Bolidophyceae
| Bolidophyceae | |
|---|---|
| Scientific classification | |
| Clade: | SAR |
| Phylum: | Ochrophyta |
| Class: | Bolidophyceae L.Guillou & M.-J.Chrétiennot-Dinet |
| Orders | |
| Synonyms | |
| |
Bolidophyceae is a class of photosynthetic heterokont picophytoplankton, and consist of less than 20 known species.[1][2][3] They are distinguished by the angle of flagellar insertion and swimming patterns as well as recent molecular analyses.[4] Bolidophyceae is the sister taxon to the diatoms (Bacillariophyceae). They lack the characteristic theca of the diatoms,[5] and have been proposed as an intermediate group between the diatoms and all other heterokonts.[4][6]
Taxonomy[]
- Class Bolidophyceae Guillou & Chretiennot-Dinet 1999[7]
- Order Parmales Booth & Marchant 1987
- Family Marchant 1987
- Genus Marchant 1987
- Species Marchant 1987
- Genus Marchant 1987
- Family Booth & Marchant 1988
- Genus Tetraparma Booth 1987
- Species
- Species
- Species Bravo-Sierra & Hernández-Becerril 2003
- Species Booth & Marchant 1987
- Species Fujita & Jordan 2017
- Species Fujita & Jordan 2017
- Genus Triparma Booth & Marchant 1987
- Species Booth 1987
- Species Ichinomiya & Lopes dos Santos 2016
- Species Booth 1987
- Species (Guillou & Chrétiennot-Dinet) Ichinomiya & Lopes dos Santos 2016
- Species (Guillou & Chrétiennot-Dinet) Ichinomiya & Lopes dos Santos 2016
- Species Booth 1987
- Species Booth 1987
- Species Booth 1987
- Genus Tetraparma Booth 1987
- Family Marchant 1987
- Order Parmales Booth & Marchant 1987
Gallery[]
In the gallery, all scale bar represent 1 μm.

The silicified Tetraparma pelagica
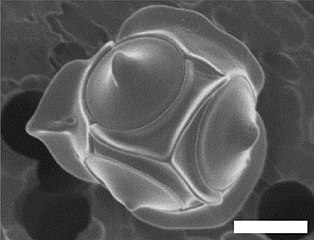
The silicified Triparma laevis f. inornata

The silicified Pentalamina corona
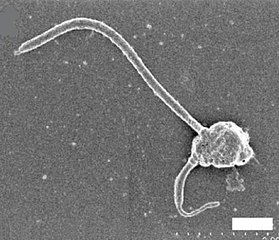
The flagellated Triparma eleuthera
References[]
- ^ Ruggiero; et al. (2015), "Higher Level Classification of All Living Organisms", PLOS ONE, 10 (4): e0119248, Bibcode:2015PLoSO..1019248R, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0119248, PMC 4418965, PMID 25923521
- ^ Silar, Philippe (2016), "Protistes Eucaryotes: Origine, Evolution et Biologie des Microbes Eucaryotes", HAL Archives-ouvertes: 1–462
- ^ Alverson Lab, University of Arkansas | Projects - Diatoms of North America
- ^ a b Guillou, Laure; Chrétiennot-Dinet, Marie-Josèphe; Medlin, Linda K.; Claustre, Hervé; Goër, Susan Loiseaux-de; Vaulot, Daniel (April 1999). "Bolidomonas: A New Genus with Two Species Belonging to a New Algal Class, the Bolidophyceae (Heterokonta)" (PDF). Journal of Phycology. 35 (2): 368–381. doi:10.1046/j.1529-8817.1999.3520368.x. S2CID 13704085.
- ^ Daugbjerg, N.; Guillou, L. (March 2001). "Phylogenetic analyses of Bolidophyceae (Heterokontophyta) using gene sequences support their sister group relationship to diatoms". Phycologia. 40 (2): 153–161. doi:10.2216/i0031-8884-40-2-153.1. S2CID 84171410.
- ^ Ichinomiya, Mutsuo; dos Santos, Adriana Lopes; Gourvil, Priscillia; Yoshikawa, Shinya; Kamiya, Mitsunobu; Ohki, Kaori; Audic, Stéphane; de Vargas, Colomban; Noël, Mary-Hélène; Vaulot, Daniel; Kuwata, Akira (22 March 2016). "Diversity and oceanic distribution of the Parmales (Bolidophyceae), a picoplanktonic group closely related to diatoms". The ISME Journal. 10 (10): 2419–2434. doi:10.1038/ismej.2016.38. PMC 5030691. PMID 27003244. Retrieved 6 April 2018.
- ^ M.D. Guiry (2016), AlgaeBase, World-wide electronic publication, National University of Ireland, Galway, retrieved 25 October 2016
External links[]
| Wikispecies has information related to Bolidophyceae. |
- SEM images of Bolidophyceae (Parmales): http://www.mikrotax.org/Nannotax3/index.php?dir=non_cocco/Parmales
Categories:
- Heterokont classes
- Ochrophyta



