Assimineidae
| Assimineidae Temporal range:
| |
|---|---|
| |
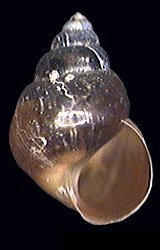
| Apertural view of a shell of Assiminea grayana | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Mollusca |
| Class: | Gastropoda |
| Subclass: | Caenogastropoda |
| Clade: | Hypsogastropoda |
| Order: | Littorinimorpha |
| Superfamily: | Truncatelloidea |
| Family: | Assimineidae H. Adams & A. Adams, 1856 |
| Subfamilies | |
|
| |
| Diversity[1] | |
| About 20 freshwater species and numerous amphibious terrestrial/marine species | |
| Synonyms | |
| |
Assimineidae is a family of minute snails, also known as palmleaf snails, with an operculum, gastropod mollusks or micromollusks in the superfamily Rissoidae. Many of these very small snails live in intermediate habitats, being amphibious between saltwater and land; others live in freshwater.
Distribution[]
The distribution of the Assimineidae is worldwide.[2] The oldest fossils are known from the Cenomanian aged Burmese amber.[3]
Ecology[]
Various species in this family occur in estuarine habitats, in salt marshes and in freshwater. Some are terrestrial or amphibious.
Description[]
The shell is small to medium large, more or less egg-conelike shaped.[2] The apertural margin is simple.[2] The operculum is in most cases horny.[2]
Species in this family are characterized by rudimentary cephalic tentacles, a trunklike snout, a foot with a groove and rudimentary to absent ctenidium (a comb-like respiratory apparatus).[4]
Taxonomy[]
The following three subfamilies were recognized in the taxonomy of Bouchet & Rocroi (2005):
- Subfamily Assimineinae H. Adams & A. Adams, 1856 - synonym: Synceratidae Bartsch, 1920
- Subfamily Thiele, 1929 - synonyms: Paludinellidae Kobelt, 1878 (n.a.); Cyclotropidae Iredale, 1941
- Subfamily Thiele, 1927 - Realiinae L. Pfeiffer, 1853 (inv.); Adelomorphinae Kobelt, 1906 (inv.); Garrettiinae Kobelt, 1906; Pseudocyclotini Thiele, 1929; Thaanumellinae Clench, 1946; Tutuilanidae Hubendick, 1952
Genera[]
Genera in the family Assimineidae include:[5][6][7]
subfamily Assimineinae
- Assiminea Fleming, 1828 - type genus of Assimineidae, synonym: Assiminia
- Thiele, 1927
- Aviassiminea Fukuda & Ponder, 2003
- Conassiminea Fukuda & Ponder, 2006
- Cryptassiminea Fukuda & Ponder, 2005
- Heude, 1882
- Thiele, 1927
- Thiele, 1927
- Heude, 1882
- Sculptassiminea Thiele, 1927
subfamily Ekadantinae
- Acmella Blanford, 1869
- Cyclotropis Tapparone Canefri, 1883
- Rao, 1928
- Metassiminea Thiele, 1927
- Optediceros Leith, 1853
- Paludinella Pfeiffer, 1841
- Rugapedia Fukuda & Ponder, 2004
- Heude, 1882
- Kuroda & Habe, 1950
subfamily Omphalotropidinae
- Omphalotropis Pfeiffer, 1851 - type genus of the subfamily Omphalotropidinae
- Paetel, 1873
- Thiele, 1894
- Thaanumella Clench, 1946
Subfamily Garrettiinae Kobelt, 1906
- B. Rensch, 1932
- Atropis Pease, 1871
- Austroassiminea Solem, Girardi, Slack-Smith & Kendrick 1982
- Crosse, 1891
- Chalicopoma Möllendorff, 1894
- Conacmella Thiele, 1925
- Thiele, 1927
- Pease, 1871
- Iredale, 1933
- Duritropis Iredale, 1944
- Baird, 1850
- Eussoia Preston, 1912
- Cooke & Clench, 1943
- Paetel, 1873
- Kubaryia Clench, 1948
- Thiele, 1927
- Limborelia Iredale, 1944
- Clench, 1958
- Omphalotropis L. Pfeiffer, 1851
- Opinorelia Iredale, 1944
- Habe, 1994
- Ponapella Clench, 1946
- Thiele, 1927
- Thiele, 1894
- Dautzenberg, 1890
- Quadrasiella Moellendorff, 1894
- Cooke & Clench, 1943
- Thiele, 1927
- Pease, 1867
- Brandt, 1974
- Clench, 1955
- Kobelt & Möllendorff, 1900
- Suterilla Thiele, 1927
- Möllendorff, 1898
- Telmosena Iredale, 1944
- Thaanumella Clench, 1946
- Thiele, 1927
- Hubendick, 1952
- Wrayanna Clench, 1948
subfamily ?
- Angustassiminea Habe, 1943
- Heteropoma Benson, 1856
- incertae sedis
- Assimineidae incertae sedis vulgaris Webster, 1905 [8]
References[]
This article incorporates public domain text from the reference.[2]
- ^ Strong E. E., Gargominy O., Ponder W. F. & Bouchet P. (2008). "Global Diversity of Gastropods (Gastropoda; Mollusca) in Freshwater". Hydrobiologia 595: 149-166. hdl:10088/7390 doi:10.1007/s10750-007-9012-6.
- ^ a b c d e "Family summary for Assimineidae". AnimalBase, last change 15-08-2006, accessed 4 August 2010.
- ^ Bullis, David A.; Herhold, Hollister W.; Czekanski-Moir, Jesse E.; Grimaldi, David A.; Rundell, Rebecca J. (March 2020). "Diverse new tropical land snail species from mid-Cretaceous Burmese amber (Mollusca: Gastropoda: Cyclophoroidea, Assimineidae)". Cretaceous Research. 107: 104267. doi:10.1016/j.cretres.2019.104267.
- ^ Abbott, R.T. (1958). "The gastropod genus Assiminea in the Philippines". Proceedings of the Academy of Natural Sciences of Philadelphia. 110: 213–278.
- ^ "Assimineidae". Integrated Taxonomic Information System.
- ^ Ingentaconnect
- ^ ZipCodeZoo Archived February 10, 2012, at the Wayback Machine
- ^ Rosenberg, G. (2012). Assimineidae incertae sedis vulgaris. Accessed through: World Register of Marine Species at http://www.marinespecies.org/aphia.php?p=taxdetails&id=598622 on 2012-05-31
External links[]
![]() Media related to Assimineidae at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Assimineidae at Wikimedia Commons
- Assimineidae