Angeles National Forest
| Angeles National Forest | |
|---|---|
 The San Gabriel Mountains, part of the Angeles National Forest. The southwest view from Islip Saddle shows Bear Creek, a tributary of the San Gabriel River that lies within the San Gabriel Wilderness, and Twin Peaks 7,761 feet (2,366 m). | |
 | |
| Location | Los Angeles, San Bernardino, and Ventura counties, California, United States |
| Nearest city | Los Angeles |
| Coordinates | 34°20′N 118°08′W / 34.333°N 118.133°WCoordinates: 34°20′N 118°08′W / 34.333°N 118.133°W |
| Area | 655,387 acres (2,652.26 km2) |
| Established | July 1, 1908 |
| Governing body | U.S. Forest Service |
| Website | Angeles National Forest |
California Historical Landmark | |
| Reference no. | 717[1] |

The Angeles National Forest (ANF) of the U.S. Forest Service is located in the San Gabriel Mountains and Sierra Pelona Mountains, primarily within Los Angeles County in southern California. The ANF manages a majority of the San Gabriel Mountains National Monument.
The national forest was established in 1908, incorporating the first San Bernardino National Forest and parts of the former Santa Barbara and San Gabriel National Forests. Angeles National Forest headquarters are located in Arcadia, California.
Geography[]
The Angeles National Forest covers a total of 700,176 acres (1,094.0 sq mi; 2,833.5 km2), protecting large areas of the San Gabriel Mountains and Sierra Pelona Mountains. It is located just north of the densely inhabited metropolitan area of Greater Los Angeles.
While primarily within Los Angeles County, a small part extends eastward into southwestern San Bernardino County, in the Mount San Antonio ("Mount Baldy") area, and a tiny section also extends westward into northeastern Ventura County, in the Lake Piru area.
The San Gabriel Mountains National Monument, established in 2014 and managed by the U.S. Forest Service, is largely within the Angeles National Forest.
The John D. Dingell Jr. Conservation, Management, and Recreation Act of 2019 established the Saint Francis Dam Disaster National Memorial and Saint Francis Dam Disaster National Monument at and around the ruins of the St. Francis Dam in the Forest's San Francisquito Canyon.[2]
Wilderness areas[]
The Angeles National Forest contains five nationally designated wilderness areas. Two of these also extend into neighboring San Bernardino National Forest:
- Cucamonga Wilderness — mostly in San Bernardino NF
- Magic Mountain Wilderness
- Pleasant View Ridge Wilderness
- San Gabriel Wilderness
- Sheep Mountain Wilderness — partially in San Bernardino NF
Climate[]
| hideClimate data for Angeles National Forest (at San Gabriel Canyon) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Average high °F (°C) | 68.5 (20.3) |
69.1 (20.6) |
70.0 (21.1) |
73.3 (22.9) |
77.9 (25.5) |
84.0 (28.9) |
91.5 (33.1) |
91.7 (33.2) |
87.5 (30.8) |
80.9 (27.2) |
75.5 (24.2) |
68.5 (20.3) |
78.2 (25.7) |
| Average low °F (°C) | 47.2 (8.4) |
47.3 (8.5) |
47.8 (8.8) |
49.7 (9.8) |
53.1 (11.7) |
55.8 (13.2) |
58.7 (14.8) |
59.9 (15.5) |
58.7 (14.8) |
55.1 (12.8) |
52.7 (11.5) |
47.9 (8.8) |
52.8 (11.6) |
| Average precipitation inches (mm) | 4.40 (112) |
5.06 (129) |
3.50 (89) |
1.69 (43) |
0.62 (16) |
0.19 (4.8) |
0.04 (1.0) |
0.11 (2.8) |
0.39 (9.9) |
0.86 (22) |
1.92 (49) |
3.49 (89) |
22.28 (566) |
| Source: [3] | |||||||||||||
| hideClimate data for Angeles National Forest (at Hughes Lake) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Average high °F (°C) | 51 (11) |
55 (13) |
59 (15) |
64 (18) |
71 (22) |
80 (27) |
89 (32) |
89 (32) |
84 (29) |
73 (23) |
60 (16) |
53 (12) |
68 (20) |
| Average low °F (°C) | 35 (2) |
37 (3) |
39 (4) |
44 (7) |
50 (10) |
59 (15) |
66 (19) |
66 (19) |
60 (16) |
51 (11) |
41 (5) |
35 (2) |
48 (9) |
| Average precipitation inches (mm) | 4.20 (107) |
1.30 (33) |
3.11 (79) |
0.80 (20) |
0.18 (4.6) |
0 (0) |
0.01 (0.25) |
0.03 (0.76) |
0.15 (3.8) |
0.26 (6.6) |
1.81 (46) |
2.48 (63) |
14.32 (364) |
| Average snowfall inches (cm) | 0 (0) |
0.5 (1.3) |
0.1 (0.25) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
1.5 (3.8) |
2.1 (5.3) |
| Source: [4] | |||||||||||||
| hideClimate data for Angeles National Forest (at Mt. Baldy Notch) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Average high °F (°C) | 42.7 (5.9) |
42.3 (5.7) |
41.7 (5.4) |
48.0 (8.9) |
59.1 (15.1) |
67.7 (19.8) |
75.3 (24.1) |
77.4 (25.2) |
68.1 (20.1) |
59.8 (15.4) |
48.3 (9.1) |
42.2 (5.7) |
56.0 (13.3) |
| Average low °F (°C) | 26.4 (−3.1) |
25.7 (−3.5) |
25.2 (−3.8) |
29.4 (−1.4) |
37.3 (2.9) |
43.2 (6.2) |
53.2 (11.8) |
52.6 (11.4) |
46.3 (7.9) |
40.2 (4.6) |
30.9 (−0.6) |
26.0 (−3.3) |
36.4 (2.4) |
| Average precipitation inches (mm) | 8.45 (215) |
7.80 (198) |
3.70 (94) |
4.62 (117) |
0.81 (21) |
0.07 (1.8) |
0.37 (9.4) |
0.35 (8.9) |
1.24 (31) |
0.65 (17) |
5.71 (145) |
6.58 (167) |
40.36 (1,025) |
| Average snowfall inches (cm) | 11.9 (30) |
20.5 (52) |
29.5 (75) |
44.6 (113) |
3.2 (8.1) |
0.3 (0.76) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0.5 (1.3) |
0.9 (2.3) |
6.3 (16) |
13.5 (34) |
131.3 (334) |
| Source: [5] | |||||||||||||
History[]
The San Gabriel Forest Reserve was established on December 20, 1892, the San Bernardino Forest Reserve was established on February 25, 1893, and the Santa Barbara Forest Reserve was established on December 22, 1903. Together, they became National Forests on March 4, 1907, and they were combined on July 1, 1908, with all of the San Bernardino forest and portions of San Gabriel forest and Santa Barbara forest composing the new Angeles National Forest. On September 30, 1925, portions of the Angeles National Forest and the Cleveland National Forest were detached to re-establish the San Bernardino National Forest.[6]
Angeles National Forest is registered as California Historical Landmark #717, for being the first National Forest in the state.[1]
The campgrounds at Broken Blade, Twisted Arrow and Pima Loops were closed on July 26, 2013 after squirrel infected with bubonic plague was discovered.[7]
Wildfires[]

