Charleroi
Charleroi
Tchålerwè (Walloon) | |
|---|---|
 Skyline of Charleroi | |
 Flag  Coat of arms | |
 Charleroi Location in Belgium
show Location of Charleroi in the province of Hainaut | |
| Coordinates: 50°24′N 04°26′E / 50.400°N 4.433°ECoordinates: 50°24′N 04°26′E / 50.400°N 4.433°E | |
| Country | Belgium |
| Community | French Community |
| Region | |
| Province | Hainaut |
| Arrondissement | Charleroi |
| Government | |
| • Mayor | Paul Magnette (PS) |
| • Governing party/ies | PS, CDH, MR |
| Area | |
| • Total | 102.08 km2 (39.41 sq mi) |
| Population (2018-01-01)[1] | |
| • Total | 201,816 |
| • Density | 2,000/km2 (5,100/sq mi) |
| Postal codes | 6000, 6001, 6010, 6020, 6030–6032, 6040–6044, 6060, 6061 |
| Area codes | 071 |
| Website | www.charleroi.be |
Charleroi (UK: /ˈʃɑːrlə.rwʌ/, US: /-rɔɪ, -rwɑː/,[2][3] French: [ʃaʁləʁwa]; Walloon: Tchålerwè [tʃɑːlɛʀwɛ]) is a city and a municipality of Wallonia, located in the province of Hainaut, Belgium. By 1 January 2008, the total population of Charleroi was 201,593.[4] The metropolitan area, including the outer commuter zone, covers an area of 1,462 square kilometres (564 sq mi) with a total population of 522,522 by 1 January 2008, ranking it as the 5th most populous in Belgium after Brussels, Antwerp, Liège, and Ghent.[4][5] The inhabitants are called Carolorégiens or simply Carolos.
Geography[]
The municipality of Charleroi straddles both banks of the river Sambre in an area marked by industrial activities (coal mining and steel industry), which has been nicknamed the Pays Noir ("Black Country"), part of the larger sillon industriel. Even though most of the factories have closed since the 1950s, the landscape remains dotted with spoil tips and old industrial buildings.
Charleroi lies around 50 kilometres (31 mi) south of Brussels.
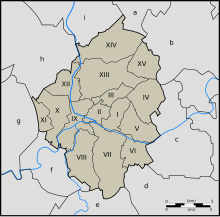
The municipality comprises:
- I. the central city of Charleroi
and the following former municipalities, merged into Charleroi in 1977:
- II. Dampremy
- III. Lodelinsart
- IV. Gilly
- V. Montignies-sur-Sambre
- VI. Couillet
- VII. Marcinelle
- VIII. Mont-sur-Marchienne
- IX. Marchienne-au-Pont
- X. Monceau-sur-Sambre
- XI. Goutroux
- XII. Roux
- XIII. Jumet
- XIV. Gosselies
- XV. Ransart
Neighboring municipalities:
- a. Les Bons Villers
- b. Fleurus
- c. Châtelet
- d. Gerpinnes
- e. Ham-sur-Heure-Nalinnes
- f. Montigny-le-Tilleul
- g. Fontaine-l'Évêque
- h. Courcelles
- i. Pont-à-Celles
Climate[]
Similar to the rest of Belgium Charleroi has an oceanic climate as a result of the Gulf Stream influence warming winters, while also moderating summer warmth in spite of its inland position.
