Scottish nation : a modern history. London: Penguin. ISBN 978-0-7181-9673-8. OCLC 1004568536.
- ^ "Scottish Referendums". BBC. Retrieved 16 March 2016.
- ^ Bambery 2014, p. ?.
- ^ The Humble Address of the Commissioners to the General Convention of the Royal Burrows of this Ancient Kingdom Convened the Twenty-Ninth of October 1706, at Edinburgh.
- ^ Notes by John Purser to CD Scotland's Music, Facts about Edinburgh.
- ^ Jump up to: a b "The commissioners". UK Parliament website. 2007. Archived from the original on 19 June 2009. Retrieved 5 February 2013.
- ^ "The course of negotiations". UK Parliament website. 2007. Archived from the original on 21 July 2009. Retrieved 5 February 2013.
- ^ "Ratification". UK parliament website. 2007. Archived from the original on 19 June 2009. Retrieved 5 February 2013.
- ^ "1 May 1707 – the Union comes into effect". UK Parliament website. 2007. Archived from the original on 19 June 2009. Retrieved 5 February 2013.
- ^ Riley 1969, pp. 523–524.
- ^ G.N. Clark, The Later Stuarts, 1660–1714 (2nd ed. 1956) pp 290–93.
- ^ Gordon Brown (2014). My Scotland, Our Britain: A Future Worth Sharing. Simon & Schuster UK. p. 150. ISBN 9781471137518.
- ^ House of Lords – Written answers, 6 November 2006, TheyWorkForYou.com
- ^ Announced by the Scottish Culture Minister, Patricia Ferguson, 9 November 2006
Sources and further reading[]
- Bambery, Chris (2014). A People's History of Scotland. Verso. ISBN 978-1786637871.
- Campbell, R. H. “The Anglo-Scottish Union of 1707. II. The Economic Consequences.” Economic History Review vol. 16, no. 3, 1964, pp. 468–477 online
- Cullen, K. J. (2010). Famine in Scotland: The "Ill Years" of the 1690s. Edinburgh University Press. ISBN 978-0748638871.
- Harris, Tim (2007). Revolution: The Great Crisis of the British Monarchy, 1685–1720. Penguin. ISBN 978-0141016528.
- Harris, Tim (2015). Rebellion: Britain's First Stuart Kings, 1567–1642. OUP Oxford. ISBN 978-0198743118.
- Horwitz, Henry (1986). Parliament, Policy and Politics in the Reign of William III. MUP. ISBN 978-0719006616.
- Jackson, Clare (2003). Restoration Scotland, 1660–1690: Royalist Politics, Religion and Ideas. Boydell Press. ISBN 978-0851159300.
- Kaplan, Lawrence (May 1970). "Steps to War: The Scots and Parliament, 1642–1643". Journal of British Studies. 9 (2): 50–70. doi:10.1086/385591. JSTOR 175155.
- Larkin, James F.; Hughes, Paul L., eds. (1973). Stuart Royal Proclamations: Volume I. Clarendon Press.
- Lynch, Michael (1992). Scotland: a New History. Pimlico Publishing. ISBN 978-0712698931.
- Lockyer, R (1998). James VI and I. London: Addison Wesley Longman. ISBN 978-0-582-27962-9.
- MacIntosh, Gillian (2007). Scottish Parliament under Charles II, 1660–1685. Edinburgh University Press. ISBN 978-0748624577.
- McDonald, Alan (1998). The Jacobean Kirk, 1567–1625: Sovereignty, Polity and Liturgy. Routledge. ISBN 978-1859283738.
- Mitchison, Rosalind (2002). A History of Scotland. Routledge. ISBN 978-0415278805.
- Morrill, John (1990). Oliver Cromwell and the English Revolution. Longman. ISBN 978-0582016750.
- Munck, Thomas (2005). Seventeenth-Century Europe: State, Conflict and Social Order in Europe 1598–1700. Palgrave. ISBN 978-1403936196.
- Richards, E (2004). OBritannia's Children: Emigration from England, Scotland, Wales and Ireland since 1600. Continuum. ISBN 1852854413.
- Riley, PJW (1969). "The Union of 1707 as an Episode in English Politics". The English Historical Review. 84 (332): 498–527. JSTOR 562482.
- Robertson, Barry (2014). Royalists at War in Scotland and Ireland, 1638–1650. Routledge. ISBN 978-1317061069.
- Smout, T. C. “The Anglo-Scottish Union of 1707. I. The Economic Background.” Economic History Review vol. 16, no. 3, 1964, pp. 455–467. online
- Stephen, Jeffrey (January 2010). "Scottish Nationalism and Stuart Unionism". Journal of British Studies. 49 (1, Scottish Special). doi:10.1086/644534. S2CID 144730991.
- Watt, Douglas (2007). The Price of Scotland: Darien, Union and the wealth of nations. Luath Press. ISBN 978-1906307097.
- Whatley, C (2001). Bought and sold for English Gold? Explaining the Union of 1707. East Linton: Tuckwell Press. ISBN 978-1-86232-140-3.
- Whatley, C (2006). The Scots and the Union. Edinburgh University Press. ISBN 978-0-7486-1685-5.
- Whatley, Christopher (1989). "Economic Causes and Consequences of the Union of 1707: A Survey". Scottish Historical Review. 68 (186).
Other books[]
- Defoe, Daniel. A tour thro' the Whole Island of Great Britain, 1724–27
- Defoe, Daniel. The Letters of Daniel Defoe, GH Healey editor. Oxford: 1955.
- Fletcher, Andrew (Saltoun). An Account of a Conversation
- Lockhart, George, "The Lockhart Papers", 1702–1728
External links[]
 The full text of Act of Union 1707 at Wikisource
The full text of Act of Union 1707 at Wikisource- Union with England Act and Union with Scotland Act – Full original text
- Treaty of Union and the Darien Experiment, University of Guelph, McLaughlin Library, Library and Archives Canada
- Text of the Union with Scotland Act 1706 as in force today (including any amendments) within the United Kingdom, from legislation.gov.uk.
- Text of the Union with England Act 1707 as in force today (including any amendments) within the United Kingdom, from legislation.gov.uk.
- Union with England Act 1707, from Records of the Parliaments of Scotland
- Image of original act from the Parliamentary Archives website
- 1706 in England
- 1706 in law
- 1707 in law
- 1707 in Great Britain
- 1707 in Scotland
- Acts of the Parliament of England
- Acts of the Parliament of England still in force
- Acts of the Parliament of Scotland
- Unionism in the United Kingdom
- Constitutional laws of the United Kingdom
- England–Scotland relations
- Political history of Great Britain
- National unifications
- Political charters
- Unionism in Scotland
- Treaties of England
- Treaties of Scotland
- 1707 in British law
- 1706 in politics
- Church of Scotland

