Congenital amegakaryocytic thrombocytopenia
| Congenital amegakaryocytic thrombocytopenia | |
|---|---|
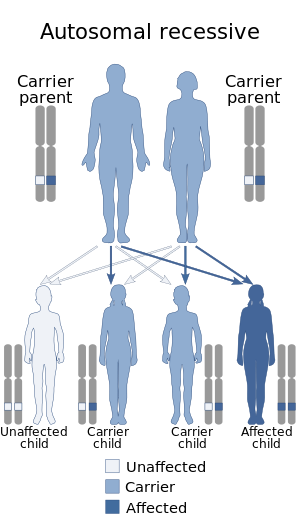 | |
| Congenital amegakaryocytic thrombocytopenia is inherited in an autosomal recessive manner | |
| Specialty | Hematology |
Congenital amegakaryocytic thrombocytopenia (CAMT) is a rare inherited disorder.[1][2][3]
Presentation[]
The primary manifestations are thrombocytopenia and , or low numbers of platelets and megakaryocytes. There is an absence of megakaryocytes in the bone marrow with no associated physical abnormalities.[4]
Cause[]
The cause for this disorder appears to be a mutation in the gene for the TPO receptor, c-mpl, despite high levels of serum TPO.[5][6] In addition, there may be abnormalities with the central nervous system including the cerebrum and cerebellum which could cause symptoms.[5]
Treatment[]
The primary treatment for CAMT is bone marrow transplantation.[7]
Bone Marrow/Stem Cell Transplant is the only thing that ultimately cures this genetic disease. Frequent platelet transfusions are required to ensure that platelet levels do not fall to dangerous levels, although this is not always the case. It is known for patients to continue to create very small numbers of platelets over time.[citation needed]
See also[]
- Thrombopoietin
- Myeloproliferative leukemia virus oncogene
References[]
- ^ Ballmaier M, Germeshausen M, Schulze H, et al. (January 2001). "c-mpl mutations are the cause of congenital amegakaryocytic thrombocytopenia". Blood. 97 (1): 139–46. doi:10.1182/blood.V97.1.139. PMID 11133753.
- ^ Germeshausen M, Ballmaier M, Welte K (March 2006). "MPL mutations in 23 patients suffering from congenital amegakaryocytic thrombocytopenia: the type of mutation predicts the course of the disease". Hum. Mutat. 27 (3): 296. doi:10.1002/humu.9415. PMID 16470591.
- ^ Rose MJ, Nicol KK, Skeens MA, Gross TG, Kerlin BA (June 2008). "Congenital amegakaryocytic thrombocytopenia: the diagnostic importance of combining pathology with molecular genetics". Pediatr Blood Cancer. 50 (6): 1263–5. doi:10.1002/pbc.21453. PMID 18240171. S2CID 5285793.
- ^ Freedman MH, Estrov Z (1990). "Congenital amegakaryocytic thrombocytopenia: an intrinsic hematopoietic stem cell defect". Am. J. Pediatr. Hematol. Oncol. 12 (2): 225–230. doi:10.1097/00043426-199022000-00020. PMID 2378417. S2CID 23164119.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Ihara K, Ishii E, Eguchi M, Takada H, Suminoe A, Good RA, Hara T (1999). "Identification of mutations in the c-mpl gene in congenital amegakaryocytic thrombocytopenia". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 96 (6): 3133–6. Bibcode:1999PNAS...96.3132I. doi:10.1073/pnas.96.6.3132. PMC 15907. PMID 10077649.
- ^ Ballmaier M, Germeshausen M, Schulze H, Cherkaoui K, Lang S, Gaudig A, Krukemeier S, Eilers M, Strauss G, Welte K (2001). "C-mpl mutations are the cause of congenital amegakaryocytic thrombocytopenia". Blood. 97 (1): 139–46. doi:10.1182/blood.V97.1.139. PMID 11133753.
- ^ King S, Germeshausen M, Strauss G, Welte K, Ballmaier M (December 2005). "Congenital amegakaryocytic thrombocytopenia: a retrospective clinical analysis of 20 patients". Br. J. Haematol. 131 (5): 636–44. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2141.2005.05819.x. PMID 16351641. S2CID 23998393.
External links[]
| Classification | |
|---|---|
| External resources |
- Coagulopathies
- Cell surface receptor deficiencies