| hideClimate data for Charleroi (1981–2010 normals, sunshine 1984–2013) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Average high °C (°F) | 5.2 (41.4) |
6.2 (43.2) |
10.0 (50.0) |
13.7 (56.7) |
17.8 (64.0) |
20.5 (68.9) |
23.1 (73.6) |
22.8 (73.0) |
18.9 (66.0) |
14.5 (58.1) |
9.1 (48.4) |
5.7 (42.3) |
14.0 (57.2) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | 2.6 (36.7) |
3.0 (37.4) |
6.0 (42.8) |
8.9 (48.0) |
13.0 (55.4) |
15.7 (60.3) |
18.0 (64.4) |
17.8 (64.0) |
14.5 (58.1) |
10.7 (51.3) |
6.2 (43.2) |
3.3 (37.9) |
10.0 (50.0) |
| Average low °C (°F) | 0.1 (32.2) |
−0.1 (31.8) |
2.3 (36.1) |
4.3 (39.7) |
8.3 (46.9) |
11.0 (51.8) |
13.2 (55.8) |
12.7 (54.9) |
10.1 (50.2) |
7.1 (44.8) |
3.5 (38.3) |
1.0 (33.8) |
6.2 (43.2) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 81.1 (3.19) |
67.1 (2.64) |
77.8 (3.06) |
55.9 (2.20) |
71.0 (2.80) |
80.0 (3.15) |
75.4 (2.97) |
81.2 (3.20) |
64.6 (2.54) |
76.0 (2.99) |
76.8 (3.02) |
85.6 (3.37) |
892.5 (35.14) |
| Average precipitation days | 12.9 | 11.1 | 13.3 | 10.2 | 11.4 | 11.0 | 10.3 | 10.5 | 10.5 | 10.7 | 12.5 | 13.0 | 137.4 |
| Mean monthly sunshine hours | 50 | 71 | 114 | 165 | 197 | 193 | 212 | 200 | 142 | 112 | 61 | 42 | 1,557 |
| Source: Royal Meteorological Institute[6] | |||||||||||||
History[]

The Charleroi area was already settled in the prehistoric period, with traces of metallurgical and commercial activities along the Sambre. Several public buildings, temples and villas were built in the area in the Roman period. Burial places, with jewels and weapons, have been found. The first written mention of a place called Charnoy dates from a 9th-century offering in the Lobbes abbey, which lists various neighboring towns and related tithe duties. During the Middle Ages, Charnoy was one of the many small hamlets in the area, with no more than about 50 inhabitants, part of the County of Namur.
Foundation[]
Spanish territorial losses in the 1659 Treaty of the Pyrenees left a gap between the key fortresses of Mons and Namur; to fill this, Francisco Castel Rodrigo, then Governor of the Spanish Netherlands, expropriated land around Charnoy to build a fortress near the Sambre. In September 1666, it was renamed Charle-roi, or King Charles, in honour of five-year-old Charles II of Spain; the chronogram FVNDATVR CAROLOREGIVM (MDCLVVVI) can be found in the register of the parish of Charnoy.[7]
Construction had only just begun when the War of Devolution with France began in 1667, and the Spanish withdrew. France retained the town under the 1668 Treaty of Aix-la-Chapelle, and its fortifications were completed by Vauban. A bridge was built over the Sambre, connecting the Ville Haute and Ville Basse, with incentives offered to persuade people to settle there. The French relinquished control in 1678, and although it changed hands several times over the next 50 years, the town remained part of the Netherlands until the foundation of modern Belgium.[8]
1666–1830[]

Shortly after its foundation, the new city was in turn besieged by the Dutch, ceded to the Spanish in 1678 (Treaty of Nijmegen), taken by the French in 1693, ceded again to the Spanish in 1698 (Treaty of Rijswijk), then taken by the French, the Dutch and the Austrians in 1714 (Treaty of Baden). The French Prince of Conti took the city again in 1745, but it was ceded back to Austria in 1748, beginning a period of prosperity under Joseph II. Glass, steel and coal industries, which had already sprung up a century earlier, could now flourish.
Trouble began again in 1790, the year of the civil uprising that eventually led to the United States of Belgium. The Austrians occupied the city, were forced out by the French after the Battle of Jemappes on 6 November 1792, and took it back again four months later. On 12 June 1794, the French revolutionary Army of Sambre-et-Meuse under the command of Jean-Baptiste Jourdan, invested Charleroi and won a decisive victory in the ensuing Battle of Fleurus. The city took the revolutionary name of Libre-sur-Sambre until 1800. After France's defeat in 1814, the whole area was annexed to the Netherlands, and new walls were built around the city. Napoleon stayed in Charleroi for a couple of days in June 1815, just before the Battle of Waterloo.
1830 to present[]

The Belgian Revolution of 1830 gave the area its freedom from the Netherlands and ushered in a new era of prosperity, still based mostly on glass, metallurgy and coal, hence the area's name, Pays Noir ("Black Country"). After the Industrial Revolution, Charleroi benefited from the increased use of coke in the metallurgical industry. People from across Europe were attracted by the economic opportunities, and the population grew rapidly.
