CCIR System M
This article does not cite any sources. (August 2009) |
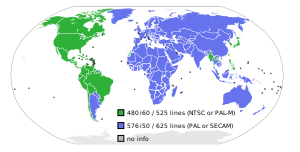
CCIR (or FCC) System M, sometimes called 525 line, is the analog broadcast television system used in the United States since July 1, 1941, and also in most of the Americas and Caribbean, South Korea, and Taiwan. Japan uses the same system with minor differences, but informally referred to as system J. The systems were given their letter designations in the ITU identification scheme adopted in Stockholm in 1961.
System M displays 525 lines of video at 30 frames per second using 6 MHz spacing between channel numbers, and is used for both VHF and UHF channels. The color system is usually NTSC, with Japan using a variant known as NTSC-J. Brazil implemented a PAL variant known as PAL-M and Cambodia and Vietnam implement a SECAM variant known as SECAM-M.
Currently (as of 2015), Systems M is being replaced by digital broadcasting in countries such as the Americas, Japan, South Korea, Taiwan and the Philippines.
Specifications[]

| System | Lines | Frame rate | Channel b/w | Visual b/w | Sound offset | Vestigial sideband | Vision mod. | Sound mod. | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M | 525 | 60i (59.94i NTSC) |
6 | 4.2 | +4.5 | 0.75 | neg. | FM | Most of the Americas and Caribbean; Myanmar, Philippines, South Korea, Taiwan (all NTSC-M) Japan (NTSC-J) Brazil (PAL-M) Cambodia, Vietnam (SECAM-M). |
Color standards[]
NTSC-M and NTSC-J[]
Strictly speaking, System M does not designate how color is transmitted. However, in nearly every System M country, NTSC is used for color television, a combination called NTSC-M, but usually referred to more recently as simply "NTSC" because of the relative lack of importance of black-and-white television. In NTSC-M and Japan's NTSC-J, the frame rate is offset slightly, becoming 30⁄1.001 frames per second, usually labeled as the rounded number 29.97.
PAL-M[]
The main exception to NTSC is Brazil, where PAL color is used instead, resulting in the PAL-M combination unique to that country, which is monochrome-compatible with other System M countries, but not compatible with other PAL countries, which use different basic systems as their base.
SECAM-M[]
Between 1970 and 1991 a variation of the SECAM color system, known as SECAM-M, was used in Cambodia and Vietnam (Hanoi and other northern cities).
See also[]
- NTSC — dominant color system used with System M, so much so that System M is often referred to as "NTSC". Much of the information in the NTSC article is actually about System M.
- Broadcast television systems — explains other types of television system standards
- Multichannel television sound — usual method for adding stereo to System M audio
- Telecommunications-related introductions in 1941
- ITU-R recommendations
- Television technology
- Video formats
- CCIR System
