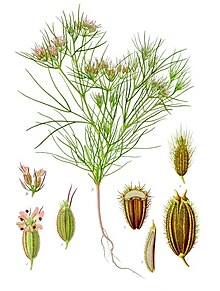
Cumin
| Cumin | |
|---|---|
| |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Clade: | Tracheophytes |
| Clade: | Angiosperms |
| Clade: | Eudicots |
| Clade: | Asterids |
| Order: | Apiales |
| Family: | Apiaceae |
| Genus: | Cuminum |
| Species: | C. cyminum
|
| Binomial name | |
| Cuminum cyminum | |
Cumin (/ˈkjuːmɪn/[2][3] or US: /ˈkuːmɪn/,[2][4][5][6] or /ˈkʌmɪn/[2][3]) (Cuminum cyminum) is a flowering plant in the family Apiaceae, native to the Irano-Turanian Region.[7] Its seeds – each one contained within a fruit, which is dried – are used in the cuisines of many cultures in both whole and ground form. Although cumin is thought to have uses in traditional medicine, there is no high-quality evidence that it is safe or effective as a therapeutic agent.[8]
Etymology[]
The term comes via Middle English and Old French from the Latin term cuminum. This in turn comes from the Ancient Greek κύμινον (kúminon), a Semitic borrowing related to Hebrew כמון (kammōn) and Arabic كمون (kammun). All of these ultimately derive from Akkadian