Following the Industrial revolution in Wallonia, Charleroi from the 1850s–1860s became one of the most important places where labor strikes broke out. In 1886, 12 strikers were killed by the Belgian army in Roux. In the 1880s, miners in Hainaut were recruited by the Dominion Coal Company in Glace Bay, Nova Scotia.[9] These miners were anxious to flee the repression following bloody strikes and riots in Liège and Charleroi[10] during the Walloon Jacquerie of 1886. Walloon miners from Charleroi also emigrated to Alberta, Canada.[11] The working men of Charleroi always played an important role in Belgian general strikes and particularly during the Belgian general strike of 1936, the general strike against Leopold III of Belgium, and the 1960–1961 winter general strike.
By 1871, the fortified walls around the city were completely torn down.
Heavy fighting took place during World War I due to the city's strategic location on the Sambre. The city was badly damaged with further destruction only being prevented by a treaty agreed with the German forces which required the payment of 10 million Belgian Francs, foodstuffs, vehicles and armaments.[12] Magazine Spirou, which featured the popular cartoon characters Lucky Luke and the Smurfs, was launched by the publishing company Éditions Dupuis in 1938.[13] After World War II, Charleroi witnessed a general decline of its heavy industry.[14] Following the merger with several surrounding municipalities in 1977, the city as of 2013 ranks as the largest city in Wallonia and the 4th largest in Belgium.
Politics[]

The Socialist Party (Parti Socialiste or PS) has had a stronghold in Charleroi for some time. However, in October 2006, mayor Jacques Van Gompel of the PS was jailed on fraud and forgery charges.[15] Léon Casaert, also of the PS, became the new mayor, elected by PS, MR and cdH majorities. The MR resigned from the coalition just before the 2007 general election, citing official charges of corruption leveled against a PS alderman in Charleroi.[16] After the 2007 general election, the PS placed the Charleroi local party section under full supervision of Paul Magnette, with the city executive resigning.[17] Mayor Casaert was charged with fraud on 18 June 2007, but would only step down after a new city executive had been formed.[18]
In April 2010, the director of technical services of Charleroi, Henri Stassens, was convicted in court of fraud and corruption.[19]

Municipal elections[]
| Party | 2000 (%) | 2006 (%) | 2012 (%) | 2018 (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Socialist Party (Parti Socialiste) | 51.4 | 38.4 | 47.7 | 41.3 |
| Reformist Movement (Mouvement Réformateur) | 16.1 | 24.6 | 16.3 | 11.2 |
| Humanist Democratic Centre (Centre Démocrate Humaniste) | 9.6 | 14.4 | 10.6 | 7.61(*) |
| National Front (Front National) | 6.9 | 9.5 | 5.8(**) | / |
| Ecolo | 11.4 | 8.1 | 7.4 | 7.4 |
| PTB/PTB+ | 1.3 | 2.1 | 3.4 | 15.7 |
| DéFI | / | / | 1.8 | 5.2 |
(*)Under the local list name "C+" (**)Under alternative name
Landmarks[]


- The belfry, part of the City Hall, is included in the list of World Heritage Sites.[20]
- The Maison Dorée was built in 1899 by Art Nouveau architect Alfred Frère. Its name is derived from the golden sgraffiti that adorn the façade.
- The city is home to several museums of fine art, glass and other disciplines, as well as a significant one specializing in photography, in the Mont-sur-Marchienne district.[21]
- In remembrance to the Jews of Charleroi being murdered by the Nazi regime, the German artist Gunter Demnig has collocated nine Stolpersteine in Charleroi.
Economy[]
The municipality contains an industrial area for electrical engineering and the production of iron, steel, glass and chemicals. The conglomerate ArcelorMittal subdivided its Industeel unit to encompass the Charleroi steelworks.[22][23]
Charleroi is in the center of a coal basin. Even so, due to the widespread loss in industrial power in the area since the 1970s, the area suffered some of the highest unemployment and poverty rates in Europe for most of the 1980s and 1990s. However, from the early 2000s, the overall economy of the area has diversified to include health care, transportation and telecommunications. Nevertheless, the poverty rates are still significant.
Education[]
Charleroi is Belgium's biggest city without having its own university. Since 1966, the University of Louvain is implemented in Charleroi, with three faculties, on its UCLouvain Charleroi campus based in the city center and in Montignies-sur-Sambre, including the Louvain School of Management and, more recently, the Louvain School of Engineering, organising Bachelor's and Master's degrees, and research. Other universities have since started operations in Charleroi, including the Universities of Namur, Mons and the Université libre de Bruxelles.