Loop Fire[]
On 1 November 1966, a fire started at 5:19 a.m. on the Los Pinetos Nike Site (LA-94). The fire spread, threatening medical facilities and residential areas south edge of the national forest. 12 firefighters with United States Forest Service's El Cariso "Hot Shot" crew were killed they were caught in a flare up in a canyon. 11 more firefighters were seriously burned in the incident.[8] The fire was brought under control on at 1:00 p.m. on 2 November, having burned 2,028 acres (8.21 km2).[8]
Station Fire[]
In the Station Fire, more than 161,000 acres (650 km2) of the forest were burned by an arson fire that began on August 26, 2009, near Angeles Crest Highway in La Cañada and quickly spread, fueled by dry brush that had not burned for over 150 years. The fire burned for more than a month and was the worst in Los Angeles County history, charring 250 square miles (650 km2), approximately one-fourth of the forest; displacing wildlife, and destroying 91 homes, cabins and outbuildings and the family-owned Hidden Springs Cafe.
During the fire, two firefighters died after driving off the Mt. Gleason County Road looking for an alternate route to get the inmates out at Camp 16. The Station Fire threatened the Mount Wilson Observatory atop Mt. Wilson . The site includes two telescopes, two solar towers, and transmitters for 22 television stations, several FM radio stations, and police and fire department emergency channels. Although the fire scorched one side of the outhouse at amateur-owned Stony Ridge Observatory, six miles northeast of Mt. Wilson, aside from minor damage from smoke and ash infiltration, the remainder of the observatory and its historic 30-inch Carroll telescope survived.
Bobcat Fire (2020)[]
In September and October 2020, the Bobcat Fire burned 115,796 acres (180.931 sq mi) (468 km2) in the central San Gabriel Mountains of the Angeles National Forest. It was one of the largest wildfires in Los Angeles County history.[9]
Natural history[]
The Angeles National Forest manages the habitats, flora and fauna ecosystems, and watersheds. Some of the rivers with watersheds within its boundaries provide valuable non-groundwater recharge water for Southern California. The existing protected and restored native vegetation absorb and slow surface runoff of rainwater to minimize severe floods and landslides in adjacent communities.[10] The land within the forest is diverse, both in appearance and terrain. Elevations range from 1,200 to 10,064 ft (366 to 3,068 m). The Pacific Crest Trail crosses the forest.
Flora[]

