Casticin
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
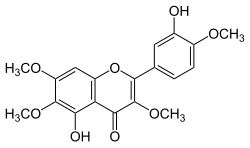
5-Hydroxy-2-(3-hydroxy-4-methoxyphenyl)-3,6,7-trimethoxy-4H-1-benzopyran-4-one | |
| Other names
Vitexicarpin
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C19H18O8 | |
| Molar mass | 374.34 g/mol |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Casticin is a methyoxylated flavonol, meaning the core flavonoid structure has methyl groups attached. Found in Artemisia annua, the flavonoid has been shown to enhance the antimalarial activity of artemisinin though casticin itself has no direct antimalarial effects.[1][2] It has been shown to have anti-mitotic activity. It is also found in Vitex agnus-castus.[3]
References[]
- ^ Elford BC; Roberts MF; Phillipson JD; Wilson RJ (1987). "Potentiation of the antimalarial activity of qinghaosu by methoxylated flavones". Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 81 (3): 434–436. doi:10.1016/0035-9203(87)90161-1. PMID 3318019.
- ^ Liu KC; Yang SL; Roberts MF; Elford BC; Phillipson JD (1992). "Antimalarial activity of Artemisia annua flavonoids from whole plants and cell cultures". Plant Cell Rep. 11 (12): 537–640. doi:10.1007/bf00236389. PMID 24213368. S2CID 9405266.
- ^ Hoberg, Eva; Meier, Beat; Sticher, Otto (2000). "An analytical high performance liquid chromatographic method for the determination of agnuside and p-hydroxybenzoic acid contents in Agni-casti fructus". Phytochemical Analysis. 11 (5): 327–329. doi:10.1002/1099-1565(200009/10)11:5<327::AID-PCA523>3.0.CO;2-0.
External links[]
- Liu, Enyu; Kuang, Yongqin; He, Weiqi; Xing, Xuemin; Gu, Jianwen (2013). "Casticin induces human glioma cell death through apoptosis and mitotic arrest". Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 31 (6): 805–14. doi:10.1159/000350098. PMID 23816816.
Categories:
- Flavones
- Aromatic compound stubs