Primary and secondary schools[]
Secondary schools include:[24]
Transport[]
Air[]
The Brussels South Charleroi Airport in Gosselies, 7 km (4.3 mi) north of the centre, opened in 1919 as a flight school.[25] Later, it housed the Fairey aircraft-factory building.[26]
Gosselies is now used as an alternate airport for Brussels. Low-cost carrier Ryanair is the largest airline to provide service there; others include Wizz Air, Jetairfly. Seasonal holiday charters also use the airport.
A new terminal opened in January 2008,[27] replacing a much smaller building which had exceeded capacity.
Brussels is 47 km (29 mi) north of Charleroi Airport.
Rail[]
Charleroi is connected by train to other Belgian major cities through the main Charleroi-South railway station. The city also has a secondary railway station, Charleroi-West,[7] on the Charleroi-to-Ottignies line.
Public transport[]


Public transport is provided by TEC (Transport En Commun), the Walloon public transport service. The greater Charleroi region is served by bus lines and a light-rail Metro system, (Métro Léger de Charleroi). Part of the latter is famous for incorporating one of the few remnants of the Vicinal, the former Belgian national tramway network.
Charleroi Metro[]
The Charleroi Metro is equally famous for the parts of the system which were never built, partially built or fully completed but not opened. It was planned in the 1960s as a 48 km (30 mi.) light-rail network, operating on the heavy rail metro infrastructure, consisting of eight branch lines radiating from a central loop downtown.[28] However, only one line (to Petria), part of another line (to Gilly) and three-quarters of the loop were actually built and opened to traffic, all from 1976 to 1996. Another branch line toward the suburb of Châtelet (Châtelineau) was almost fully built, to the extent of installing power cables, escalators and still-working electric signals in the first three stations[29] but was never opened as passenger numbers would be too low to economically justify the extra staff. The high costs of construction, a decline in Charleroi's traditional "smokestack" industries and questioning of the scope of the whole project in proportion to the actual demand for it are cited as reasons for the original plan's becoming unfulfilled.
The central loop and the Gilly branch as far as Soleilmont were completed in 2012, with funds from the European Investment Bank.[30] The Gosselies branch opened as a street-level tramline in 2013. There are no plans to open any part of the Châtelet branch.[31]
Crime[]
During the 1990s, Charleroi was notorious for some violence due to its high poverty and unemployment rates.[32] Marc Dutroux lived in Marcinelle, a suburb of Charleroi.[33] On 6 August 2016, a man attacked two policewomen with a machete.[34]
Sports[]
Charleroi is home to a number of champion teams in various sports. Spirou Charleroi in basketball has been an eight-times winner in the Basketball League Belgium. La Villette Charleroi in table tennis is the most successful club in the Champions League with five titles and has been the Belgian champion multiple times. Action 21 Charleroi in futsal has won one UEFA Futsal Cup and nine titles in the Belgian Division 1. In football, Royal Charleroi SC and ROC Charleroi have finished second in the Belgian Pro League. The 30,000-capacity Stade du Pays de Charleroi was a venue at UEFA Euro 2000.[35]
Notable people from Charleroi[]

Born in Charleroi[]
- Jean-Marie Andre, scientist
- Pierre Carette, extreme-left terrorist
- Alexandre Czerniatynski, football player
- Jules Delhaize, 19th-century grocer and businessman, founder of what would become the Delhaize Group
- Louis Delhaize, founder of the Louis Delhaize Group
- Jules Destrée, lawyer and politician, born in Marcinelle, 19th century
- Karel Erjavec, Slovenian lawyer and politician, Minister of Foreign Affairs; born in Aiseau
- Albert Frère, businessman and the richest person in Belgium
- Régis Genaux, football player
- Emile Grumieaux, painter, born in Gosselies