Much of this National Forest is covered with dense chaparral shrub forests with oak woodlands, which changes to pine and fir-covered slopes in the higher elevations. Subsequent to the fire there was a heavy growth of poodle-dog bush, apparently triggered by the fire's effect on dormant seeds, that lasted for several years. The plant produces prolific lavender flowers. Unfortunately, as visitors to the Forest discovered, contact with it may cause a poison-oak-like rash.
Tree species for which the forest is important include bigcone Douglas-fir (Pseudotsuga macrocarpa), Coulter pine (Pinus coulteri), and California walnut (Juglans californica). The National Forest also contains some 29,000 acres (12,000 ha) of old growth, with: Jeffrey pine (Pinus jeffreyi) forests and mixed conifer forests (Coast Douglas-fir (Pseudotsuga menziesii var. menziesii), ponderosa pine (Pinus ponderosa), and white fir (Abies concolor)), and lodgepole pine (Pinus contorta) the most abundant types.[11]
Fauna[]
This forest is home to black bears, gray foxes, bobcats, cougars, mule deer, bighorn sheep, rattlesnakes and coyotes.
Access[]
A National Forest Adventure Pass is required for parking at many locations in the Angeles National Forest and other National Forests in Southern California, and this can be obtained online or from visitor centers and local merchants.[12] Los Angeles County has declared that passes are not required on county-maintained roads. There are also many other areas that do not require the pass.
General information[]
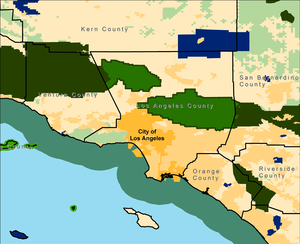
- Acres of land: 700,176 (2652 km2)
- Wilderness areas acres: 80,284 (324.9 km2)
- Miles of roads: 1,032 (1661 km)
- Visitor centers: 4
- Information centers: 4
- Fire lookout towers: 2
- Recreational residences: 505
- Picnic areas: 36
- Campgrounds: 66
- Ski areas: 2
- Entrance stations: 2
Ranger Districts[]
- Los Angeles Gateway Ranger District
- Station: San Fernando, California
- San Gabriel Mountains National Monument
- Station: Glendora, California
Trails[]
- Trailheads: 53
- Trail miles: 697 (1122 km)
- Off highway vehicle areas: 3
- Off highway vehicle route miles: 261 (420 km)
Natural features[]

- Wilderness areas: 5
- Lakes and reservoirs: 10
- Rivers and stream miles: 240
Sensitive species[]
- Sensitive plants: 22
- Sensitive wildlife: 23
- Threatened & endangered species: 16
Mountain peaks[]

