Baudh State
| Baudh State | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Princely State of British India | |||||||
| 14th cen–1948 | |||||||
 Flag | |||||||
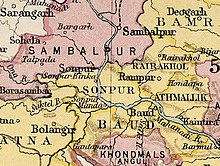 Baudh State in the Imperial Gazetteer of India | |||||||
| Area | |||||||
• 1921 | 3,274 km2 (1,264 sq mi) | ||||||
| Population | |||||||
• 1921 | 130,103 | ||||||
| History | |||||||
| History | |||||||
• Established | 14th cen | ||||||
• Accession to the Union of India | 1948 | ||||||
| |||||||
| Baudh Princely State | |||||||
Baudh State, also known as Boudh State, was one of the princely states of India during the period of the British Raj. It was recognized as a state in 1874[1] and had its capital in Boudh town. Its last ruler signed the accession to the Indian Union on 1 January 1948.
History[]
According to traditions, with the advent of Eastern Ganga rule over the region post the defeat of the Somavamshi dynasty, there were local chieftains ruling over Baudh as Eastern Ganga feudatories. Upon time the Brahmin chieftain was childless and hence adopted the nephew of the neighbouring Raja of Keonjhar who belonged to the Bhanj dynasty. This prince named Ananga Bhanja then styled himself Ananga Deva and became the King of Baudh in the 14th century.[2][3][4]
In late 15th century, Naren Bhanja, the brother of the Raja of Baudh was made chieftain of the Daspalla region, from which he later seceded and declared his independent kingdom leading to the creation of the Daspalla State.[5]
The princely state acceded to India in 1948 and its territory became part of the now Boudh District.
Rulers[]
The rulers of the Baudh state of the Bhanj dynasty:
- Ananga Bhanja (Ananga Deba) (14th cen CE)
- ...
- Siddhabhanja Deba (Siddheswar Deba) (1640s)
- Pratap Deba
- Bswambhar Deba (1778-1817)
- Chandrasekhar Deba (1817-1839)
- Pitamber Deo (1839-5 October 1879)
- Jogendra Deo (5 October 1879–1913)
- Narayan Prasad Deo (1913-1 January 1948)
Titular[]
- Narayan Prasad Deo
- Nabin Prasad Deo
- Debendra Prasad Deo
See also[]
References[]
- ^ Princely States of India A-J
- ^ ODISHA DISTRICT GAZETTEERS BOUDH (PDF), GAD, Govt of Odisha, 1991, p. 23
- ^ Imperial Gazetteer of India, v. 7, p. 140.
- ^ Malleson, G. B. An historical sketch of the native states of India, London 1875, Reprint Delhi 1984
- ^ ODISHA DISTRICT GAZETTEERS NAYAGARH (PDF), GAD, Govt of Odisha, 2015, p. 42
- States and territories disestablished in 1948
- Princely states of India
- History of Odisha
- Boudh district
- 14th-century establishments in India
- 1948 disestablishments in India
- Indian history stubs