- Axel Hervelle, Real Madrid basketball player
- Paul-François Huart-Chapel, industrialist, 19th century
- Jean-Pierre Lecocq (1947–1992), molecular biologist and entrepreneur
- Georges Lemaître (1894–1966), priest, and astronomer, 20th century
- Fabrice Lig, music producer, 20th century
- Joseph Maréchal, Jesuit priest, philosopher, 20th century
- Didier Matrige, painter and draughtsman, 20th century
- Joëlle Milquet, politician, 20th century
- Chantal Mouffe, political theorist, 20th century
- François-Joseph Navez, painter, 18th century
- Paul Pastur, lawyer and politician
- Gaston Salmon (1878–1917) – épée fencer, Olympic champion[36]
- Marcel Thiry, poet, 19th century
- Jeanne Toussaint (1887–1976), jeweller
- Raymond Troye, wartime writer, 20th century
- Annette Vande Gorne, composer
- Fernand Verhaegen, painter and etcher, born in Marchienne-au-Pont, 19th century
Resided in Charleroi[]
- Robert Arcq, writer
- Paul Cuvelier, painter and comics artist
- Muriel Degauque, suicide bomber in Iraq
- Marc Dutroux, convicted child molester and serial killer
- Arthur Grumiaux, violinist
- René Magritte, painter[13]
- , drummer for Nightrage/Firewind
- Arthur Rimbaud, poet
- Paul Verlaine, poet
Twin cities[]
 Hirson, France
Hirson, France Saint-Junien, France
Saint-Junien, France Schramberg, Germany
Schramberg, Germany Waldkirch, Germany
Waldkirch, Germany Manoppello, Italy
Manoppello, Italy Casarano, Italy
Casarano, Italy Follonica, Italy
Follonica, Italy Himeji, Japan
Himeji, Japan Donetsk, Ukraine
Donetsk, Ukraine Pittsburgh, US
Pittsburgh, US Uşak, Turkey
Uşak, Turkey Alvdal, Norway
Alvdal, Norway Bjugn, Norway
Bjugn, Norway
See also[]
- Aéropole Science Park
- Dauphines Charleroi
- ICDI affair
- List of municipalities in Wallonia
- Municipalities of Belgium
- R. Charleroi S.C.
- R.O.C. Charleroi
References[]
- ^ "Wettelijke Bevolking per gemeente op 1 januari 2018". Statbel. Retrieved 9 March 2019.
- ^ "Charleroi". The American Heritage Dictionary of the English Language (5th ed.). Boston: Houghton Mifflin Harcourt. Retrieved 17 April 2019.
- ^ "Charleroi" (US) and "Charleroi". Oxford Dictionaries UK Dictionary. Oxford University Press. Retrieved 17 April 2019.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Statistics Belgium; Population de droit par commune au 1 janvier 2008 (excel-file) Archived 26 January 2009 at the Wayback Machine Population of all municipalities in Belgium, as of 1 January 2008. Retrieved on 19 October 2008.
- ^ Statistics Belgium; De Belgische Stadsgewesten 2001 (pdf-file) Archived 29 October 2008 at the Wayback Machine Definitions of metropolitan areas in Belgium. The metropolitan area of Charleroi is divided into three levels. First, the central agglomeration (agglomeratie) with 288,549 inhabitants (2008-01-01). Adding the closest surroundings (banlieue or suburbs), the total of 405,236. And, with the outer commuter zone (forensenwoonzone), the population is 522,522. Retrieved on 19 October 2008.
- ^ "Klimaatstatistieken van de Belgische gemeenten" (PDF) (in Dutch). Royal Meteorological Institute. Retrieved 29 May 2018.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Dunford, Martin; Lee, Phil (2002). Belgium & Luxembourg. Rough Guides. p. 303. ISBN 9781858288710.
charleroi 1666.
- ^ "Charleroi". Fortified Places. Retrieved 2 March 2020.
- ^ But a consular report indicated they were dissatisfied with wages and working conditions, and they moved to other mining centers. These Walloon miners were experienced in organizing unions and working-men's associations. They immigrated also to collieries on Vancouver Island in Canada. See Louis Balthazar, Leen Haenens, Images of Canadianness: Visions on Canada's Politics, Culture, Economics, International Council for Canadian Studies, University of Ottawa Press, 1998, ISBN 0-7766-0489-9.
- ^ Louis Balthazar and Leen Haenens, Images of Canadianness: Visions on Canada's Politics, Culture, Economics, International Council for Canadian Studies, University of Ottawa Press, 1998, p. 73, ISBN 0-7766-0489-9.