Mountains within the Angeles National Forest include:
- Mount San Antonio 10,064 ft (3,068 m) — also known as "Mt. Baldy"
- Pine Mountain 9,648 ft (2,941 m)
- Dawson Peak 9,575 ft (2,918 m)
- Mount Harwood 9,556 ft (2,913 m)
- Mount Baden-Powell 9,407 ft (2,867 m)
- Throop Peak 9,142 ft (2,786 m)
- Mount Burnham 9,001 ft (2,744 m)
- Telegraph Peak (California) 8,989 ft (2,740 m)
- Mount Islip 8,250 ft (2,510 m) — site of historic Mt. Islip fire lookout tower [13]
- Waterman Mountain 8,041 ft (2,451 m)
- Iron Mountain (Los Angeles County) 8,010 ft (2,440 m)
- South Mount Hawkins 7,783 ft (2,372 m) Lookout destroyed in Curve Fire 2002
- Mount Gleason 6,502 ft
- San Gabriel Peak 6,164 ft (1,879 m)
- Mount Disappointment (California) 5,963 ft (1,818 m)
- Vetter Mountain 5,911 ft (1,802 m) ) — site of historic Vetter Mountain fire lookout tower
- Burnt Peak 5,788 ft (1,764 m)
- Mount Wilson 5,710 ft (1,740 m) — location of the Mount Wilson Observatory
- Mount Lowe (California) 5,606 ft (1,709 m)
- Mount Lukens 5,074 ft (1,547 m)
- Echo Mountain 3,210 ft (980 m)
All the above mountains are part of the San Gabriel Mountains, except for Burnt Peak, which is in the Sierra Pelona Mountains.
Water recreation[]
- Pyramid Lake is located next to Interstate 5 (take Smokey Bear exit), 20 miles (32 km) north of Magic Mountain Amusement Park in Valencia, California.
- Castaic Lake is located 7 miles (11 km) north of Magic Mountain Amusement Park in Valencia, California, just off Interstate 5 (take Lake Hughes exit.) The lake is managed by the L.A. County Department of Parks and Recreation
- Elizabeth Lake is located approximately 10 miles (16 km) west of Palmdale, California, on Elizabeth Lake Rd. It can completely dry up in drought years.
- Crystal Lake is a small natural lake located near the northern end of Highway 39.
- Jackson Lake is another natural lake located on the San Andreas Fault about 2 miles (3.2 km) west of the community of Big Pines and roughly 9 miles (14 km) west of the town of Phelan, California.
Volunteer organizations[]
- Angeles National Forest Fire Lookout Association: Restoration and operation of fire lookout towers in the ANF
- Altadena Mountain Rescue Team: Saving lives through mountain rescue and safety education
- Concerned Off-Road Bicyclists Association: Restoration and maintenance of multi-use trails in the ANF
- Sierra Madre Search & Rescue: A group of dedicated volunteers committed to saving lives in the wilderness[14]
- San Gabriel Mountains Trailbuilders: California's hiking and nature trail repair group[15]
- West Fork Conservancy: Maintains the West Fork of the San Gabriel River and Beer Creek[16]
- Angeles Volunteer Association: Organizes Visitor Center information, trail repair, and a broad spectrum of forestry efforts[17]
- Fisheries Resource Volunteer Corps: works with the Forest Service, helping with various projects during the year[18]
- San Dimas Mountain Rescue Team: Highly trained mountain rescue team[19] http://www.savetheeastfork.org/
- Los Angeles County Sheriff's Air Rescue 5: Volunteer Reserve Deputy Sheriffs are paid $1 a year for their work
- Save The East Fork Association: Works along the East Fork of the San Gabriel River [20]
- Helping Our Mountain Environment: HOME—Glendora Mountain Road (GMR) trash and spray paint cleaning [21]
- Lowelifes Trail Crew: Lowelifes focuses on trail work in Southern California’s Angeles National Forest, fostering conservation, sustainability, & community in Los Angeles County.[22]
Gallery[]

