Cobalt monosilicide
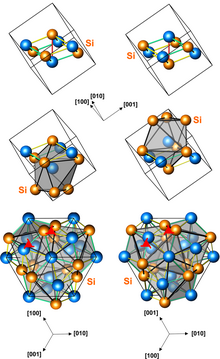 Structures of left-handed and right-handed CoSi crystals (3 presentations, with different numbers of atoms per unit cell)
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Cobalt silicide
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| CoSi | |
| Molar mass | 87.018 g/mol |
| Density | 6.3 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 1,415 °C; 2,579 °F; 1,688 K[2] |
| -0.44×10−6 emu/g[1] | |
| Thermal conductivity | 20 W/(m·K)[1] |
| Structure | |
| Cubic[3] | |
| P213 (No. 198), cP8 | |
a = 0.4444(1) nm
| |
Formula units (Z)
|
4 |
| Hazards | |
| Flash point | Non-flammable |
| Related compounds | |
Other anions
|
Cobalt germanide |
Other cations
|
Iron silicide Manganese monosilicide |
Related compounds
|
Cobalt disilicide |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Cobalt monosilicide (CoSi) is an intermetallic compound, a silicide of cobalt. It is a diamagnetic semimetal[3] with an electrical resistivity of ca. 1 mOhm·cm.[1]
References[]
- ^ a b c Dutta, Paromita; Pandey, Sudhir K (10 April 2019). "Effects of correlations and temperature on the electronic structures and related physical properties of FeSi and CoSi: a comprehensive study". Journal of Physics: Condensed Matter. 31 (14): 145602. doi:10.1088/1361-648X/aafdce.
- ^ Gas, P.; d’Heurle, F. M. (1998). "Diffusion in silicides". In Beke, D. L. (ed.). Landolt-Börnstein - Group III Condensed Matter. 33A. Springer. pp. 1–38. doi:10.1007/10426818_13.
- ^ a b Stishov, Sergei M.; Petrova, Alla E. (2011). "Itinerant helimagnetic compound MnSi". Uspekhi Fizicheskikh Nauk. 181 (11): 1157. doi:10.3367/UFNr.0181.201111b.1157.
Categories:
- Cobalt compounds
- Transition metal silicides
- Iron monosilicide structure type
- Alloy stubs