Infratrochlear nerve
The infratrochlear nerve is a branch of the nasociliary nerve, itself a branch of the ophthalmic nerve.
| Infratrochlear nerve | |
|---|---|
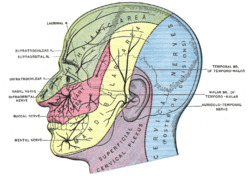 Sensory innervation of the head. The infratrochlear nerve is seen in the green area, emerging from the orbit. | |
| Details | |
| From | Nasociliary nerve |
| Innervates | skin of eyelids, conjunctiva, lacrimal sac, lacrimal caruncle, side of nose above medial canthus |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | Nervus infratrochlearis |
| TA98 | A14.2.01.035 |
| TA2 | 6214 |
| FMA | 52693 |
| Anatomical terms of neuroanatomy | |
Structure[]
The nasociliary nerve terminates by bifurcating into the infratrochlear and the anterior ethmoidal nerves. The infratrochlear nerve travels anteriorly in the orbit along the upper border of the medial rectus muscle and underneath the trochlea of the superior oblique muscle. It exits the orbit medially and divides into small sensory branches.[1]
Function[]
The infratrochlear nerve provides sensory innervation to the skin of the eye lids, the conjunctiva, lacrimal sac, lacrimal caruncle and the side of the nose above the medial canthus.
Etymology[]
The infratrochlear nerve is named after a structure it passes under. Infratrochlear means "below the trochlea". The term trochlea means "pulley" in Latin. Specifically, the trochlea refers to a fibrocartilaginous loop at the superomedial surface of the orbit called the trochlea, through which the tendon of the superior oblique muscle passes.
Additional images[]

Nerves of the orbit. Seen from above. The infratrochlear nerve is labelled at the top left, and can be seen as a terminal branch of the nasociliary nerve, along with the anterior ethmoidal nerve.
References[]
External links[]
- MedEd at Loyola GrossAnatomy/h_n/cn/cn1/cnb1.htm
- cranialnerves at The Anatomy Lesson by Wesley Norman (Georgetown University) (V)
- Ophthalmic nerve