San Gabriel Mountains

San Gabriel Canyon

San Gabriel River

Jackson Lake

Along the Icehouse Canyon Trail
Sierra Pelona Mountains

San Francisquito Canyon

View west from Angeles Crest Highway

Riparian zone habitat.
Montane chaparral ecotone with the Mojave Desert. Yellow sulphurflower buckwheat flowers in foreground.
California Historical Landmark[]
The California Historical Landmark Marker NO. 717 at San Gabriel Mountain, Clear Creek vista point, State Hwy 2, 8.3 mi N of I-210, La Canada reads:[23]
- NO. 717 THE ANGELES NATIONAL FOREST - The first national forest in the State of California and second in the United States, Angeles National Forest was created by proclamation of President Benjamin Harrison on December 20, 1892. The first name given to the forest, "'San Gabriel Timberland Reserve," was changed to "San Gabriel National Forest" March 4, 1907 and then to "Angeles National Forest" on July 1, 1908..
See also[]
- San Gabriel Mountains−related topics
- San Gabriel Mountains National Monument−related topics
- Henninger Flats
- Los Padres National Forest — adjacent northwest
- San Bernardino National Forest — adjacent on east
References[]
- ^ Jump up to: a b "Angeles National Forest". Office of Historic Preservation, California State Parks. Retrieved 2012-10-07.
- ^ "Trump's signature means St. Francis Dam memorial is coming". Ventura County Star. Retrieved 2019-04-01.
- ^ "SAN GABRIEL CANYON, CALIFORNIA (047776)". www.wrcc.dri.edu. Retrieved April 19, 2021.
- ^ "LAKE HUGHES, CALIFORNIA". www.weatherbase.com. Retrieved April 19, 2021.
- ^ "MT BALDY NOTCH, CALIFORNIA (045901)". www.wrcc.dri.edu. Retrieved March 27, 2021.
- ^ Davis, Richard C. (September 29, 2005), National Forests of the United States (PDF), The Forest History Society
- ^ "Plague squirrel closes Calif. campgrounds". USA Today. July 26, 2013. Retrieved 26 July 2013.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Pyles, Hamilton; Spaulding, Alfred; Wilson, Carl; Moore, William; Brunton, George (n.d.). "The Loop Fire Disaster" (PDF). Fireleadership.gov. United States Forest Service. Archived from the original (PDF) on 16 May 2019. Retrieved 29 June 2019.
- ^ "Bobcat Information - InciWeb the Incident Information System". inciweb.nwcg.gov.
- ^ Lockman, Ronald F., 1981. Guarding the Forests of Southern California: Evolving Attitudes Toward Conservation of Watershed, Woodlands, and Wilderness (Glendale: A. H. Clarke).
- ^ Warbington, Ralph; Beardsley, Debby (2002), 2002 Estimates of Old Growth Forests on the 18 National Forests of the Pacific Southwest Region, United States Forest Service, Pacific Southwest Region
- ^ "Angeles Passes and Permits". Angeles Permits. Archived from the original on 17 January 2013. Retrieved 2008-02-14.
- ^ USFS.gov: Mt. Islip fire lookout tower
- ^ Sierra Madre Search & Rescue
- ^ San Gabriel Mountain Trailbuilders
- ^ West Fork Conservancy
- ^ Angeles Volunteer Association
- ^ Fisheries Resource Volunteer Corps
- ^ San Dimas Mountain Rescue Team
- ^ Save The East Fork
- ^ (Facebook: Helping Our Mountain Environment page)
- ^ "Lowelifes RCC". Lowelifes Respectable Citizens' Club. Retrieved 2021-07-27.
- ^ californiahistoricallandmarks.com 717, Angeles National Forest
Further reading[]
- Russ Leadabrand, A Guide o the San Gabriel Mountains of California (L.A.: Ritche Press, 1963).
- John W. Robinson, The San Gabriels: Southern California Mountain Country (San Marino: Goldwest Books, 1977).
- W. W. Robinson, The Forest and the People: The Story of the Angeles National Forest (LA: Title and Trust Insurance co., 1946).
External links[]
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Angeles National Forest. |
| Wikivoyage has a travel guide for Angeles National Forest. |
- Official Angeles National Forest website—at National Forest Service (Accessed 05 Dec 2014)
- Crystal Lake Recreation Area—Largest campground in the Angeles National Forest (Accessed 05 Dec 2014)
- Southern California Trails at Local Hikes (Accessed 05 Dec 2014)
- Hiking Trails around Wrightwood, in the Angeles National Forest—Wrightwood Hiking Trails (Accessed 05 Dec 2014)
- Mountains around Wrightwood, in the Angeles National Forest—San Gabriel Mountains (Accessed 05 Dec 2014)
- Canyons and Valleys around Wrightwood, in the Angeles National Forest—Canyons and Valleys in the Angeles National Forest (Accessed 05 Dec 2014)
- Photograph of Angeles National Forest fire bulldozer transport December 2017 - saved at archive.org
- Image of vacationers at Crystal Lake, Angeles National Forest, 1935. Los Angeles Times Photographic Archive (Collection 1429). UCLA Library Special Collections, Charles E. Young Research Library, University of California, Los Angeles.
- Angeles National Forest
- National Forests of California
- Parks in Los Angeles County, California
- Protected areas of Los Angeles County, California
- Protected areas of the Mojave Desert
- San Gabriel Mountains
- Sierra Pelona Ridge
- California Historical Landmarks
- Parks in Southern California
- Protected areas established in 1908
- 1908 establishments in California
- Protected areas of the Southern California area
- Tourist attractions in Los Angeles County, California











