Anterior superior alveolar nerve
| Anterior superior alveolar nerve | |
|---|---|
 | |
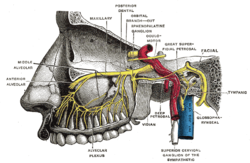 Alveolar branches of superior maxillary nerve and sphenopalatine ganglion. | |
| Details | |
| From | Infraorbital nerve |
| Innervates | dental alveolus |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | rami alveolares superiores anteriores nervi maxillaris, ramus alveolaris superior anteriores |
| TA98 | A14.2.01.052 |
| TA2 | 6241 |
| FMA | 52935 |
| Anatomical terms of neuroanatomy | |
The anterior superior alveolar nerve (or anterior superior dental nerve), is a branch of the infraorbital nerve, itself a branch of the maxillary nerve (V2). It branches from the infraorbital nerve within the infraorbital canal before the infraorbital nerve exits through the infraorbital foramen. It descends in a canal in the anterior wall of the maxillary sinus, and divides into branches which supply the incisor and canine teeth.[1]
It communicates with the middle superior alveolar nerve, and gives off a , which passes through a minute canal in the lateral wall of the inferior meatus, and supplies the mucous membrane of the anterior part of the inferior meatus and the floor of the nasal cavity, communicating with the nasal branches from the sphenopalatine ganglion.
Dental considerations for this nerve are important. The anterior superior alveolar usually innervates all anterior teeth, loops backwards to join the middle superior alveolar nerve to form the superior dental plexus.
See also[]
- Anterior superior alveolar arteries
- Middle superior alveolar nerve
- Posterior superior alveolar nerve
References[]
- ^ Jones, Frederic Wood (July 1939). "The anterior superior alveolar nerve and vessels". Journal of Anatomy. 73 (Pt 4): 583–591. PMC 1252464. PMID 17104781.
![]() This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 891 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 891 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
External links[]
- MedEd at Loyola GrossAnatomy/h_n/cn/cn1/cnb2.htm
- cranialnerves at The Anatomy Lesson by Wesley Norman (Georgetown University) (V)
- Wikipedia articles incorporating text from the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
- Maxillary nerve
- Neuroscience stubs