- ^ Miners from Wallonia began arriving at the collieries in Alberta to work for West Canadian Collieries, founded in 1903 by a group of French and Belgian entrepreneurs, and for Canadian Coal Consolidated, a Paris-based firm. Léon Cabeaux, a well-known union leader, who had organized a particularly violent strike in Hainaut in 1886, settled in Lethbridge and soon attracted disgruntled compatriots from the collieries in Pennsylvania in the US. The miners soon became deeply involved in labor radicalism, because in Alberta the mine disasters were among the worst anywhere, and there were no provisions for the welfare of families of the miners maimed or killed in the workplace. Frank Soulet, Joseph Lothier and Gustave Henry emerged as dedicated socialist union leaders. in Louis Balthazar and Leen Haenens, Images of Canadianness: Visions on Canada's Politics, Culture, Economics, International Council for Canadian Studies, University of Ottawa Press, 1998, p. 75, ISBN 0-7766-0489-9.
- ^ Harriet O'Brien. "Charleroi: Phoenix from the flames | Europe | Travel". The Independent. Retrieved 2016-08-07.
- ^ Jump up to: a b "Charleroi: A richly rewarding gem | Europe | Travel". The Independent. Retrieved 7 August 2016.
- ^ Meerman, Ester. "The 10 Best Things To Do In Charleroi, Belgium". Culture Trip.
- ^ "deredactie.be". Vrtnieuws.net. Retrieved 7 August 2016.
- ^ "Le MR quitte la majorité à Charleroi". La Dernière Heure (in French). 28 May 2007. Retrieved 10 June 2007.
- ^ "Le collège carolo démissionnera ce mardi" (in French). Le Soir. 11 June 2007. Retrieved 12 June 2007.[permanent dead link]
- ^ "Casaert reste bourgmestre". La Libre (in French). 19 June 2007. Retrieved 19 June 2007.
- ^ [1] Archived 27 April 2010 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ "Charleroi Belfry, UNESCO World Heritage Site". Opt.be. 3 January 2016. Retrieved 7 August 2016.
- ^ "Museum of Photography in Charleroi". Opt.be. 2 March 2015. Retrieved 7 August 2016.
- ^ "ArcelorMittal se donne six mois pour vendre Industeel". Le Journal de Saône et Loire. 20 November 2020.
- ^ "Vente d'Industeel : la CGT en appelle à l'intervention de l'Etat". Le Journal de Saône et Loire. 11 January 2021.
- ^ "Ecoles Secondaires". City of Charleroi. Retrieved 28 December 2019.
- ^ How it all started. Charleroi-airport.com
- ^ Avions Fairey Gosselies. Baha.be. Retrieved on 21 December 2012.
- ^ "Brussels South Charleroi Airport". Archived from the original on 29 June 2012. Retrieved 7 February 2008.
- ^ "Urbanrail.net". Archived from the original on 10 April 2010. Retrieved 7 August 2016.CS1 maint: bot: original URL status unknown (link)
- ^ "Diggelfjoer: Abandoned". Diggelfjoer.swalker.nl. Retrieved 7 August 2016.
- ^ "EIB loan for Charleroi light metro". Railway Gazette International. Retrieved 7 August 2016.
- ^ > Europe > Belgium > Charleroi Prémétro (Belgium). UrbanRail.Net (28 August 1992). Retrieved on 21 December 2012.
- ^ Mcneil, Donald G.. (5 September 2001) Charleroi Journal – A Rust-Belt City's Mean Streets Keep Their Edge. NYTimes.com. Retrieved on 21 December 2012.
- ^ Belgian Faces Trial at Last In Sex Killings – New York Times. Nytimes.com (2 March 2004). Retrieved on 21 December 2012.
- ^ "Islamic State Claims Machete Attack In Belgium". News.sky.com. Retrieved 2016-08-07.
- ^ "EURO 2000 - The Official Site". Web.archive.bibalex.org. Archived from the original on 10 August 2001. Retrieved 7 August 2016.
- ^ "La médaille d'or d'un Carolo en vente à Hollywood!". Édition digitale de Mons. 23 October 2017.
External links[]
-![]() Media related to Charleroi at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Charleroi at Wikimedia Commons
 Charleroi travel guide from Wikivoyage
Charleroi travel guide from Wikivoyage- Official web site
- Unofficial history of tramways in Charleroi (in French)
- Urban adventurers explore and photograph an unused Métro line
- "Welcome to Charleroi: Tourism trebles in the world's ugliest town" Scotsman newspaper, April 7, 2009
- Charleroi
- Sub-municipalities of Charleroi
- Municipalities of Hainaut (province)
- World Heritage Sites in Belgium
- 1666 establishments in the Holy Roman Empire
- Vauban fortifications in Belgium